Every day, healthcare institutions handle enormous volumes of data, ranging from test findings and prescriptions to patient information and claims. But not every piece of data is made equal. Data interchange can be costly, error-prone, and challenging when several systems and formats are used. About 50% of US hospitals think that the largest barrier to enhancing healthcare interoperability and undermining connected care initiatives would be the increasing amount of unstructured data. Thankfully, healthcare EDI transactions offer a dependable option that hospitals can use to get beyond these obstacles.
Companies can automate numerous healthcare procedures, including invoicing, open enrollment solutions, eligibility verification, and referrals and can make it simpler. They can save time and money while enhancing the security, quality, and accuracy of their data by implementing EDI transactions.
What is EDI?
The standardization of official document communication between companies is known as electronic data exchange, or EDI for short. Buy orders, invoices, and other paper-based documents are replaced by standard electronic formats known as electronic data interchange, or EDI. By automating paper-based transactions, organizations can decrease errors and save time.
Information is transferred straight from one organization’s computer program to another through EDI software solutions. The location and sequence of data in a document format are specified by EDI standards. With these automated capabilities, sharing data is now easier and faster than with paper papers or other antiquated techniques that might take hours, days, or even weeks.
Organizations in a variety of industries that handled document sharing by conventional means including email, fax, and paper have seen less strain thanks to electronic data interchange, or EDI. It is a global standard for document management that uses technology to organize paperwork and cut down on human error. Transmitting business documents between trading partners in a safe manner using internationally recognized message standards and formats is known as electronic data interchange. In this instance, the parties involved in manufacturing and the supply chain, patients, and insurers or claim management firms will share documents.
Importance of EDI in Healthcare
Streamlining administrative procedures is the main way that EDI in healthcare aims to increase accuracy and overall quality of patient care. By substituting electronic data interchange (EDI) for manual and paper-based tasks, healthcare companies can decrease paperwork, eliminate errors, and speed up information flow.
Keeping Efficiency and Standardization in Mind
88% of hospitals share health information, per an ONC Interoperability survey. However, hospitals that wish to efficiently use public health data face considerable obstacles due to the unpredictability of information systems and the lack of data standards. Healthcare stakeholders may share data in a standardized and secure manner thanks to EDI solutions. It ensures system consistency and compatibility by establishing a consistent language and structure for information transmission.
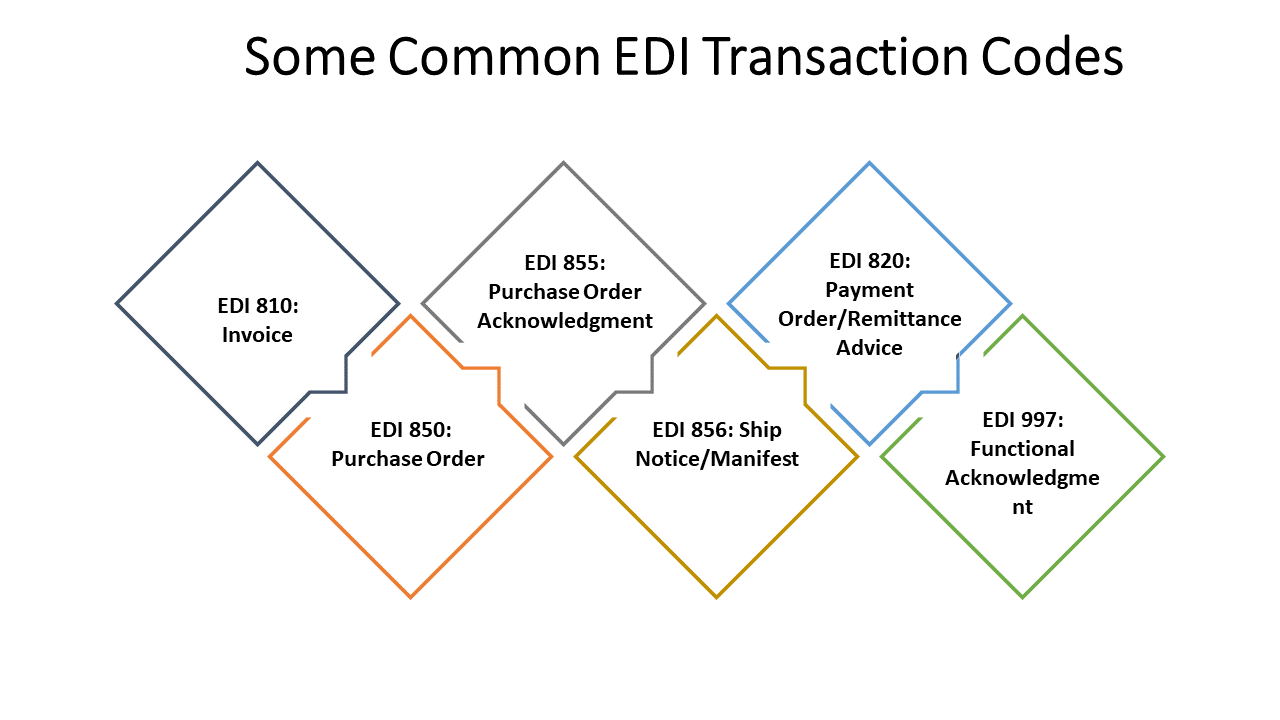
The submission of claims using Healthcare EDI transactions, such as EDI 834, is a prime illustration of this. Healthcare providers can electronically transmit complete claim information, EDI transaction codes, including patient demographics, diagnosis codes, conducted procedures, and related expenses, in place of laboriously drafting and submitting paper-based claims.
By doing away with the necessity for handwritten documentation, this automated method significantly lowers the possibility of mistakes or missing data. Using Healthcare EDI has advantages beyond efficiency. Payers are able to receive and process electronic claims more quickly, which leads to speedier reimbursement and better financial management. Providers benefit from faster claim processing and adjudication.
