Table of Contents
Electronic Data Interchange is the most popular communication method for businesses. From small enterprises to large corporations, almost all organizations across the world rely on EDI services. We know that to run a business and interact with trading partners, it is essential to exchange and process many documents on a daily business. Of course, paper-based methods or manual processes cannot accomplish these tasks effectively, and even if they could, it is time-consuming and involves higher chances of errors. Hence, EDI is an automated, faster, and more efficient electronic mode.
In the EDI world, the two standards used most frequently across various industries are ANSI ASC X12 and EDIFACT. Though in many ways, one is incredibly similar to the other, there are loads many differences that part both these. In this blog, we are going to understand these standards in detail and compare them based on various factors.
Reach to Our EDI Experts and Synchronise Your Data Efficiently
A Brief Introduction to EDI X12
EDI is a flat-file technology or format used by businesses or trading partners in different organizations to securely share business transactions, information, or files. The EDI X12 format is based on ASC, Accredited Standards Committee, and X12 standards. Organizations prepare the documents according to ASC X12 data standards and then translate them into a common language.
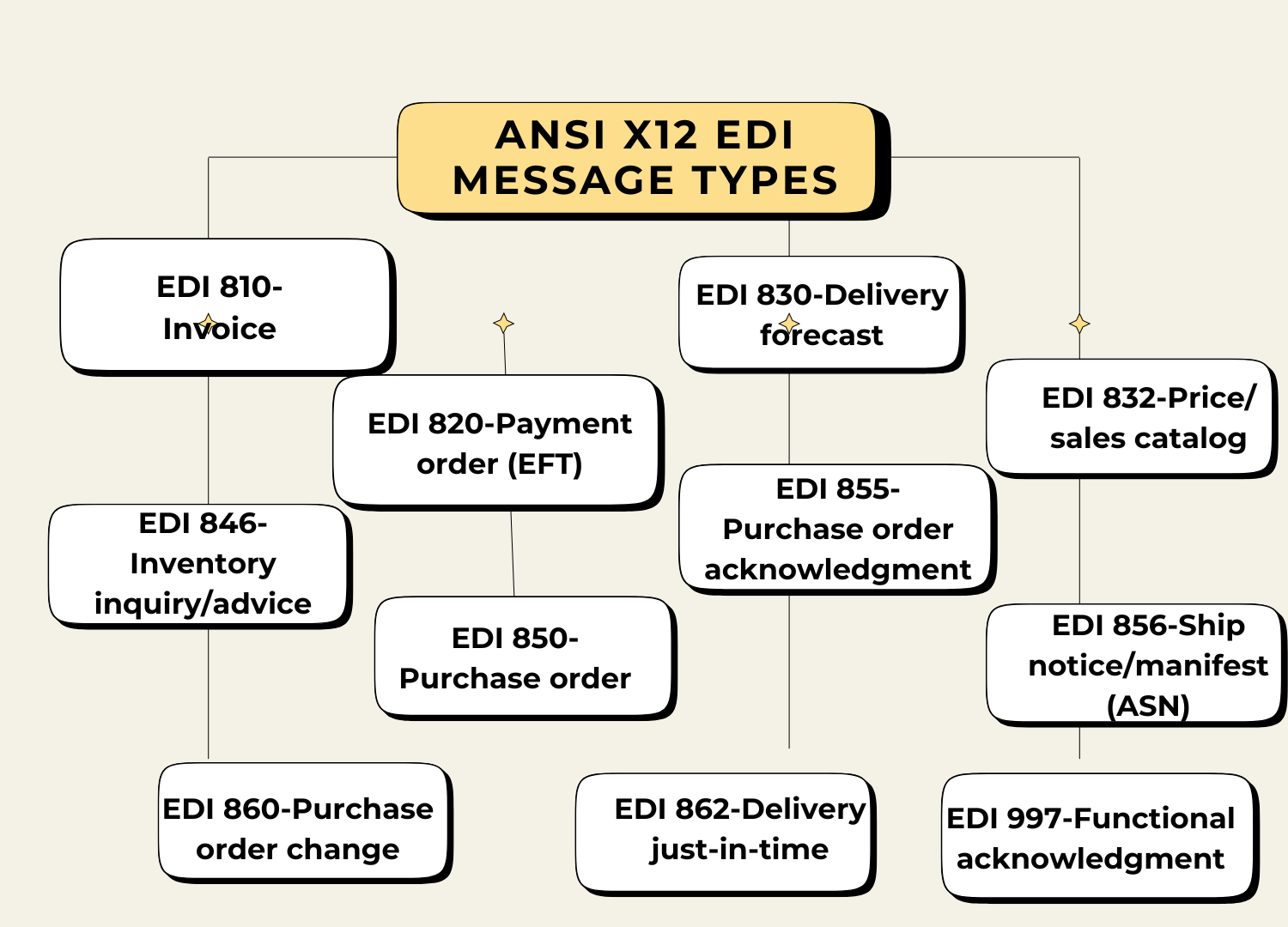
After that, they send the translated documents through a point-to-point secure EDI connection. The protocols used for this format include FTP, API-based systems, such as AS4, web-based via AS2, etc. The segregation of this standard was further into sub-standards or formats for easier and quicker information exchange. Additionally, every industry vertical was leveraging and using ANSI X12 with a dedicated format to transmit a specific data type.
