Table of Contents
Big Data Analytics is practiced by many businesses across the globe in order to facilitate business transformation and implement an operational strategy. It requires no rocket science to come up with the idea that any business in today’s scenario, irrespective of its size, needs data insight to flourish. Big data analytics is the means to understand the needs and preferences of the audience.
Around 2.5 quintillion bytes worth of data are generated each day. Big data in business helps you manage your competitors one step ahead by understanding what your audience wants. A Big data analytics company is able to evaluate the data efficiently, assisting businesses in reaching and maintaining their objectives over an extended period of time. The biggest challenge that businesses face in integrating big data analytics into their operations is undervaluing the technology and assuming that it would be very expensive. There are many myths about using big data that should be addressed since they hinder the firms from fully exploiting the technology.
Regardless of the business size one serves, it is gathering data and subsequently analyzing it that will remain the most important thing to determine successfulness in the future.
Big data: What is it?
Although the amount of data involved can be astounding, the term isn’t totally deceptive, so don’t consider it as a comprehensive definition. Large data sets are undoubtedly the focus of big data analytics solution, but in the same company, we have seen numerous data lakes created for the purpose of storing big data that were smaller than traditional data warehouses. However, it is generally true that large amounts of data are associated with big data.
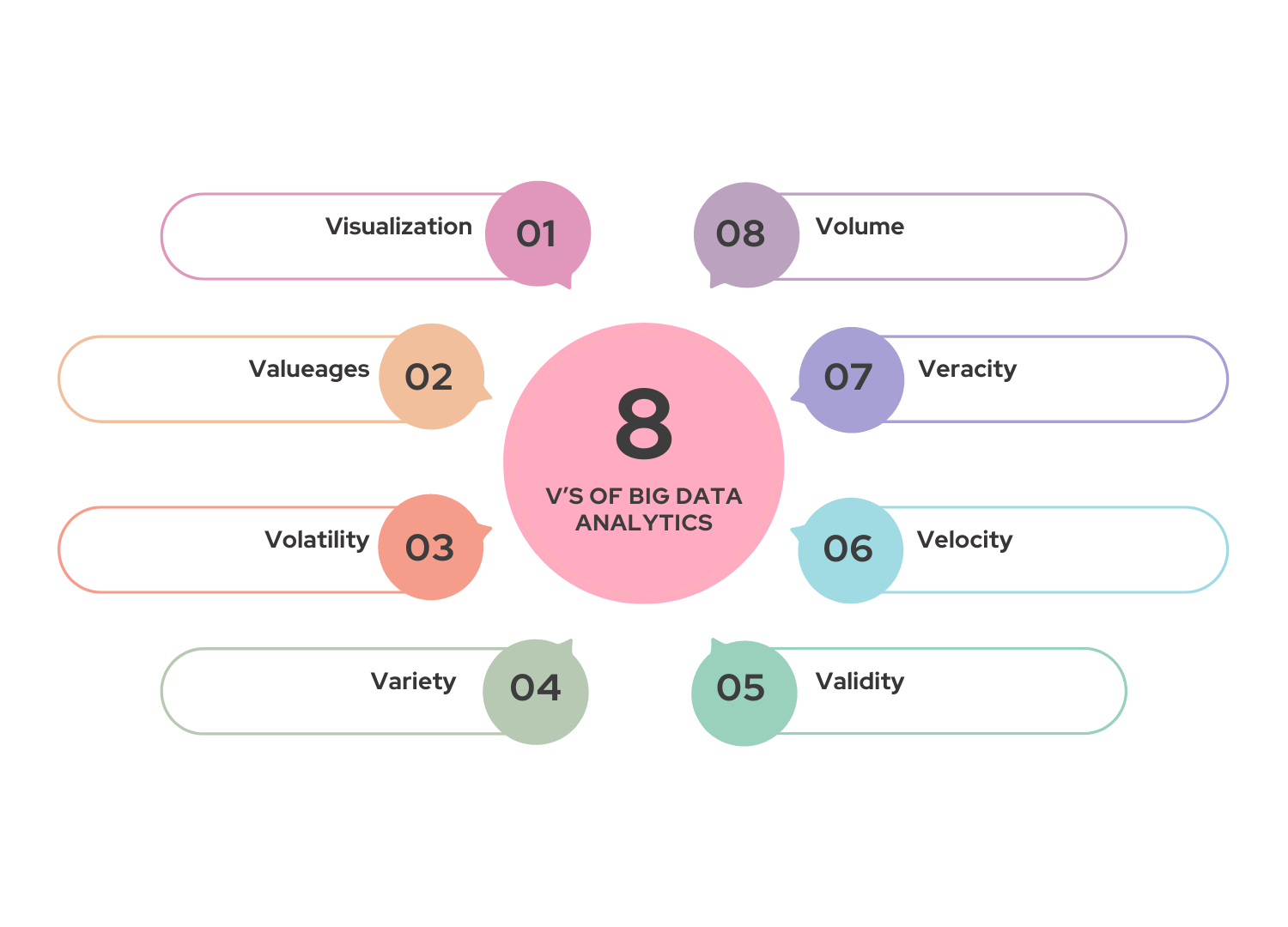