Additionally, claim documentation’s data completeness and accuracy are guaranteed via EDI. The possibility of claim rejections or denials is significantly decreased by the standardized format and validation tests included in EDI healthcare transactions, which aid in the early detection of errors or missing information. Additionally, providers have the option to electronically attach any required supporting documentation, guaranteeing a complete and accurate description of the services rendered.
Finally, EDI transaction codes fosters better cooperation and communication between payers and providers. All parties may effectively communicate about claim status updates, requests for more information, and any discrepancies thanks to this streamlined communication.
Ensuring Compliance
For healthcare providers, utilizing EDI solutions is both a tactical and strategic requirement. Healthcare providers that failed to comply with HIPAA were fined about $2 million in 2023 alone.
The CMS Interoperability and Patient Access rule states that emails and fax numbers are not enough to be in compliance. Healthcare organizations must use the ASC X12 protocol for all EDI transactions pertaining to healthcare, as required by the HIPAA EDI Rule. As a result, using EDI guarantees adherence to legal mandates like HIPAA and Medicare, protecting patient privacy and data security throughout the course of treatment.
By decreasing errors and guaranteeing compliance, providers can use EDI provider to satisfy quality reporting requirements for initiatives like PQRS and MIPS. EDI solution providers can show compliance through rewards programs and achieve EHR rich use criteria because of EDI’s ability to support electronic health records.
By following the compliance and security guidelines, healthcare firms decrease the chances of data breaches, unauthorized access and other non compliance fines. By proving its ability to safeguard the patient information, it has successfully built confidence among patients. Payers and other third parties involved.
Reduction of Claim Rejections
Claim denials have a substantial financial impact; unresolved denials cost hospitals $5 million on average per year, or up to 5% of their net patient revenue. In the last five years, the average claim denial rate has increased to above 20%, and it is currently at 10% or higher on average.
In order to reduce claim denials and maximize revenue cycle management for innovative healthcare delivery models, Healthcare EDI transactions are essential. Through standardized claims data transmission and real-time validation made possible by EDI, accuracy and completeness are guaranteed before submission. By assisting providers in promptly identifying and fixing problems, this feature lowers the possibility of denials brought on by erroneous or incomplete information.
Additionally, the uniform structure of EDI transactions guarantees adherence to payer specifications, reducing rejections and raising the percentage of accepted claims. Furthermore, automated EDI claims submission shortens response times, simplifies the processing of claims, and improves correspondence with payers. These transactions thereby lessen the possibility of mistakes or delays as well as the possibility of claims being denied or being delayed.
Finally, comprehensive justifications for claim denials are provided by EDI transactions in the healthcare industry, such as the 835 Claim Payment Advice transaction, sometimes referred to as remittance advice. With this knowledge, providers can take preventative measures to avoid future recurrence of the same problems and proactively address the reasons for denials.