Below are a few formats :
These standards were –
- EDI 834– Benefit Enrollment and Maintenance
- EDI 837- Healthcare Claim Transaction Set
- EDI 835 – Healthcare Claim Payment/Advice
- EDI 270/271 – Healthcare Eligibility, Coverage or Benefit and Information Response
- EDI 278 – Healthcare Services Review – Request for Review and Response
- EDI 820 – Payroll Deducted and Other Group Premium Payment for Insurance Products
Aside from business, X12 is also used in terms of sending and receiving EDI documents and files: invoices, purchase orders, and others. Indeed, this particular EDI solution is used across other industries, for instance, insurance, health, electronic commerce, et cetera, because of its audit trails; it ensures security and cost-saving features as it is automated and time-saving. Moreover, it provides a common language for information exchange between organizations and reduces risks from paper-based and email data transmission
Advantages and disadvantages
Given in the table below are the advantages and disadvantages of using the ANSI Standard X12 EDI format:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Widely Adopted: Popular across various industries in North America, especially in healthcare and retail. | Complex Implementation: Challenging for businesses with limited technical resources due to numerous transaction sets and data elements. |
| Structured Format: Easy to interpret and integrate with other systems, facilitating data mapping and automation. | Limited Global Adoption: Primarily used in North America, requiring additional EDI solutions for global communication. |
| Robust and Comprehensive: Supports various business transactions and data sets, suitable for businesses of all sizes. | Costly Maintenance: High maintenance costs, especially for frequent updates to comply with new regulations or standard changes, impact small businesses. |
Use cases
An ANSI Standard X12 format EDI is widely used in Canada and the United States to exchange electronic data between different trading partners. It is implemented across a wide range of industries. Some of the industries include.
- Retail and supply chain management:
Retail and supply chains adopt the X12 EDI format for purchase orders, invoices, and advanced shipping notices. Such a setup eliminates manual order-taking tasks and thus speeds up processing, further eliminating errors.
- Healthcare:
The X12 EDI format is used in the provision of patient health information, medical claims, and other administrative health documents between healthcare providers, insurers, and other players. It helps improve health system effectiveness and flows down to costs, which is achieved by the use of fewer paperwork and manual processes.
- Finance and banking:
X12 EDI format can be applied in the following finance and banking industries for electronic funds transfers, wire transfers, and remittance advice—all these greatly speed up the process of money transactions, contributing to lowering it with the minimal risk of making mistakes and encountering fraud.
- Manufacturing and distribution:
Manufacturing and distribution industries follow the X12 EDI format for documents exchange, such as product catalogs, inventory reports, and shipping notices. This usage supports good visibility across the supply chain and reduces time and costs spent on manual data entry.
- Government:
Government agencies can exchange tax forms, permits, and licensing applications of agencies in the X12 EDI format, thereby making those workings more efficient in providing services.
An EDI solution provider offers some EDI solutions, supporting the ANSI Standard X12 EDI format; such software and services allow businesses to exchange electronic documents securely and efficiently with their trading partners. Some features common in the EDI solutions offered are document translation, data mapping, and trading partner management.
Empower Your Business With Our Cutting Edge EDI Services
A Brief Introduction to EDIFACT
EDIFACT stands for Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport. It’s an international EDI standard, under the United Nations. EDI is structured to work for multi-country and multi-industry exchanges.
