Table of Contents
Artificial intelligence is transforming the manufacturing industry with its immense potential for enhancement. Major manufacturers are leveraging AI to boost efficiency, accuracy, and productivity across diverse operations. Top applications of AI in the manufacturing industry include a wide range of use cases, including predictive maintenance, quality control, supply chain optimization, and demand forecasting, providing a disruptive approach to traditional processes. For manufacturers, embracing AI now represents a strategic move towards upgrading workflows and staying ahead in a competitive world.
According to a Deloitte report, manufacturing stands out as the foremost industry in terms of data creation. This suggests that a large amount of information is generated within the manufacturing sector, demonstrating the industry’s substantial effect on the data landscape. Manufacturers must deploy AI to examine the huge amounts of data created in the field.
Additionally, as per a recent VentureBeat poll, 26% of companies are actively leveraging generative AI to improve their decision-making processes. Furthermore, 66% of manufacturers implementing AI into their daily operations indicate a rising reliance on this groundbreaking technology, highlighting an accelerating trend of AI deployment in the manufacturing industry.
In this blog, we will explore various use cases of AI in Manufacturing examples that demonstrate how the merging of AI and manufacturing boosts efficiency and ushers in a new era of smart manufacturing. We will also analyze the influence of AI in the manufacturing industry and how it empowers businesses to scale.
Understanding AI in Manufacturing
Artificial intelligence in manufacturing entails applying AI technologies to improve manufacturing processes and operations. Fundamentally, applications of AI in manufacturing industry leverage machine learning algorithms to discover patterns, forecast outcomes, and optimize decisions by evaluating huge volumes of structured and unstructured production data.
Some key characteristics of AI in manufacturing include:
- Data-driven decision-making: AI manufacturing allows manufacturers to make informed, fact-based choices by delving into massive datasets from sensors, machinery, and other digitized manufacturing systems.
- Adaptability: With machine learning’s inherent adaptability, AI manufacturing introduces responsiveness and flexibility into rigid traditional workflows, enabling seamless adjustments based on evolving demands or conditions.
- Distributed Intelligence: Integrating AI across networked infrastructure injects situational awareness, enabling intelligent decision-making at the edge for rapid corrections while optimizing centralized coordination.
- Scalability: Advanced algorithms can analyze sprawling manufacturing ecosystems comprising millions of data points, providing unified visibility and coordination lacking in decentralized legacy systems.
- Predictive Insights: By revealing patterns and anomalies in operational performance, predictive AI helps envision risks, avoid disruptions and maximize productivity across complex manufacturing ecosystems.
- Knowledge Reuse: The transferability of AI models trained on ample industrial data lets manufacturing stakeholders recreate insights across varied contexts for versatile problem-solving.
Fundamentally, AI is changing the manufacturing paradigm by enabling an adaptive, collaborative and data-driven approach centered on continuous optimization and innovation. Altogether, AI provides manufacturers agility, resilience and competitive differentiation crucial in dynamic business environments.
AI in Manufacturing: Key Statistics and Facts
AI is undoubtedly disrupting and transforming the manufacturing sector globally. Let’s explore a few notable AI statistics from credible sources to better comprehend impact of AI in business and role in industrial operations:
Stats 1
According to a McKinsey & Company report, generative AI could contribute $2.6 trillion to $4.4 trillion annually to the global economy by 2030, accounting for up to 15-40% more economic value than previously estimated for overall AI and analytics applications. This underlines generative AI’s potential as the next wave of productivity growth.
Stats 2
A PwC study revealed that AI implementation in manufacturing contexts could increase output by over 45% – with cost reductions of over 25% – by 2030. The study placed manufacturing among the industries likely to see over 10% revenue gains directly enabled by AI, with $267 billion possible annual benefits in discrete & process manufacturing alone.
 Source:- pwc.com
Source:- pwc.com
Stats 3
A Forbes Advisor survey found over 51% of businesses already leverage AI for cybersecurity and fraud management, with other prominent uses including customer service (56%), customer relationship management (46%) and digital personal assistants (47%). This highlights AI’s frontline adoption across industry functions.
Stats 4
As per a Market Research Future report, the worldwide AI in manufacturing market is anticipated to attain around USD 28,343.6 Million by 2032 – growing at a 29.7% CAGR between 2023 to 2032. This escalating spend signifies manufacturing’s resolute will to digitally transform via AI.