What more is involved, then? A crucial element is the variety of data types that are involved. Text files, XML documents, pictures, video, audio, raw log files, and conventional organized data can all be found in a single big data system. This is referred to as the “variety of big data,” and processing and storing some of these data types—particularly the sometimes-very-large photos, video, and audio files—does demand for a system that can scale simply and rapidly.
The data’s velocity adds another layer of complexity to this. That speaks to how quickly it is created or updated. For instance, log files from websites, mobile apps, monitoring systems, and other sources frequently contain thousands of observations in a single hour of continuous data. It is possible to have large data without this kind of velocity, but a well-thought-out big data architecture ought to be able to support it.
Other qualities, such veracity and variability, have been added to these five Vs of Big Data Analytics by other analysts and practitioners.
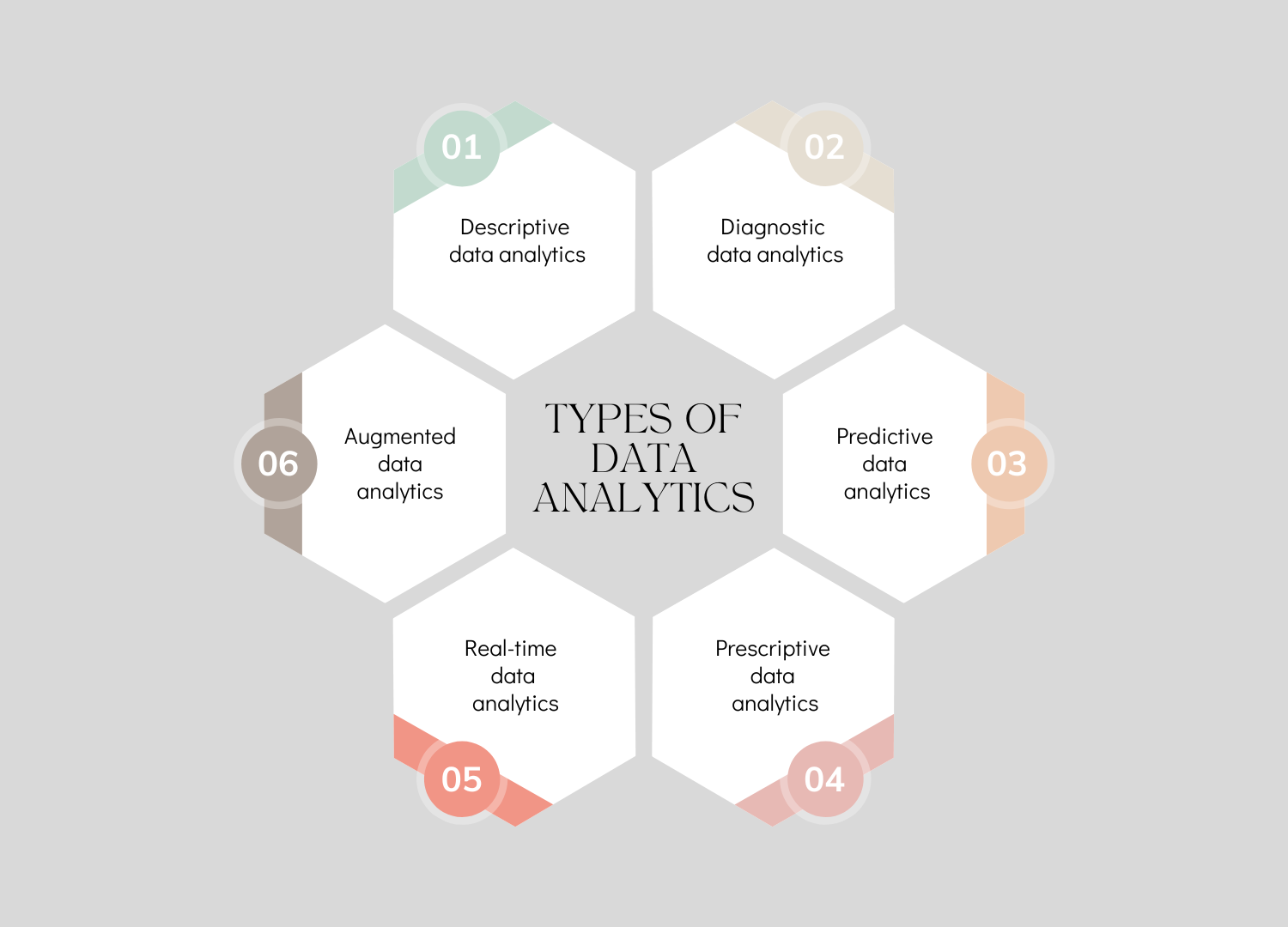
Why Big Data Matters?
Since knowledge is power, data analytics solutions are crucial. Business owners may find a wealth of information available to them to aid in making more intelligent decisions. Using data to its full potential can open up new, valuable opportunities. As a result, the following categories best describe the importance of big data analytics:
- New product creation
- Targeted marketing
- Quicker decision-making
These are all ways to cut costs and boost productivity.
Development of Products
Teams can utilize data to learn about the kinds of things consumers are usually using in this region, which is beneficial. primarily, how they are utilizing them and their interaction with the merchandise.
