Warehouses are responsible for delivery timelines, customer satisfaction, and overall profitability in the supply chain system. In the current scenario of digitization, where vast amounts of data are transferred daily, EDI in Warehouse Management.
Imagine your stockroom receiving orders via email or fax. As a result, staff must manually enter data into multiple systems. Consequently, the lack of seamless communication leads to frequent errors, incorrect deliveries, and ultimately, wasted resources.
EDI in warehouse management automates workflow between buyer and supplier. It eliminates slow, error-prone manual processes and boosts instant stock updates. By using EDI transactions for warehousing, a lot of tasks can be streamlined, including shipment handling, and confusion-free information exchange between different trading partners. Modern logistics also require the integration of automatic data transmission platforms to provide better results. To uncover the full potential of EDI in warehouse management, let’s dig into the related concepts and understand key uses as well as common transactions .

Table of Contents
Understanding EDI in Warehouse Management
EDI is a sophisticated system in the logistics industry that automates structured business document exchange between the relevant parties, including suppliers, carriers, and retailers. This data integration tool simplifies the complicated and huge amount of routine transactions, improving accuracy and operational efficiency.
In WMS (Warehouse Management System), electronic document exchange enables direct data transmission, eliminating human errors and ensuring accurate information sharing.
Real-time tracking, operational clarity, and end-to-end monitoring are key use cases of EDI in warehouse management. Essential EDI transactions like 940, 945, and 856 ensure inventory accuracy, streamlined shipments, and seamless communication with third-party logistics partners.
Cost reduction is another key benefit of implementing this digital technology, as it eliminates the need for extra staff and paper-based processes. Additionally, stockroom and goods movement messages are recorded using standardized electronic formats like ANSI X12 or EDIFACT.
Real-World EDI Statistics for Warehouse Professionals
The following statistics show the impact of using EDI transactions for warehousing:
- Distribution centers relying on Automated data transmission record a shortened order processing time by 30%-50%.
- Manual order processing costs $38 per order, whereas with EDI, it is $1.35, showcasing a drastic difference between the expenses from both methods.
- In September 2023, surveys with respondents engaged in logistics and warehouse operations recorded a jump in their revenue from $301 million last year to $778 million that year due to increased order fulfillment on e-commerce platforms through the adoption of automated technologies like EDI.
- 84% of warehouse management systems use related software and automation.
Key Use Cases of EDI in Warehouse Management
Let’s have a glance over some of the top use cases of EDI in warehouse management, which is reshaping the industry.
1. Automating Inventory Updates
B2B data transfer systems synchronize real-time inventory updates, informing accurate stock levels available in the order fulfillment center. It facilitates the administrator to make correct decisions regarding stock replenishment, preventing overstock as well as shortage. Instant tracking of goods movement guides in demand forecasting and better planning for the purchase of new stock. Warehouse managers can maintain an optimum level of supply by adjusting the storage according to current and near-future needs.
2. Optimizing Order Processing and Fulfillment
EDI streamlines all the operations associated with shipment execution, such as order generation, transmission, confirmation, transportation, and delivery. The digital tool eliminates manual transaction recording and exchange. The software automates the whole process and provides error-free, accurate details like order picking, packing, shipping, etc. It not only reduces the errors in data transfer that may cause delays in the complete flow of products but also reduces the time consumption during the supply cycle.
3. Enhancing Supplier Collaboration
Automated document exchange fosters smooth communication between the different parties, including the warehouse, supplier, carrier partner, and end customer. The structured exchange of purchase orders, invoices, and delivery queries fosters strong trading relationships. Moreover, EDI streamlines shipment tracking, logistics, and delivery details, thereby enhancing collaboration across the supply chain.
4. Streamlining Returns and Reverse Logistics
Reverse logistics is much smoother with the data integration tool as it accelerates the return request approval and shipment receipt process. It also forwards restocking instructions instantly for returned products. EDI gathers data to analyze return patterns, providing feedback on areas for improvement like supplier performance and product quality.
Real-time payment updates and fast transactions enable quicker resolution of return requests and refunds, boosting customer satisfaction and encouraging repeat purchases.
5. Improving Warehouse Compliance and Security
EDI enables the stock administration to be systematic with routine audits and standardised transaction formats, elevating accurate data exchange and live inventory status. All this comprises enhanced security and support in following regulatory protocols.

6. Reducing Paperwork and Manual Errors
Automated document exchange removes the hectic physical data entry workloads, eliminating inconsistencies and the chances of mistakes in feeding the figures. The platform uses only standardized formats of transactions, which ensures accurate content transfer between the business parties involved in the matrix. All the relevant units get real-time updates, maintaining input uniformity across the supply chain. The digitization of document transmissions removes the need for printing and posting, along with storage of a stack of papers, reducing significant costs by using EDI in warehouse management.
7. Seamless Integration with Transportation & Logistics Partners
A warehouse that can easily track its goods movement and other logistics details can manage its inventory operations smoothly. A B2B data transfer system makes it possible by uninterrupted communication with suppliers and transportation providers. It prompts fast information exchange related to shipment, delivery, and stock levels between WMS, delivery partners, shipment agencies, carriers, and transport management systems. This way, EDI benefits warehouse operations by coordinating multiple tasks associated with the product procurement pipeline.