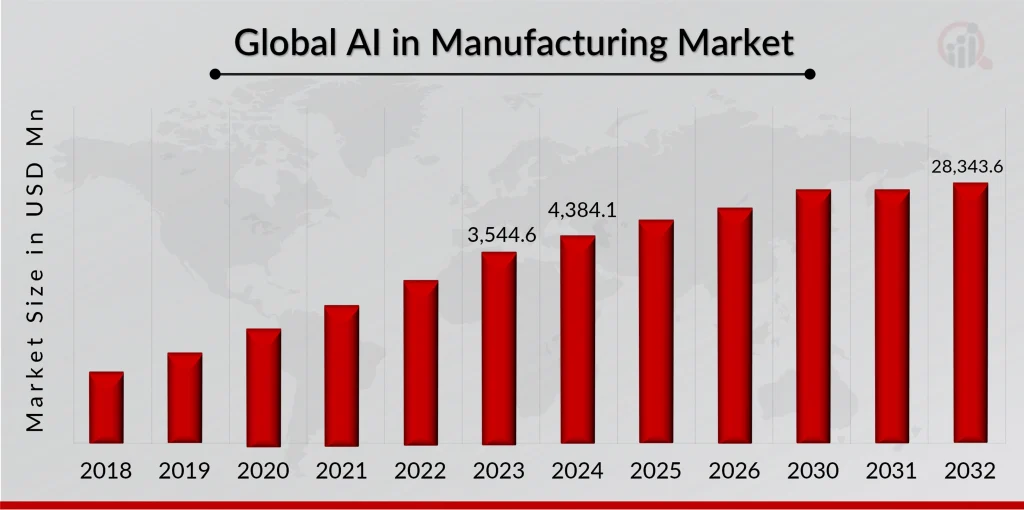 Source:- marketresearchfuture.com
Source:- marketresearchfuture.com
Stats 5
A 2021 Gartner survey noted that 65% of organizations piloting or adopting AI say that it has helped them drive innovation and achieve better business results. The success stories reinforce AI’s long-term strategic worth over mere tech experimentation.
Notably, over 50% of manufacturing firms surveyed now see AI as a prerequisite for competitive differentiation versus a strategic ‘nice-to-have’. This paradigm shift heralds AI’s imminent core role in powering industrial excellence. Overall, these figures unveil AI’s expanding business impacts and manufacturing’s dedication to technological progress in a data-centric paradigm.
Use Cases of AI in Manufacturing
Applications of AI in manufacturing are optimizing manifold processes across manufacturing value chains. Let’s explore 20 prominent use cases of AI in Manufacturing, including real businesses leveraging each application:
1. Market Trends Research
Use cases of AI in Manufacturing gain actionable insights from vast data sets. Machine learning algorithms analyze unstructured data sources like social media to identify patterns and emerging trends, aiding strategic decision making. For instance, consumer packaged goods firms use AI to perform market basket analyses and spot purchase correlations.
2. Historical Data Analysis
Machine learning is deployed to obtain valuable intuitions from past data, assisting with smarter moves ahead. Chip manufacturers analyze historical fabrication data employing deep learning to accelerate chip design optimization and enhance yields.
3. Defect Detection
Computer vision algorithms powered by AI visually inspect products and components at scale, surpassing human abilities to precisely flag any imperfections, inconsistencies or deviations. Electronics manufacturer Foxconn deployed AI vision systems for real-time quality verification on assembly lines.
4. Assembly Line Integration
Advanced robots complemented by AI efficiently take over repetitive or hazardous tasks on flexible production lines adaptable to fluctuating demands. Automaker Rivian has introduced robots capable of identifying and storing inventory 75% faster than manual operations using AI prediction technology.
5. Predictive Analytics
AI algorithms continually assess real-time sensor outputs alongside maintenance records to forecast potential equipment failures in advance. Ford factories have built digital twins of each vehicle model and leverage predictive maintenance via AI and digital twin technology.
6. Real-time Monitoring and Analysis
AI technology empowers constant oversight of converting processes, accumulation of data and provisions of evaluations to enhance general proficiency. GE harnesses machine learning algorithms to study information from facilities and equipment, pinpointing bottlenecks for well-timed remedy.
7. Process Optimization
Through continuous refining founded on sensor readings and production metrics, AI systems advance optimization of operational parameters for maximal outputs. Energetic electric vehicle manufacturer Tesla actively masters firmware and hardware of their plants employing AI.
8. Supply Chain Optimization
ML aids with demand anticipation, stock regulation, logistics scheduling and various SCM tasks for minimized expenses and greatest responsiveness. Retail major Walmart extensively applies AI to accurately predict client demands, reducing transport costs and deficiencies.
