Edi in manufacturing industry flourish on connectivity with its buying partners. These can be wholesalers under the indirect sales or final consumers in case of ecommerce. Along with the spread of global supply chains, business transactions have become complex and traditional methods of data handling manually fail.
Here EDI in manufacturing works as a game changer and helps in establishing fast and seamless coordination between a producing and a purchasing party.
Both have a long history of working together since the 1980s with the beginning of digital document flow in the making industry.
EDI streamlines the transactions and product movement-related operations by eliminating the need for tons of paperwork and adding electronic communication between the trading partners.
To enhance operational efficiency, goods-producing companies are increasingly integrating EDI technology into their ERP systems. This allows them not only to conduct direct business with wholesalers but also to seamlessly engage with end consumers through their online platforms. In this article, you will explore the concept of EDI for manufacturing in depth. Moreover, we will delve into the key transactions involved, highlight the numerous benefits it offers, and, finally, discuss the emerging trends shaping its future.

Table of Contents
What is EDI in Manufacturing
EDI in manufacturing industry refers to the electronic exchange of business documents between the producers and their supply chain partners. It includes interchange of papers including invoices, purchase orders, shipping notices, and payment details in the standardized formats. Data automation speeds up the key transactions, eliminates the human errors and increases overall accuracy. Manufacturers have been using this technology for the past several years due to its reliability and efficiency which contributes in avoiding delays and strengthening the business relationships through performance satisfaction.
Supplier and partner onboarding have become much easier with the EDI application in manufacturing, which is critical for the industry to maintain its supply chain. Along with the connectivity, this digital solution accelerates the production and distribution process by reducing high labor and storage costs. Improved data exchange practices lighten the product movement operations and allows the producers to innovate new production methods enhancing quality and customer services. Ordering raw materials from suppliers, receiving order acknowledgments, production planning on basis of demand forecast, sending shipping notices to logistics partners, issuing invoices and processing payments, etc. are the most common EDI application in manufacturing.
Integration of Electronic Data Interchange in the goods making industry has become a necessity rather than an option. It simplifies the daily business operation associated with data sharing among trading partners and providing updates to customers end. However, it is important that the company select modern techniques for Electronic document flow to get the best results.
EDI in Manufacturing: Statistical Insights
- More than 85% of total sale volume of big manufacturers like Brother International rely on EDI.
- It is observed that manually order processing costs approximately $70 per order, whereas with automated process it comes to $0.01-$0.02, showing a significant cost reduction in order processing.
- Electronic invoicing saves up to 60%-70% of transaction costs saving a lot of money for the other key tasks like innovations and improving customer services.
- As per Quality Magazine, average error rate in manual data entry is around 1%, which can create significant issues in manufacturing and delivery process. But EDI Solutions eliminates these errors, leading to accurate and quick document exchange.
Above figures show that EDI application in manufacturing brings high sales volume, speedy information flow, cost reduction, and error-free data exchange.
Why is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) Essential for Manufacturing?
Businesses based on goods production operate in a dynamic industry demanding coordination, speed, and correctness in the data sharing routines. Key reasonsfor making EDI for manufacturing essential are listed below:
1. Substantial savings
Automated transaction platforms replace the traditional data entry system which once demanded high labor and tones of materials along with being time consuming. But modern data exchange methods have cut down the various operational costs and overhead expenses associated with the communication of product flow among trading partners. Also, the technology fastens the processing cycle of routine tasks like getting order, invoicing, and movement of goods, saving a lot of time.
2. Scalability
As the production business grows, transaction volume also increases due to negotiation methods adopted by different trading partners. Electronic data interchange provides scalability with the various dealing parties matching their transactional formats and standards. This way, a huge number of contracts and numerous dealing per day does not become a heavy task for the manufacturing company and facilities expansion.
3. Compliance
Every firm needs to meet some predefined legal and partner specific requirements. Likewise, goods producing companies are also obliged to comply with industry regulations and EDI works the best in this criterion. It ensures that the exchanged documents fulfill all the required formalities and align with the standards of those connecting parties in the supply chain.
4. Operational Efficiency
Automated transaction platform offers seamless connectivity with the logistic software systems such as ERP (enterprise resource planning), MES (manufacturing execution system), and WMS (warehouse management system). It makes the communication effortless between the key supply chain partners and boosts cooperation, resulting in productivity and revenue.