On the other hand, manual review or survey participation may have been necessary for traditional approaches. This happens in the tech industry at a much faster rate and with more information available. Consequently, this means that firms have superior knowledge about a product or service’s likelihood of success early on.
Personalized Advertising
The field has been dominated by customer interactions. Targeted advertising on social media platforms is one such example. Data-driven decisions may boost a company’s visibility and, consequently, its revenue.
Based on data collected by Google’s Economic Impact division, companies make $2 in income for every $1 invested in Google AdWords. This shows the effectiveness of sponsored search advertisements and tagging buzzwords related to your products and services or your target audience’s wants.
Quick Decision-Making
Organizations that are considerably data-driven are three times more likely to claim major advances in decision making than those that do not rely on data.
Indeed, according to a 2017 McKinsey study,35% of Amazon’s customer transactions may be traced back to the company’s product recommendations. Machine learning and Data analytics solutions are the driving forces behind all of this.
Benefits of Big Data
Now let’s take a look at the top benefits of big data analytics in businesses.
1. Improved understanding of customers
A modern corporation can choose from a variety of sources when using data to understand its clients, either as individuals or as groups. Some data analytics companies that provide insights into clients are as follows:
- Conventional sources of client information, like purchases and customer service calls.
- Outside sources, like credit reports and bank activities.
- Social media engagement.
- Survey data, both internal and external.
- Cookies on computers.