Cutting Expenses
In the US, administrative expenses make up 25% of total healthcare spending, or $250 billion annually. By automating procedures, cutting paperwork, increasing productivity, decreasing transaction costs, and boosting accuracy, EDI is essential for healthcare providers looking to cut expenses.
Providers can save time and money by using EDI, which automates a variety of administrative processes like data entry and claims administration. Getting rid of paper-based procedures lowers expenses and lowers the possibility of mistakes. Increased data accuracy through EDI lowers the number of rejected claims and related administrative costs.
Because most medical data is digital, healthcare EDI lowers handling costs for document processing (e.g., purchases of paper, forms, supplies, and mailing). The Workgroup for Electronic Data Interchange (WEDI) estimates that by putting EDI into practice, hospitals can save $0.86, physicians can save $1.49, and other parties can save $0.83 each claim.
Increased Security and Productivity
EDI transactions are crucial for enabling safe data exchange between approved parties, such as patients, insurers, and suppliers, in the healthcare industry. This is due to the fact that EDI mapping lowers the possibility of data breaches by converting business files into a format that is difficult for humans to read. HIPAA standards further improve EDI security by guaranteeing that only authorized personnel can access the data. Lastly, B2B file transfers utilizing secure protocols like SFTP, MLLP, and AS2 are used to exchange all files.
Through the facilitation of real-time data connections between multiple parties, healthcare EDI increases efficiency. It also removes the requirement to confirm that the receiver has received the information, which lowers the frequency of denials and rework requests. As a result, this reduces administrative load and enables healthcare personnel to make better use of their time by ensuring that crucial data is delivered on time and error-free.
Build a More Efficient Healthcare System With Our EDI Solutions
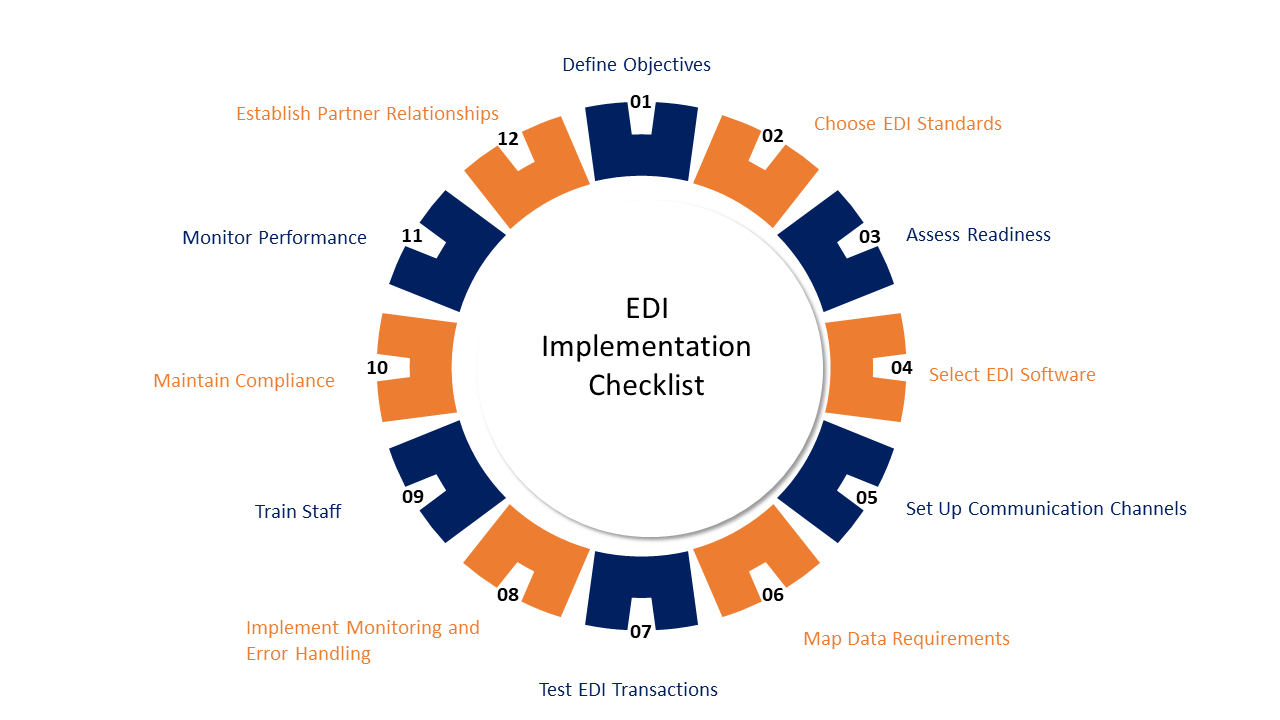
EDI Checklist 101 for Healthcare Providers
-
Examine Your Company’s Requirements
Prior to implementing EDI in healthcare, it is important to clearly define the objectives and needs. Examine your internal systems carefully to see if they are prepared for integration. Moreover, list any difficulties or advancements you hope to accomplish with EDI services. If you require help assessing the viability and possible advantages of EDI for your business, think about speaking with an experienced IT supplier.