Key EDI Transactions for Manufacturing
There are several types of EDI transactions that are repeatedly used in the manufacturing industry. Following are some of the most common EDI transactions that happens in manufacturing industry:
1. Purchase and Order Processing
- EDI 850 – Purchase Order (PO)
Manufacturers send to suppliers to buy raw material or services, containing details such as name of the required items, quantity, price, shipping, payment and discount information.
- EDI 855 – Purchase Order Acknowledgment
Supplier sends to manufacturer for the confirmation of EDI 850 and communicates about the acceptance, rejection or changes made in the purchase order for further processing.
- EDI 860 – Purchase Order Change Request
Producer uses this document to request any changes in the previously sent EDI 850.
- EDI 865 – Purchase Order Change Acknowledgment
The manufacturer sends this to inform the supplier about the acceptance of changes made later in the purchase order.
2. Inventory and Shipment Transactions
- EDI 846 – Inventory Inquiry/Advice
The producer sends this document to the members of the supply chain network to notify them about the inventory status.
- EDI 856 – Advance Shipping Notice (ASN)
The manufacturer sends or receives this transaction paper, which contains particulars about the shipment of the product, such as order details, description of items, types of packaging used, carrier information, etc.
- EDI 810 – Invoice
Seller/producer uses this billing document to charge its customers for the goods and services provided.
- EDI 820 – Payment Order/Remittance Advice
This form is a response to invoice 810, informing about the payment initiation and/or requesting any change in the billing amount.
3. Logistics and Supply Chain Transactions
- EDI 940 – Warehouse Shipping Order
Electronic documents used to instruct the warehouse to ship the product to the customer and includes the details like item quantity, customer address, product description, and order number.
- EDI 945 – Warehouse Shipping Advice
A logistics provider or remote warehouse handler sends this set to their client to confirm thatthe shipment has been completed.
- EDI 214 – Shipment Status Message
Transportation bearer or third-party logistic provider such as trucking company use this transaction paper to inform about the shipment status to the consignee or shipper. It contains particulars like Shipment identification numbers, date, time, and location of pickup, arrival, and delivery of goods.
- EDI 210 – Freight Invoice
Commercial carriers send EDI 210 to the manufacturer or distributor to convey billing for transportation services.
4. Production and Planning Transactions
- EDI 830 – Planning Schedule with Release Capability
The producer forwards this form to its supplier to convey to them the anticipated needs for a particular quantity of goods for a certain period of time.
- EDI 862 – Shipping Schedule
EDI 862 provides shipping instructions to the suppliers for the requirements estimated in the previous Planning Schedule 830.
- EDI 824 – Application Advice
When a party receives an Electronic data interchange transaction document, he alerts the sender about the acceptance, rejection or required changes in the transaction through this application advice.
5. Compliance and Regulatory Transactions
- EDI 997 – Functional Acknowledgment
One of the parties sends this receipt known as FA to another party as an acknowledging response after receiving Electronic data interchange messages.
- EDI 821 – Financial Information Reporting
The report shares the particulars like information about financial accounts, balances, and a summary of dealings.
- EDI 834 – Benefits Enrollment and Maintenance
It is a standardized form used to digitally transmit the health insurance enrollment and maintenance information. Employers, government or labor unions use this to enroll the employees and other members in the health insurance plans.