Commercial and governmental organizations use EDIFACT to transmit information using a common language. It is commonly used in Europe, and many businesses in the US and the Asia Pacific regions have also started adopting this EDI standardized process for secure data exchange.
Advantages and disadvantages
In the table below we have mentioned the advantages and disadvantages of using the EDIFACT EDI format:
| Advantages of EDIFACT | Disadvantages of EDIFACT |
|---|---|
| Global Acceptance: Supported by the United Nations and widely used worldwide, facilitating international trade. | Learning Curve: Challenging to learn and implement, requiring training and resources. |
| Wide Range of Messages: Offers a vast array of pre-built messages for various industries, saving time and effort. | Limited Usage in North America: Less common in North America, necessitating different EDI standards for local trade. |
| Cross-Industry Standard: Applicable to all types of businesses, enabling communication across different industries. | Customization Limitations: Limited options for sending customized messages. |
| Reduced Manual Processing: Automation reduces processing time and improves accuracy, saving time and resources. | Incompatible with Legacy Systems: This may not be supported by some legacy systems, requiring additional customization or upgrades. |
Use cases
EDI Service providers offer EDI Solutions facilitating the EDIFACT standard to an extensive level of use-case scenarios. Some of the most evident use cases where the EDIFACT standard is used consist of General utility and business-to-business e-commerce.
International Trade
EDIFACT was commonly used to exchange data related to shipment, customs clearance, and various other trade-related activities. The standard contains support for a diverse set of numerous documents, for instance, invoice purchase orders, bills of lading, etc.
Healthcare
The healthcare industry uses EDIFACT to share data such as patient information, medical histories, and other medical condition reports between any two healthcare providers along with the insurance companies and government bodies.
Automotive
The automobile industry uses EDIFACT for data interchange related to the production and supply chain of automobile parts and cars.
Retail
EDIFACT finds its use in the retail industry for sharing data over order information, invoices, and shipment information between the retailer and supply chains.
Transportation
For transportation, it means EDIFACT exchanging information regarding shipping, logistics, and freight forwarders.
ANSI Standard X12 EDI Format is more common in North America, and hence regional business corporations use it. Some critical dissimilarities between EDIFACT and ANSI X12 are the message structure, the data elements and segments utilized, and the syntax of messages. EDI Providers offer solutions that support both standards: EDIFACT and ANSI X12 standards for businesses to choose from. At the end of the day, the choice of EDIFACT or ANSI X12 depends on various matters such as his or her industry, the trading partners leveraged in the implementation, and the use case.
EDIFACT vs X12
EDI is one of the key tools for any business that wishes to enhance communication efficiency. It ensures higher data accuracy and minimizes costs arising from manual data entry. Managed EDI Service Providers provide a smooth flow of electronic documents between trading partners. Two of the most common EDI standards are X12 and EDIFACT. The difference between these two highly esteemed standards is provided below.
Geographical Location
Geographical location plays one big role for a company in choosing between X12 and EDIFACT when looking for EDI services. Most EDI service providers specialize in one given geographical region and may have different packages ready for different locations. UN/EDIFACT, being standardized EDI transactions, comes in handy more in Europe and probably the rest of the world, except for X12, which is the way in use in the whole of North America. Different requirements may apply by different regional standards, which companies may have to follow if they want to operate in a different region legally or within industry norms.
Moreover, the distance between trading partners can also affect the choice of EDI format. X12 messages are usually shorter and require less bandwidth, which makes them more suitable for companies with partners located far away. On the other hand, EDIFACT messages are more robust and better suited for companies with nearby partners, as they can handle larger volumes of data.
| EDIFACT CODE | MESSAGE |
|---|---|
| DELFOR | delivery forecast |
| DELJIT | delivery Just-in-Time |
| DESADV | despatch advice message |
| IFTMIN | instructions for transport |
| IFTMBF | transport booking request |
| IFTMBC | transport booking confirmation |
| INVOIC | invoice message |
| ORDERS | purchase order message |
| PAYORD | payment order message |
| PRICAT | price catalog message |
| PRODAT | product data message |
| INVRPT | inventory report |
| RECADV | receipt advice |
| MSCONS | Metered Services |
| UTILMD | UTILities Master Data message |
| ORDCHG | purchase order change request |
| CONTRL | functional acknowledgment |
| REMADV | remittance advice |
| SLSRPT | outgoing sales report |
| ORDRSP | purchase order response |
Use Cases
- ANSI X12 EDI is used primarily in healthcare to ensure that healthcare documents comply with HIPAA.