-
Comprehend the Fundamentals
Make yourself familiar with the basic terms and principles of EDI. Discover the differences between purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, among other document kinds. Recognize the popular formats and structures, like ANSI X12 or EDIFACT.
-
Research Industry Guidelines
Check the specific industry rules and regulations that are applicable in the field that you are planning to work in. When it comes to certain industries like healthcare, retail and logistics, EDI standards can be pretty specific. Familiarize yourself with the particular requirements and procedures that re-ensures adherence and productive data transfer.
-
Set Specific Goals
Establish the aims and objectives for the EDI implementation in your company or for your clients. Recognize your goals, such as increasing data accuracy, decreasing manual processes, or increasing efficiency. Your implementation plan will be guided by well-defined objectives.
-
Select the Appropriate Providers and Software
Look for reliable, knowledgeable EDI managed service providers with experience in the healthcare industry. Create a detailed plan and approach jointly for integrating EDI into your present systems. You can begin your search by looking up reputable software development companies on sites like Clutch, which offer verified ratings and reviews for software development suppliers globally. Take special note of the suppliers’ EDI installation experience, familiarity with regulations and industry standards, and ability to understand your particular needs. To ensure the confidentiality and securityof important healthcare data, take into account their background in data security and compliance as well.
-
Work together with the Stakeholders
To fully grasp the needs and requirements of internal stakeholders, including IT teams, operations departments, and business departments, collaborate closely with them. Involve them in the planning and execution phase to guarantee seamless EDI adoption and integration.
-
Assure Data Accuracy
Collaborate with your IT partner to design or select healthcare EDI software that meets your company’s needs. Connect your existing systems, including billing, electronic health record (EHR), and practice management systems, with the EDI solution. Ensure that there is smooth interaction and communication between all systems. Keep an eye out for data integrity and accuracy. To find and fix problems early on, put error handling procedures and data validation checks into place. To uphold strict requirements for data quality, audit and monitor data on a regular basis.
-
Examine and Confirm
Make sure your EDI processes are thoroughly tested and validated before implementing them on a large scale. With trading partners, conduct end-to-end testing to confirm system integration, document mapping, and data transmission. Resolve any problems or inconsistencies found during the testing process.
-
Continue to Uphold Security and Compliance
Since critical company information is sent during EDI, make sure you have strong security measures in place. To prevent unwanted access to data, put access controls, firewalls, encryption, and other security measures into place. Respect all applicable data protection and compliance laws, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
-
Processes and Procedures for Documents
Make thorough records that detail all of your EDI protocols and processes. This material will be used as a guide for new hire orientation, troubleshooting, and maintaining uniformity in your EDI processes.
-
EDI Support and Maintenance
New technologies and standards are continually being developed in the EDI industry. Keep abreast of the most recent advancements, market patterns, and legislative modifications. Evaluate your EDI integration on a regular basis to find areas for development and take advantage of fresh chances. When it comes to any issues, upgrades, or enhancements pertaining to the EDI system, continue to be in constant communication and collaboration with your IT partner. To maintain compliance and optimal performance, stay up to date on any changes to the legislation or EDI standards. Regularly assess the effectiveness of the healthcare EDI implementation and make the necessary modifications to maximize its benefits. Reach out to EDI support specialists for the same.
Use Cases for EDI in Healthcare
By enabling a more effective, secure exchange of healthcare data, EDI service has played a significant role in revolutionizing the healthcare sector. Other nations have followed suit, with the United States having compelled its implementation in the healthcare sector through laws like HIPAA.