9. Demand Forecasting
By translating past deals records, seasonal fluctuations and beyond into actionable anticipations, AI streamlines planning and sourcing based on needs instead of estimates. Social publishing firm Pinterest employs AI to cleverly project demand spikes for holidays or major events.
10. Warehouse Management
AI fuels enhanced visibility and optimum logistical coordination through operational oversight. Manufacturing biggie Amazon launched hundreds of thousands of robots to aid fulfillment centers, slashing transportation times via optimized warehousing with AI.
Ready to Future-Proof Your Manufacturing?
AI can revolutionize your operations and give you a competitive edge.
11. Performance Optimization
From predictive servicing to continuous refining, AI bolsters optimization of tools, sequences and parameters. Pharmaceutical giant Merck has introduced ML for establishing ideal parameters to successfully manufacture component substances.
12. Quality Assurance
AI powers 100% quality assessment for flaws at low costs. Taiwan Semiconductor adopts AI systems and computer vision capable of recognizing defects invisible to the human eye, maintaining perfection across chip fabrication lines.
13. Streamlined Paperwork
Through robotic process automation and natural language capabilities, AI simplifies administrative duties. Whirlpool utilizes bots to mechanize manufacturing paperwork including assembly line quality reviews for uniformity.
14. Additive Manufacturing
AI accelerates 3D printing R&D by testing model behaviors in simulations, and facilitates on-demand production. Biz aviation part maker GE Additive teams AI with metal 3D printing for developing injection molding tooling with shorter design cycles.
15. Digital Twin Simulations
Digital replicas allow evaluating designs within virtual production settings. Ford pairs AI with digital twins capturing feedback mechanisms to rapidly experiment with powertrain calibrations, enhancing fuel proficiency.
16. Order Management
AI optimizes order handling from forecasting to fulfillment. IBM’s Watson Order Optimizer analyzes client profiles and purchase histories to efficiently coordinate deliveries as per carrier abilities.
17. Cobots
Collaborative robots perform repetitive/hazardous tasks cooperatively. Automaker Kia has introduced multiple collaborative robots to shared functions like spot welding with people on production lines for boosted safety and efficiency.
18. Connected Factories
IIoT integrates autonomous systems for real-time optimization. At networked plants, GE’s Predix platform pairs AI with device connectivity to keep tabs on equipment wellness, predict breakdowns and expedite operations.
19. Generative Engineering
AI handles arduous design challenges like multi-criteria optimization. Aerospace firm Airbus employs generative design techniques to conceive less heavy aircraft door structures meeting resilience needs.
20. Personalization
Data-led tailoring boosts client satisfaction. Apparel retailer Levi’s experiments with AI recommending precise jeans cuts based on body scans to better fit client physiques.
Overall, AI is revolutionizing manufacturing across the value chain to enhance output quality, minimize costs and boost competitiveness sustainably. Its integration delivers speed, scalability and strategic pivots transforming industrial operations globally.
Benefits of AI in Manufacturing
The fusion of AI and manufacturing unlock immense efficiencies with transformational impacts:
Increased Efficiency
AI streamlines redundant jobs, shedding wasted work hours for heightened output. At consumer products major Procter & Gamble, AI has helped eliminate over 300 million hours of requisite work.
Cost Savings
By improving yield, reducing defects and minimizing downtime, AI lowers overhead burdens. Aerospace pioneer Airbus deploys AI to cut aircraft structural testing costs up to 30%.
Improved Product Quality
AI-led quality checks at scale catch flaws untraceable to the human eye like micron-sized anomalies, enhancing manufacturing standards.
Better Decision-Making
AI augments strategic planning by swiftly aggregating and analyzing enormous operational datasets beyond human capabilities.
Enhanced Worker Safety
Robots handle hazardous lifting, grinding or spraying jobs, reducing industrial accident risks. Collaborative robots work safely alongside employees.
Scalability with AI in Manufacturing
AI manages production changes dynamically, ensuring efficiency across production volumes from low to mass levels.
Sustainability through AI in Manufacturing
Optimized resource consumption through AI-powered energy management and predictive maintenance aids eco-compliance.
Overall, AI technologies power competitive differentiation, resilience and profitability for industry leaders embracing digital transformation.
Manufacturing Industry Challenges
While promising gains, AI adoption also presents hurdles manufacturers must address:
High Implementation Cost
Expensive infrastructure investments, skills shortages and long pilot periods can deter early adoption, especially for SMEs. However, cloud-based offerings mitigate risks.
Materials Procurement
Fluctuating raw material prices pose supply chain vulnerabilities AI can help predict, but incomplete historical cost data hinders model precision initially.