In an increasingly digital marketplace, clickstream analysis of e-commerce activity is particularly helpful as Big Data Analytics provides insight into how buyers search through a company’s several web pages and menus for goods and services. Businesses are able to observe which products customers added to their carts but later deleted or abandoned without making a purchase; this gives valuable insight into what customers might want to buy even if they decide not to.
In addition to online retailers, physical stores can also obtain valuable insights on their clientele. This is sometimes achieved by comparing the way in which people browse a physical store with that of a website through the analysis of videos.
2. Enhanced understanding of the market
Big Data Analytics may both enhance and expand our grasp of market dynamics and assist us in more thoroughly analyzing the intricate shopping behaviors of our clients.
Market research for a variety of product categories, from breakfast cereal to trip packages, is frequently obtained through social media. People share their preferences, experiences, recommendations, even selfies for nearly every type of commercial transaction you can think of. Indeed, including their morning meal. For marketers, these collective viewpoints are priceless.
Apart from competition analysis, Big Data Analytics can also aid in the development of new products by giving distinct client desires priority, for instance. Big data actually helps with more than just contemporary market intelligence; in virtually any online or e-commerce market, diversified, constantly-evolving data drives nearly all market intelligence.
3. Management of the supply chain with agility
You should know by now that modern supply chains are shockingly fragile. It can be due to the economic upheaval caused by Brexit, or pandemic-driven shortages of items like toilet paper. It’s unexpected since, in most cases, supply chains go unnoticed until there is a significant disruption. Our global network of demand, production, and distribution is mostly kept in good working order by Data analytics solutions that permits predictive analytics, frequently in almost real time.
This is made feasible by the ability of big data systems to combine supplier information, real-time pricing, and even shipping and weather information. This along with data on customer trends from retail applications and e-commerce websites to deliver a degree of knowledge never previously seen.
Not only do big businesses profit from these insights. Customer data and real-time pricing can help even small e-commerce companies make better business decisions about risk reduction, stock levels, and temporary or seasonal hiring.
4. More astute audience targeting and suggestions
Recommendation engines have become so commonplace in our lives as customers that we may not even realize how much they have changed since big data analytics tools first appeared. Recommendation engines used to use relatively simple predictive analysis: association rules would identify similar products in market baskets. You can still anticipate seeing this as an option on e-commerce sites informing us that buyers of fidgets also purchased widgets.
Building on the advanced customer insights we have just covered, more recent recommendation systems are far more intelligent than that, which allows them to be more responsive to customer behavior and demographics. Nor are big data analytics tools exclusive to online shopping. The suggestions made by a kind waiter may very well be data-driven; they may be the result of a point-of-sale system that assesses social media trends, popular combos, high-profit goods, and pantry stock levels. You are giving the big data analytics tools even more information to process when you post a photo of your dinner.
Providers of streaming material employ even more advanced strategies. They might not even inquire as to what patrons would like to see next: The next movie, show, or song begins to play even before the current one ends. This feature keeps viewers from binge-watching by combining their own preferences with a ton of big data research from social media and other users.
5. Innovation fueled by data
Creativity is more than simply inspiration. Finding subjects that hold promise for further research and experiments requires a lot of hard work.
The different big data analytics tools and technologies that are accessible can improve research and development, which frequently results in the creation of new goods and services. At times, data that has been cleaned, organized, and regulated for distribution turns into a product unto itself. For instance, the London Stock Exchange currently generates more revenue from the sale of data and analysis than it does from the trading of equities.
Even with the greatest big data analytics tools, data by itself won’t yield novel insights. The human component—the knowledge and creativity of data scientists, BI analysts, and other analytics experts—is still necessary. The importance of big data analytics and its reach, particularly when kept in a single Hadoop cluster or cloud data lake, can help teams see patterns that would be challenging to identify in a less integrated setting.
6. A variety of data set use scenarios
Throughout professional life, we have witnessed numerous instances where meticulously prepared and modeled data was wholly inappropriate for a different business objective.