Let’s examine the amazing developments that this technology has brought about in the healthcare sector to obtain a better understanding of the expanding significance of healthcare EDI.
Claims Processing
Managing EDI healthcare claims is one of the main applications of EDI in the healthcare industry. It is used by healthcare practitioners to electronically file standardized-format insurance claims to insurance carriers. This EDI healthcare review and response improves cash flow and reimbursement speed for healthcare organizations while also cutting down on the time and resources needed to process claims.
Verification of Eligibility
Before offering medical care, healthcare professionals must confirm a patient’s eligibility for such care. By using EDI services and solutions, they can send an eligibility request to the insurance provider and get a prompt answer outlining the patient’s coverage, which lowers the possibility of mistakes and boosts open enrollment for benefits and the overall effectiveness of medical procedures.
Payment and Remittance
Another procedure that EDI healthcare transactions streamline is payment. Payment advice (ANSI X12 835) is a document that insurance companies can use to inform providers on what has been paid, rejected, or requires additional clarification. As a result, providers may more easily and quickly reconcile payments and claims with their data.
Authorizations and Referrals
When a patient wants to see a specialist or needs a certain service, an authorization or referral is frequently required. Healthcare organizations can expedite the process and enhance care coordination by using Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) to electronically transmit referrals and authorizations across healthcare providers.
Orders and Results for the Laboratory
EDI services are used in the laboratory to automate the ordering and reporting of experiments. A lab can receive an electronic order from a healthcare provider, and the lab can return the results as soon as they are prepared. This decreases errors, gets rid of paperwork, and speeds up processes. This integration guarantees that results are directly incorporated into the patient’s electronic health record (EHR) and lowers the possibility of errors resulting from manual entry.
Pharmacy Transactions
Prescription dispensing and benefit coordination are two examples of the transactions that pharmacies employ EDI to handle. The EDI standards that are frequently utilized in pharmacy transactions have also been made available by the National Council for Prescription Drug Programs (NCPDP). This expedites the billing process and facilitates payment receipt, saving pharmacies from having to play the waiting game.
| Healthcare Use Case | Transaction Set | Role for Payers | Role for Providers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Processing Claims | EDI 837 | Receive and process claims for payment | Submit claims for reimbursement |
| Verifying Patient Eligibility/Benefits | EDI 270/271 | Determine patient’s coverage and benefits | Obtain information on patient’s benefits |
| Inquiring/Verifying Prior Authorization | EDI 278 | Request pre-authorization for services | Respond to pre-authorization requests |
| Enabling Remittance Advice | EDI 835 | Provide payment details and explanations | Track payments and reconcile accounts |
| Exchanging Referral Information | EDI 278 | Request and verify referral information | Respond to referral requests |
| Transmitting Provider Information | EDI 274 | Update provider information | Communicate changes to provider details |
| Coordinating Benefits | EDI 837 COB | Coordinate benefits with other payers | Coordinate benefits with other providers |
| Exchanging Patient Information | EDI 275 | Share patient information with stakeholders | Receive and integrate patient information |
| Managing Payments/Remittance | EDI 820 | Initiate payment orders and remittance | Receive and reconcile payment information |
| Managing Benefit Enrollment/Maintenance | EDI 834 | Manage benefit enrollment and changes | Transmit enrollment and changes |
| Acknowledgment/Confirmation | EDI 997, EDI 999, EDI TA1 | Confirm receipt and acceptance of EDI transactions | Acknowledge receipt and validation of EDI transactions |
Regulatory Compliances for Healthcare EDI
Healthcare industry regulations, standards, and organizations oversee Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) to ensure security, privacy, and interoperability of health information. Some of the primary legislation and initiatives that regulate EDI in the medical industry are listed below:
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA):
The HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is a rule that establishes uniform guidelines for the use and disclosure of protected health information (PHI). It is important for EDI healthcare transactions to follow these guidelines when it comes to data access, transmission security, and patient authorization for information exchange.
The main focus of HIPAA is to ensure the security of electronic PHI. This is through the implementation of administrative, physical, and technical safeguards. It is crucial for EDI systems to have strong security measures in place to prevent unauthorized access, data breaches, and maintain data integrity during transmission.