8. Predictive Demand Planning and Stock Optimization
Unified data exchange contributes to demand forecasting and better planning for the future needs of supplies. Predicting upcoming requirements in advance helps in maintaining an optimum level of inventory across several locations of warehouses. In addition, with live updates about the stored units in and out, managers can make informed decisions regarding reordering after looking into pending orders and upcoming deliveries when an item runs out of stock. EDI benefits the WMS in fulfilling sudden spikes in purchase requests during a peak period by enabling readiness for the urgent supply.
9. Multi-Warehouse Coordination
When an enterprise possesses multiple warehouses at different locations, electronic document exchange advances centralized control over each of the units. Goods movement and inter-location coordinates develop a fast supply of products by implementing EDI in warehouse management, avoiding delays. Inventory handling gets considerably smooth, and a balanced approach can be integrated into the supply operations despite the distinct position of the storage facilities.
Top Benefits of Implementing EDI in Warehouses
The implementation of EDI transactions for warehousing brings numerous benefits to the fence. The most leverage benefits of EDI in warehouse management are-
Increased Efficiency and Accuracy
A single mistake of one digit with hand-driven typing or order writing can create a massive amount of difference in the transaction. For instance, instead of creating a purchase order of 500 units, a wrong addition of zero will result in ordering 5000 units, leading to a wastage of money and resources. Automation saves warehouse transactions from these kinds of blunders by terminating handwritten orders and invoices. EDI in warehouse management accurately records inventory and other key dealings in standardized formats and also detects errors before they create any major issues in supply operations.
Reduced Operational Costs
Traditional data transmission methods include hidden costs such as intensive labor payouts, printing and posting expenses, paper buying and storing costs, and resource overheads, along with wastage of money due to false/duplicate orders or inaccurate delivery. By adopting EDI transactions for warehousing, managers can cut these costs and minimize labour time effectively without compromising the quality of data exchange.
Faster Order Fulfillment and Delivery
B2B digital data transfer fastens the warehouse management system, where document exchange takes minutes only accelerating the order fulfillment processes. Imagine an online business that gets thousands of orders daily. EDI helps to send those purchase requests directly to storage units for instant packing and dispatching. This way, the product movement becomes uninterrupted during high-demand periods.
Improved Supply Chain Visibility
On-the-spot tracking of inventory levels gets in your hand with the use cases of EDI in warehouse management. Automated document transmission and live updates of order requests and fulfillment processes provide sharp visibility of the supply chain. It helps the storage supervisors to make proactive decisions regarding stock replenishment and transportation performance.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
The right EDI services give advantages like timely response to customer requests, deliveries without delay, and quick return and refund if needed. Customers can track their orders right from their homes and can request the appropriate delivery time. These features enhance the shopping experience among consumers and create trust and loyalty.
Best Practices for Integrating EDI in WMS
Warehouse management is more than just transferring products from one point to another. An effective WMS includes efficient order fulfillment with minimum errors and delays while maintaining an optimum level of inventory with easy accessibility. But when the whole system is following traditional methods, including manual processes for data exchange, mistakes are inevitable. Here, EDI comes in the role of handling storage and distribution operations efficiently. Below is the list of steps for integrating an automated transaction system in WMS:
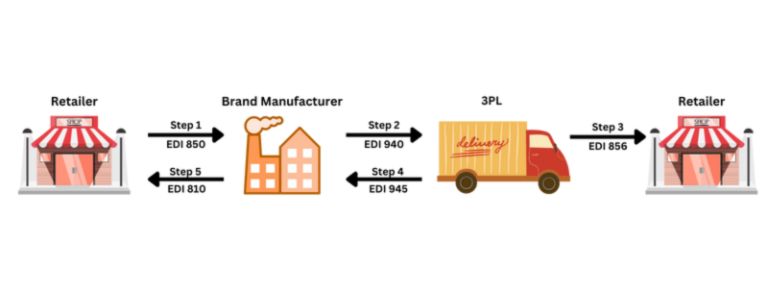
Source:- commport.com
- First, choose the right digital solution provider who can offer services that match your warehouse needs. For this, you must be clear about your requirements and what you expect from the technology. Also, the selected tool should be scalable with the growing demands of your supply chain.
- Integrate the electronic document exchange directly into your existing ERP and WMS. Here, it is necessary that the adopted EDI easily merge with the current warehouse management system to ensure smooth data flow.
- Before launching the digital tool on the entire supply chain, test it with your trading partner’s requirement to avoid any kind of disruptions later.
- Ensure that the chosen B2B data transfer system complies with the industry regulations and support standards like ANSI X12, EDIFACT.
- Provide training to the internal staff to run the adopted EDI smoothly in warehouse management and troubleshoot workflow.
- Regulate and monitor the electronic transaction process on a daily basis to resolve any type of error before it turns into a major issue.
Key EDI Transactions for Warehousing
EDI 940 – Warehouse Shipping Order
A seller sends this document to its storage facility to instruct about the shipment of the order. It includes the address and contact details of the buyer, the order number, and other related specifications.