One credit card issuer’s marketing staff, for instance, was interested in learning how its clients used the cards they carried. They found that there were multiple unsuccessful swipe attempts and canceled transactions that were frequent at the time—often as a result of issues with the payment terminal’s connection or defects in the cards’ magnetic stripes. Thus, the failed transactions were eliminated by thoroughly cleaning the data.
However, because they were interested in seeing those unsuccessful transactions that may have indirectly deleted the records of the usage of fake cards, therefore fraud prevention team was unable to use it. Furthermore, the deleted material was difficult to obtain because it was kept on tape storage.
In the era of big data, all of the raw data can be kept in its original form in a data lake, and data models can only be applied to it when specific applications of big data analytics require it. Then, to fill in the analytics processes, we can create data pipelines especially for each use case or we can just execute ad hoc queries. This allows for a great deal of flexibility in terms of how many different kinds of applications can be run on the same piece of data.
7. Enhanced company workflow
Using Big Data Analytics can enhance business operations of all kinds. It facilitates the streamlining of corporate procedures to cut expenses, raise output, and improve client satisfaction. HR management and hiring practices can improve. Enhanced fraud detection, risk mitigation, and cybersecurity readiness assist companies in minimizing financial losses and averting possible commercial risks.
Using big data analytics to enhance physical operations is one of the most important benefits of big data analytics. For instance, predictive maintenance plans can be informed by the combination of big data and data science services to lower the cost of repairs and downtime for vital systems and equipment.
Examining the item’s age, state, location, warranty, and service information is a good place to start. However, other everyday corporate factors, including staffing and production schedules, have a significant impact on things like security and HVAC systems in buildings. These activities may then have an impact on sales cycles and, consequently, consumer behavior. All of this is made possible by well-integrated large data sets, which enable you to repair equipment at the best possible time.
8. Encouraging and enhancing generative models and AI
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing innovation and commercial processes, particularly in the areas of generative AI (GenAI) and large language models (LLMs). To learn patterns, comprehend context, and produce writing, photos, and other content that resembles that of a human, these sophisticated AI systems mostly rely on enormous volumes of training data. Applications of big data analytics makes it possible to upgrade and customize GenAI technologies for your own organization.
Retrieval-augmented generation is one promising area of AI (RAG). With this method, you can query pertinent information from large knowledge bases, such as your own company data, and still benefit from the strengths of LLMs. Organizations may create extensive knowledge banks that RAG models can access in real time and use to produce more accurate, insightful, and contextually relevant replies by utilizing big data technology.
To deliver highly tailored and efficient help, a customer service chatbot that is driven by RAG may, for instance, access a company’s complete product information history, user manuals, and customer interactions. Similarly, RAG might be utilized by a content creation platform to produce reports, articles, or marketing material that incorporate the most recent trends and data from the sector.
Businesses can easily update and improve their AI models based on user input and new information thanks to applications of big data analytics. For instance, through gathering and evaluating user interaction data for GenAI applications, businesses can identify areas for development, optimize their models, and eventually produce more meaningful and interesting user experiences.
Uses Cases of Big Data in Various Industries
Industries change as new technology becomes more accessible and affordable. That’s what big data is doing at the moment. Let’s examine how data is influencing performance and competition in a few important industries.
Healthcare
Big Data Analytics is revolutionizing healthcare by helping to detect and treat diseases, enhance quality of life, and stop avoidable deaths. Nowadays, the goal is to learn as much as possible about a patient at the earliest possible stage of their life in the hopes of identifying warning indicators of a serious illness early enough to enable much simpler and less expensive treatment.
Benefits of big data analytics in healthcare include; the heartbeats and breathing patterns of the premature and unwell babies are monitored using Big Data techniques in one specialized baby unit. The organization was able to create algorithms that anticipate infections 24 hours before any physical signs appear thanks to this data.