Quality Control
Establishing pass–fail thresholds and eliminating human biases in AI image analysis demands upfront validation to ensure precision and safety.
Downtime due to Equipment Failures
Unplanned stoppages sabotage schedules but predictive maintenance data is not always calibrated and normalized for AI training before anomalies surface.
Carefully piloting use cases scoped to business priorities and priorities, collecting representative high-integrity training data, combining AI assistance with human oversight and focusing on ROI critical processes can help minimize risks. With addressing preliminary design inefficiencies, manufacturers are accelerating AI payoffs.
Ethical Considerations for AI in Manufacturing
Responsible AI demands constant stakeholder efforts to proactively manage risks:
Bias and Fairness
Without representative datasets, models risk entrenching biases through outputs. Anonymizing sensitive attributes combats this.
Transparency and Explainability
Debugging complex neural decisions calls for system explainability to establish validity and accountability.
Data Privacy and Security
Strict access controls and encrypted information flows safeguard sensitive industrial secrets and customer particulars from misuse.
Accountability
Clearly defined roles and comprehensive documentation establish accountability for both intended and unintended AI application consequences on systems, workers and society.
Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Oversight
Multi-stakeholder ethical bodies help scrutinize AI alignment with industry standards and address policy gaps through consultative law-drafting.
Manufacturers prioritizing these concerns establish the responsible, human-centric standards essential for society to realize AI’s true potential while preserving trust.
Transform Your Manufacturing with AI – Book a Free 30-Minute Consultation Today!
Conclusion
The adoption of AI technologies allows manufacturers to analyze vast amounts of data generated from machines, sensors, and production processes. This capability enables real-time monitoring and predictive insights that can significantly reduce downtime, enhance product quality, and optimize resource utilization. Moreover, AI-powered solutions can automate repetitive tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more strategic activities that require creativity and critical thinking.
As the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve with Industry 4.0, organizations that embrace AI will be better positioned to adapt to changing market demands and technological advancements. If you are looking for experts to help you with Enterprise AI Chatbot Development, connect with A3Logics now!
How can A3Logics Help in Implementing AI in Manufacturing Industry
A3Logics, being the top Enterprise AI Development Company, specializes in providing tailored blockchain, AI and deep tech solutions to manufacturing enterprises seeking to digitally transform via cutting-edge innovations.
Our expertise in Artificial Intelligence Development Services, machine learning modeling and data-driven consulting equips manufacturing clients to leverage AI’s fullest benefits.
Whether optimizing production processes, achieving predictive maintenance, streamlining quality control or fortifying supply chains, A3Logics collaborates to craft industry-aligned solutions driving operational excellence.
By strategically fusing data analytics and generative AI throughout manufacturing workflows, we empower enhanced decision making, cost reductions and competitive differentiation.
Our focus on explainable, privacy-respecting solutions safeguards ethical AI integration alongside measurable business value. Contact A3Logics, one of the top AI Development Companies today to usher AI-driven transformation fostering manufacturing excellence!
FAQs
Q1. How can AI benefit the manufacturing industry?
A1. AI benefits manufacturing in various ways like improving efficiency, reducing costs, enhancing product quality, optimizing supply chains, minimizing downtime through predictive maintenance and driving innovation. AI enables data-driven decision making, automation and optimization of core manufacturing processes.
Q2. What specific challenges in manufacturing can AI address?
A2. Some challenges Artificial intelligence in manufacturing can address include quality control issues, equipment failures leading to downtime, supply chain disruptions, lack of demand forecasting accuracy and redundant paperwork processes. AI provides real-time insights, predictive analytics and automation capabilities to optimize such processes.
Q3. How does AI improve predictive maintenance in manufacturing?
A3: Artificial intelligence in manufacturing improves predictive maintenance by analyzing historical equipment data, specifications and real-time sensor readings using machine learning. It identifies patterns indicating potential equipment failures to enable proactive maintenance schedules that minimize downtime and optimize asset performance.
Q4. What is the future of AI in the manufacturing industry?
A4: The future of AI in manufacturing includes closer human-AI collaboration, democratization of AI allowing SME adoption, sustainability initiatives leveraging AI for optimized energy usage, further integration across connected ‘smart factories’ and generative AI transforming product development cycles.
Q5. How does AI optimize supply chains in manufacturing?
A5: Artificial intelligence in manufacturing optimizes supply chains via demand forecasting from past sales analysis, inventory optimization, logistics route optimization to enable just-in-time production responsive to dynamic market needs, minimizing costs and risks across the value chain.