EDI 943 – Warehouse Stock Transfer Shipment Advice
Manufacturers use this transaction to notify their 3PL facility of an incoming carrier. It includes shipment details, supplier ID, tracking number, and the estimated delivery date.
EDI 944 – Warehouse Stock Transfer Receipt Advice
Once a warehouse or 3PL provider gets the parcel, they confirm its receipt to the seller by sending this form. It includes the details about the items received, any damage or loss that happened, along carrier information.
EDI 945 – Warehouse Shipping
When an order is shipped from the warehouse, the manager or supervisor sends this document to confirm loading completion. It contains particulars like dispatch date and time, product details, and tracking number.
EDI 846 – Inventory Inquiry/Advice
This advice provides information such as real-time stock status and on-hand quantity across multiple warehouses. This electronic document facilitates accurate inventory visibility and exchange of the live status of available products between the buyer and the seller.
EDI 856 – Advance Ship Notice (ASN)
It informs the receiver about the delivery on the way and also informs him regarding packaging and shipment details along with the estimated time when an order will reach.
EDI 997 – Functional Acknowledgment
This digital paper is an acknowledgment of receipt of any EDI document, like a purchase order or any invoice. It does not specify the acceptance or rejection of the earlier sent transaction; it just confirms its receiving and helps at the time of audit.
EDI 210 – Motor Carrier Freight Details and Invoice
Motor carriers use this electronic note to send freight invoices to the shipment company whose parcel it is carrying to deliver. It includes the particulars like convey charges and facilitates transportation billing.
EDI 204 – Motor Carrier Load Tender
The virtual paper 204 is used to notify a carrier company or transportation provider about the available consignment and related details of the shipment.
EDI 214 – Transportation Carrier Shipment Status Message
It shares updates on the shipment status of the goods in transit, along with information about the expected delivery dates or any possible delays.
EDI 850 – Purchase Order
This document is shared between the buyer and seller/supplier to initiate a purchase process by creating an order notice containing the products’ details, like the name of the item, quantity, and other related specifications.
EDI 855 – Purchase Order Acknowledgment
Once a supplier receives a purchase order, he confirms its receipt through EDI 855 while indicating acceptance or rejection of 850.
EDI 810 – Invoice
Sellers share the billing details with the buyer through this electronic invoice, and it is a general statement of charges and is not according to the means of transportation.
EDI 870 – Order Status Report
This document updates the existing order status and its specifications, shipment particulars, expected delivery time, and potential slow if any.
How to Choose the Right EDI Solution for Your Warehouse?
The selection of the right digital solution is crucial for the successful automation of your warehouse. The following factors should be considered while switching to EDI transactions for warehousing:
- Look for the integration capability offered by the provider. The chosen virtual data transfer system should be able to work seamlessly with your existing ERP and WMS.
- Go for the modern features in the digital tool, such as cloud-based deployment, to get the full potential of the electronic platform.
- Security protocols, including encryption and controlled access to data, should be incorporated.
- The vendor of the application must be an expert in this field with extensive knowledge about the related industry and warehouse management and also provide customized solutions for specific needs.
- The selected electronic data interchange platform must be scalable with the evolving needs of your stock centers.
- The new B2B data transfer system must be compatible with your partner network and provide onboarding services along with timely customer support.
Future Trends in EDI for Warehouses
Here is a glance into the upcoming updates and transformation of EDI solutions in the manufacturing industry-
- AI integration with the Automated data transmission platform is making the tool smarter, optimizing warehouse management, even forecasting trends and enabling proactive decision-making.
- Cloud-based EDI applications are dominating among the advanced tools due to their easy use, flexibility, scalability, and low cost. Warehouses can implement this technique without huge capital investment, making it an affordable option for small units.
- Other advanced solutions like IoT and blockchain systems in Electronic Data Interchange are collectively transforming the way 3PL’s operations are managed and solidifying the use of EDI in warehouse management.
A3Logics: Your Trusted Partner for Streamlined Warehouse EDI
At A3Logics, we enhance your warehouse operations with our powerful EDI consulting services for WMS. This improves inventory management, speeds up order processing, and optimizes shipment handling, driving overall efficiency.
If you are migrating to a new platform or want an upgrade in your current system, we are here to guide you through every step. Our digital services align effortlessly with yours as well as your stakeholders’ existing system.
- We offer our clients well-equipped connectors for their logistics, WMS, and ERP systems.
- We provide inventory visibility and live tracking with our real-time dashboards.
- We support customized mapping of data and transactions interchange and checks for compliance with industry-specific standards.
- If you face any issues or have any queries regarding the service, our 24/7 expert team is always available to listen and help you.

Final Thought
Rationalized warehouse management relies on the integration of advanced technologies, bringing automation into the workflow with improved accuracy and flexibility. The adoption of EDI transactions in warehousing delivers strong results by simplifying critical data exchange across the supply chain.
It reduces errors, prevents delays, and accelerates order fulfillment. In today’s digital age, EDI is no longer optional but essential, and A3Logics provides the best solutions to support this transformation.