HITECH Act, or Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health:
The HITECH Act was created to:
- Improve the standard, security, and effectiveness of healthcare
- Promote widespread use of electronic health records (EHRs)
- Bring the healthcare system up to speed
Under this act:
- Healthcare providers are encouraged to adopt certified EHR systems
- They are given benefits for setting up these systems and effectively using them, such as electronically collecting and transmitting patient data
- Procedures are in place to address privacy and security concerns related to EHRs
- Healthcare organizations have necessary safeguards that protect patient records
- Fines are imposed for any unauthorized access, use, or disclosure of protected health information (PHI)
Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Initiatives
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) is a federal agency with responsibilities that include:
- The Medicare and Medicaid programs, two national health care programs benefiting about 75 million Americans
- The State Children’s Health Insurance Program
- Regulation of all non-research laboratory testing performed on humans in the United States
- Programs assisting millions of Americans and small companies in obtaining health insurance coverage.
X12 Standards
For EDI trade in both the commercial and non-commercial sectors, X12 is the standard. An ANSI standard forms the basis of X12’s syntax. There are directories containing data items, composite data elements, segments, and messages within that syntax. Messages are generally put in an “envelope” that contains information on the sender, recipient, and other aspects of the transfer. One can model X12 messages with either DFDL or MRM Tagged/Delimited String Format (TDS).
National Council for Prescription Drug Programs (NCPDP)
This healthcare organization is responsible for establishment of industry standards for the interchange of pharmacy-related data, such as electronic prescriptions, pharmacy claims, and medication histories, carried out by the National Council for Prescription Drug Programs (NCPDP).
Conclusion
The Global Healthcare EDI Market was estimated to be worth USD 3.96 billion in 2022 and is expected to rise at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.45% from 2023 to 2032, according to a study by Quince Market Insights. This emphasis on EDI in healthcare will have an impact on pharmaceutical companies and makers of medical devices, as well as the overall life sciences field.
Due to the growing demand from small and medium-sized healthcare providers searching outsourcing EDI, it is anticipated that the online and cloud-based EDI segment will propel this expansion. The healthcare industry needs to adhere to regulatory rules. These rules mandate the adoption of particular standard formats or e-invoicing procedures that utilize EDI technology.
Using accepted standards and formats, EDI healthcare transactions provide a safe and effective means of sharing data between healthcare organizations, insurers, and patients. These technologies assist healthcare companies in lowering latency and enhancing care coordination and quality. Top Healthcare companies can benefit enrollment and maintenance and handle claims, eligibility, status, and payment management more efficiently and in compliance with HIPAA regulations when they have a solid EDI system.
One of the top EDI solutions providers in USA, A3Logics provides adaptable EDI software that makes it simple for users to create, parse, validate, and convert any type of healthcare EDI transaction without the need for coding. We make it easy for healthcare businesses to integrate EDI data with any database, application, or system by using pre-built connections and a drag-and-drop interface.
Apply corporate rules, personalize EDI workflows, and onboard business partners quickly and easily in real-time.
FAQ
Why is EDI significant, and what does it mean?
EDI refers to the electronic transmission of business messages (orders, invoices, credit notes, ASNs, etc.) from your own EDI system to your own back-office, warehouse, CRM, or ERP systems reduces the need for re-keying business data.
What is the EDI 837 that the insurance company receives from the provider?
Healthcare service providers transmit encounter data, claim billing details, or both using the EDI 837 Health Care Claim transaction set. It is sent to an insurer by a healthcare provider, like a hospital or primary care physician (PCP).
What is the healthcare industry’s EDI format?
Health insurance claims and other “administrative” data related to healthcare are frequently exchanged using the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) protocol. The American National Standards Institute-chartered X12 non-profit corporation oversees EDI in the US.
What is the total number of EDI types?
Over 300 distinct X12 EDI standard types exist, each assigned a unique three-digit number and covering a wide range of sectors including banking, government, healthcare, insurance, and transportation.
What does an EDI transaction in the healthcare industry look like?
A few instances of the different EDI document types that are shared in the healthcare sector. The below are the documents shared during EDI transactions in the healthcare industry:
- Claims
- claim status and processing
- billing
- benefit eligibility questions
- health plans
- payment information, and
- even employee remuneration





![10 Top IoT Security Solution Providers in USA [2024]](https://www.a3logics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/New-Project-4-2.webp)