Retail
Our buying and selling habits are changing quickly. Retailers who are adopting a data-first approach to get to know their consumers, match them with items, and take their money are benefiting greatly, both online and off. This means that Data analytics solutions is now being used at every stage of the retail process, including identifying the customers who are most likely to be interested in a particular product, figuring out the best way to approach them, collecting their money, and determining what popular products will be based on trend analysis, forecasting where demand will be for those products, and optimizing pricing for a competitive edge.
Manufacturing
A significant part of contemporary manufacturing processes is data. Manufacturing is undergoing a significant transformation. This is due to advancements in robotics and rising automation. One well-known company that makes significant investments in automation factories is Adidas. The importance of big data analytics still reverberates through more traditional manufacturing settings. Connecting sensors to machines captures useful data that enables manufacturers to monitor their health and efficiency. A growing array of devices—from jet engines to yoga mats—now pack sensors inside them. This allows manufacturers to collect useful information about the functionality and performance of their products.
Banking, insurance, and financial services
Big Data Analytics has many uses outside of high-tech, high-profit trade. Data, for instance, is assisting credit card firms such as American Express in identifying fraudulent transactions and growing their trend research services for commercial clients.
Data is already being utilized by insurers to detect fraudulent claims, better target their marketing campaigns, and establish more equitable and accurate policy pricing. Big data analytics in business such as Progressive and Aviva are going one step further in gathering data by providing discounts to drivers who permit them to track their driving through in-car technology and smartphone apps. This enables the insurer to see how safe an individual’s driving actually is.
Education
Education institutions are starting to use the vast Big Data Analytics being generated about human learning to gain insights that can improve instruction, point out areas in which students might not be learning as well, and completely change the way that education is delivered.
Of course, not all education occurs in a classroom these days. A multitude of insights into people’s learning styles are being gained by the explosion of online courses, which is also propelling significant advancements in individualized and adaptive learning.
Logistics, supply chain management, and transportation
Digital cameras are frequently employed in warehouses to track inventory levels, and the data they collect can be utilized to send out restocking warnings. Big Data Analytics furthers by forecasting, which uses the same video data to train machine learning algorithms so that an intelligent stock management system can anticipate when a resupply is required. Not too far into the future, warehouses and distribution centers will essentially be self-managed, requiring little human input.
Additionally, transportation companies are logging and analyzing telematics data for their fleet vehicles regarding driving behavior, logistics route optimization, and fleet maintenance.
Agriculture
Even highly established industries are utilizing data’s power. American agriculture company John Deere has embraced Big Data methods wholeheartedly, introducing a number of data-enabled applications that enable farmers to take use of real-time, crowdsourced monitoring of data gathered from thousands of users.
Using Big data analytics in agriculture farmers can get aggregated data from users worldwide as well as data collected from sensors mounted to their own equipment while working the fields.
Energy
Exploration and drilling for new deposits are made more difficult by the unstable international political environment and the growing expenses associated with extracting oil and gas. The energy sector is looking towards big data consulting services to find answers to major issues. For instance, in an effort to reduce the cost of oil drilling, Royal Dutch Shell has been creating “data-driven oilfields.”
Data and the Internet of Things are changing the way we use energy within our homes in their own small but no less important way. With technologies such as Google’s Nest thermostat, which reduces wastage while providing better comfort, smart homes have become more common.
Public sector and government
In an effort to become “smart cities,” a number of communities are already conducting data analytics pilot programs. In these cities, data collecting, analytics, and the Internet of Things come together to develop integrated public services and utilities.
Hospitality
Operators in the hotel and leisure industries are looking to advanced data analytics solutions for insights into how to maintain pleased clients. Yield management is a typical use of analytics in the hotel sector. This is the procedure that makes sure every room commands the best price, accounting for seasonal fluctuations in demand as well as other elements like local events and the weather that may affect the quantity and kind of visitors who check in.
Expert services
Blue-collar industries like factory workers and taxi drivers are frequently cited as examples of how robots and algorithms may soon replace human people in the workforce in news articles and stories. However, developments in data, analytics, machine learning, robots, and artificial intelligence are causing enormous change in even highly skilled professional services, such as accountancy, law, and architecture.