- However, EDIFACT is used for documents that are not meant for HIPAA. Instead, this format is used in other industry areas, including government, supply chain, and finance.
Standards Developers
Very key in the implementation of these standards is the EDI service provider, because it is the provider of software and infrastructure necessary by a business for facilitating the sending and receiving of EDI messages. As there are many EDI service providers available, a provider that will support the standards called for by your trading partners must be chosen.
The ANSI ASC X12 EDI standard has been developed and maintained by the Accredited Standards Committee X12, that is, ASC X12, chartered by ANSI in 1979.
The UN Economic Commission for Europe and the International Organizations for Standardization fully support EDIFACT, which means Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport. Some EDI standards have their specific strengths or weaknesses, but that just depends on what will work best for the business.
Terminators/Separators
Regarding EDI services, the most commonly used standards are X12 and UN EDIFACT. One of the key differences between these two standards is the use of Terminators/Separators. Both EDI standards use special characters to separate segments and elements in the documents.
ANSI X12’s interchange header is marked ISA, and it generally uses a tilde (~) to separate segments and an asterisk (*) to terminate elements.
EDIFACT’s interchange header is marked as UNB. It uses a period or dot (.) between segments to separate them and a (+) sign between elements. However, both of them can use different characters as well based on the specific implementation.
EDI service providers must know these differences when working with clients who use different standards. For example, suppose a provider is working with a client who uses X12 and needs to send data to a client who uses UN EDIFACT. In that case, they must ensure the data is correctly formatted with the correct separators. Understanding these differences and working with X12 and UN EDIFACT can be valuable skills for EDI service providers and help them better serve their clients in the global marketplace.
Document Structure
Although the message structures of X12 and EDIFACT are similar, both use different terminologies. Messages in both EDI data formats include Transaction Set, Functional Group, Interchange, and EDI Document. Here is how our EDI-managed services provider explains the differences :
Here is how our EDI-managed services provider explains the differences –
Transaction Set and Message:
This is the main body of the message, like order details in a purchase order. It is known as a Transaction Set in X12 while a message is in EDIFACT.
The Functional Group:
The header specifies where the message will go, such as a company department. There can be multiple messages or transaction sets like invoices and POs. For both the EDI standards; there is a header and a footer segment. X12 uses GS and GE for the header and footer, respectively. EDIFACT uses UNG and UNE for the header and footer.
The Interchange:
It includes a header and footer and specifies the recipient company of the message or document. The former calls the header ISA and the footer IEA. The latter uses UNB and UNZ for them.
The EDI Document:
This is an optional segment that EDIFACT uses to define characters for terminators and separators in the document.
Composite Elements
Composite Elements comprise two or more elements similar to an array and separated by a composite separator symbol. They are available in both standards. However, they are rarely used in EDI ANSI X12 and are common in EDIFACT.
The former uses Greater Than (>) to separate elements, while the latter delimits them with a colon (:).
Security Authentication
Security authentication is available for both X12 and EDIFACT, but they support different standards.
The former uses ASC X12.58 security structures that include compression, authentication, encryption, and assurance. This ensures that the EDI files reach their destination in the original format. It monitors that there is no tampering with the files and assures the recipient of the original sender.
The latter follows the following security standards:
- ISO 9735-5 to address message, group, and interchange level security for integrity, authenticity, and non-repudiation of origin.
- ISO 9735-6 defines authentication and acknowledgment message AUTACK.
- ISO 9735-7 addresses group, message or package, and interchange level security for confidentiality.
- ISO 9735-9 is for the security key and certificate management message KEYMAN
Syntax
One of the critical differences between these two EDI standards is syntax. X12 syntax is delimiter-based. In other words, some characters, like a colon or comma will separate all the data elements that exist within a segment. EDIFACT, however, uses a hierarchical syntax wherein first is grouping into segments and then grouping into messages.
Confused By EDI Standards? Get a Free Consultation From Our Experts
Conclusion
Knowing the critical differences between EDI X12 and EDIFACT will help you select the right solution for your business. Both standards are a bit complicated to comprehend entirely. You still may have many queries before you make your decision.