| Key EDI Transactions in Manufacturing | |||
| Category | EDI Code | Transaction Name | Description |
| Purchase and Order Processing | 850 | Purchase Order | Initiates purchase of goods |
| 855 | Purchase Order Acknowledgment | Acknowledges Purchase Order receipt and terms | |
| 860 | Purchase Order Change Request | Requests change to a previous order | |
| 865 | Purchase Order Change Acknowledgment | Confirms Purchase Order changes | |
| Purchase and Order Processing | 850 | Purchase Order | Initiates purchase of goods |
| Inventory and Shipment | 846 | Inventory Inquiry/Advice | Shares inventory availability info |
| 856 | Advance Shipping Notice | Provides shipment details in advance | |
| 810 | Invoice | Billing document | |
| 820 | Payment Order/Remittance Advice | Details payment instructions | |
| Logistics and Supply Chain | 940 | Warehouse Shipping Order | Directs shipment from warehouse |
| 945 | Warehouse Shipping Advice | Shipment confirmation from warehouse | |
| 214 | Shipment Status Message | Tracks the shipping status | |
| 210 | Freight Invoice | Billing for freight services | |
| Production and Planning | 830 | Planning Schedule | Forecasts production needs |
| 862 | Shipping Schedule | Details delivery expectations | |
| 824 | Application Advice | Indicates processing feedback/errors | |
| Compliance and Regulatory | 997 | Functional Acknowledgment | Acknowledges EDI document receipt |
| 821 | Financial Information Reporting | Shares financial information | |
| 834 | Benefits Enrollment | Employee benefits enrollment info | |
Key Benefits of EDI for Manufacturers
EDI application in manufacturing brings numerous benefits out of which major are discussed below:
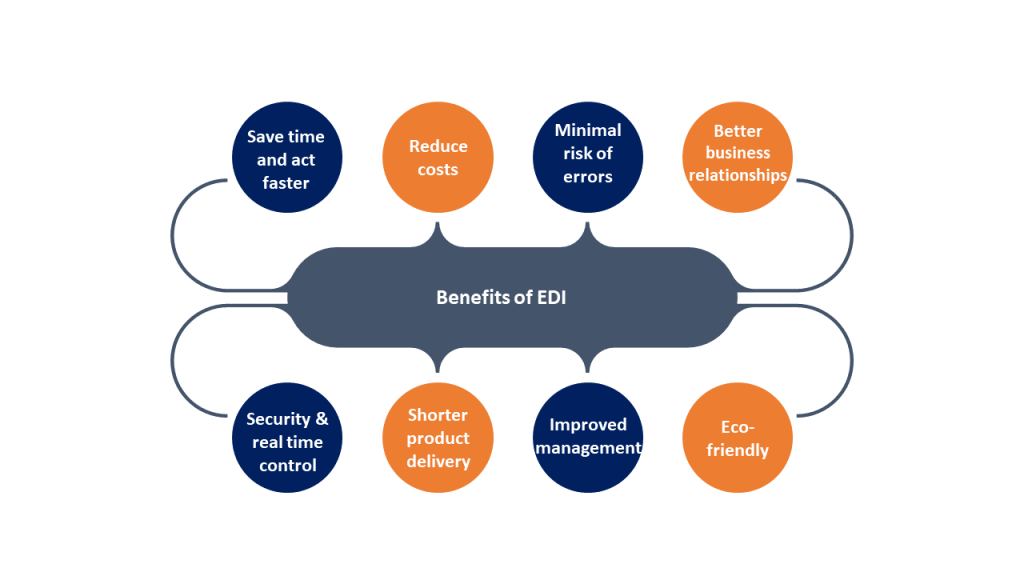
1. Automated Data Exchange
Automation eliminates manual work of data entry and reduces the chances of human mistakes bringing accuracy and efficiency in document flow. Error removal shortens the process time and saves valuable resources which otherwise had to invest in correcting the faults. Timely response leads to customer satisfaction resulting in loyalty and brings product’s repeated demand for the producers. Along with it, correct information exchange maintains consistency as all the parties receive the same set of data building trust among them.
2. Faster Transaction Processing
Electronic data transfer boosts the transmission and processing of invoices, orders and shipment records, which accelerates the whole product manufacturing and supply operations.
3. Reduced Paperwork & Administrative Costs
Extensive administration and overhead expenses are replaced by digital processes, cutting down the operational costs associated with information exchange in the manufacturing business.
4. Improved Inventory Management
Automation in information sharing tasks provides visual updates of inventory levels, making it easy to track stockouts and maintain optimum stock management.
5. Streamlined Supply Chain
When all the connected parties under a supply chain are timely informed about the relevant processes and figures, miscommunication and delays can be easily eliminated and enhancing B2B relationships.
6. Reduced Order-to-Cash Cycle
Fast transaction completion initiates quick payment from relevant partners, resulting in better cash flow within the organization.
7. Enhanced Data Security
Encrypted and compliant EDI data is exchanged while following the industry standards, which ensures cybersecurity and safety from malware actions from third parties, specifically in case of sensitive information sharing electronically.
EDI in Manufacturing Industry: Common Challenges and Solutions
Adoption of EDI solutions provides numerous benefits, but still, their implementation in the goods-making industry carries certain challenges. Let’s learn about these challenges and their relevant methods to overcome them, as described below:
> Integration
Complex setup of in-house manufacturing can make it difficult to integrate modern EDI in the existing ERP system.