Software can automatically input transactions, track digital receipts, automate payroll, and monitor taxes, for instance, in accounting. However, these days, computers are capable of performing even more difficult jobs including trend analysis, regulatory compliance, and auditing.
Sports
Today, the majority of professional sports use data analytics services. Using pattern recognition, a network of cameras placed across Premier League football stadiums currently tracks every player, producing over 25 data points per player every second! NFL players have sensors inserted in their shoulder pads to collect performance data, and British rowers used analytics to win gold at the Olympics. Data has even helped to uncover the mechanics of the ideal golf swing.
It’s actually difficult to think of a sport these days that isn’t utilizing statistics and analytics. Athletes are monitored by many professional sports teams even when they are not competing. They are tracked through social media chats and sophisticated technology that measures sleep, nutrition, and emotional health.
Starting With Big Data
When choosing between big data analytics vs data analytics and considering all of these potential advantages of big data analytics, you may want to get started on your big data journey as soon as possible. However, what must be the first step?
Get the big data infrastructure ready
The processing and analysis of data must be there at someplace. Provisioning a data lake on a cloud platform is easy, particularly if you already have a relationship with a cloud vendor. Actually, it’s usually as easy as naming the data lake, obtaining your connection string, and entering your credentials when creating a storage account. To do this, the majority of the data analytics company that offer simple-to-use tools. Of course, you may also create your own data lake, maybe utilizing an on-premises and cloud-based hybrid architecture.
Define the zones of the data lake
The majority of data lakes aren’t just large, disorganized data repositories in reality. It’s helpful to divide them up into several zones, each with distinct functions and frequently with unique permissions for various user groups.
The first one is typically the landing zone, also known as the raw or ingestion zone. Here is where newly added data is introduced to the data lake with the least amount of processing. The second area is the production zone, which is used to store cleaned, conformed, and processed data. Although it is usually less structured and regulated, this one is most comparable to a data warehouse.
Additionally, there’s typically a working zone, or sandbox, where data scientists and developers can keep project-related temporary files and data structures. Lastly, to guarantee that crucial data sets are appropriately managed, it may be essential, depending on your organization, to establish a private or sensitive data zone with extremely limited access.
Enumerate the data resources
A user-facing catalog of the data resources is extremely necessary because of the vast array of data types that can be kept in a big data system. A provider of cloud platforms may provide a simple search and cataloging system of its own. Generally speaking, though, it may be better to create a data catalog with data scientists, business users, and developers in mind.
Conclusion
You’re almost ready to let people access your big data system now that you have this fundamental architecture in place. However, given that the applications of big data analytics may differ significantly from well-known database and data warehouse technologies, considerable training is necessary. Considerations for permissions, access rights, and other security and data governance needs should also be made. In actuality, the big data journey just began here.
However, the rewards and advantages that big data may offer your firm make the work worthwhile. Big Data Analytics is essential to modern company and one of your most powerful tools for implementing strategic change within an organization and outperforming competitors.
FAQs
Why is data analytics important, and what does it entail?
Data analytics is the process of assessing and understanding huge amounts of data. IT is in a manner that creates useful and insightful business information. Its importance is in helping companies achieve data-driven decision-making and getting consumer trends correctly; it also boosts operational effectiveness.
Which sectors make use of data analytics?
The use of data analytics finds relevance in several businesses. These industries include banking, manufacturing, e-commerce industries, healthcare, and finance.
In what ways has big data altered the corporate landscape?
Big data drives modern marketing. Every online transaction and conversation is a part of a vast and intricate system. This massive data landscape can even forecast future customer or client behavior, providing insightful information about consumers.
How did the business use big data to change its operations or get over its obstacles?
Big Data aids merchants in the analysis of competitive data, customer preferences, and market trends. To understand customer attitude and preferences, they look into data provided in online forums, social media platforms, and customer reviews. This can be useful to identify emerging trends and enhance its selection of products.