Solution: Use preconfigured templates and train the workforce for new automated processes, for fast integration and smooth functioning.
> Onboarding Various Partners
Distinct parties have different requirements for digital formats and standards, making the onboarding hard and time-consuming.
Solution: Select a provider who offers a flexible data interchange system that supports several types of formats and protocols.
> High Initial Costs
Small manufacturers may find the upfront investment required for initial implementation out of their budget, creating hurdles in the setup.
Solution: Cloud based Data integration tools come with lower cost, which can be scalable for the beginner and small units in the industry.
> Incorrect data mapping
Inconsistencies in statistics create digital transmission errors, resulting in inaccurate transactions.
Solution: Ensure regular testing and validation through data mapping tools to maintain accuracy in the exchange process.
Future Trends in EDI in Manufacturing
Evolving business needs and advanced technology are shaping the future of EDI in the manufacturing industry. Key trends are listed here:
Artificial Intelligence
AI facilitates machine learning that helps in quick error detection and enhances data mapping, simplifying trading partner onboarding. Smart factories are expected to rely on AI and internet of things (IoT) for seamless communication.
Cloud-based EDI
This is a cost efficient, scalable and easy to adopt technique as compared to older versions of electronic document exchange systems. Even beginner or small-scale producers can opt for cloud-based solutions due to its cost efficiency, making its future bright in the manufacturing industry.
Blockchain Integration
This technology is becoming popular among the businesses working in highly regulated environments and require heavy compilation with maximum data security, while maintaining transparency in their transactions.
API-based EDI
When Application Programming Interfaces (API) is integrated with traditional electronic data exchange, it provides real time information sharing and offers flexibility. Manufacturing businesses are switching to API based data transmission systems for greater adaptability and extended reach beyond the traditional automated method of B2B transactions.
How A3Logics Can Help with EDI in Manufacturing Solutions?
At A3Logics, we assist the business for EDI application in manufacturing, deriving best solutions for them that goes well with their unique needs. We provide a flexible and industry specific standardized platform to the companies seeking digital options for their data exchange. Below is the list of explained EDI services, we offer to our clients:
1. Throughout Implementation and Management
- We guide our customers across the whole process of EDI implementation ranging from assessing their needs to integration into existing ERP and WMS.
- Educate the client’s team about the system and its working for effective use.
- Provide continuous monitoring and addressing of issues if any.
- Offer Cloud-based services for scalability and flexibility.
2. Enhanced Supply Chain Management
- Our company enables the manufacturer to visibly track their order status, stock management, trace shipment, and get hustle free payments. Real time inventory updates also reduce the issues of overstocking and shortages.
- We focus on smooth communication between the relevant parties in a supply chain such as producer, supplier, distributor, and customers, making the goods movement process efficient and more responsive.
- Our automated transaction platform reduces delays in the order fulfillment by implementing just-in-time processes and tracking performance over the distribution network.
3. Efficiency and Cost Savings
- We automate the whole document exchange process with our advanced EDI solutions, fastening the communication between concerned business parties.
- By eliminating manual data entry, our application eliminates the chances of human errors in transactions, saving time and effort of the producers, which he can invest on other important tasks.
- Paper, postage, and manual data entry costs are significantly reduced, channelizing the investment on key areas like innovation and customer services.
4. Compliance and Security
- A3Logics keeps up with several EDI standards, ensuring compatibility with all required Data automation protocols.
- We use safe and well encrypted document interchange software for secure transaction exchange.
5. Partner Onboarding and Testing
- A3Logics streamlines the onboarding process by establishing smooth communication between trading partners.
- Our structured approach offers customized B2B integration, facilities tailored solutions for all the relevant parties and simplifies the compliance process.
6. 24/7 Monitoring and Support
- Even after complete setup of EDI for our manufacturing client, we offer after sale services like timely response to their query related to any issue or debugging any error in the system.
Final Thoughts
EDI in manufacturing has become a crucial part of goods-producing businesses due to the need for an automatic supply chain and speed plus accuracy in the data exchange operations. Producing companies who adopt this digital platform face fewer errors and enhance the procurement-to-delivery cycle. Throughout knowledge of all necessary transactions under digital document exchange in production guides, in making informed decisions. By selecting the right EDI provider, such as A3Logics, manufacturers can overcome associated challenges and be ready for the technological transformation.





