Table of Contents
Blockchain technology has emerged as a disruptive force in the financial services industry. By facilitating transparent, secure and cost-effective transactions without any intermediaries, blockchain has the potential to transform traditional financial processes and products. It enables the digitization of assets and financial records, thereby improving efficiency while reducing costs and risks for financial institutions. The financial services sector was one of the earliest industries to recognize the far-reaching implications of blockchain. Today, all major banks and financial organizations are actively exploring blockchain Use Cases and experimenting with decentralization. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of blockchain in finance by discussing its key benefits, highlighting prominent use cases, and examining the challenges in its adoption.
What is Blockchain in Finance?
Use cases of Blockchain in finance refers to the implementation of blockchain technology in finance industry. By creating a distributed digital ledger that permanently records transactions in an unalterable way, blockchain allows financial institutions to move away from centralized databases and intermediaries. It facilitates trustless peer-to-peer transactions without the need for reconciliation. This enables faster, transparent, and cost-effective financial processes. Blockchain also supports the issuance of digital assets like cryptocurrencies and security tokens. Using smart contracts, it automates various financial functions and agreements. Further, blockchain-based digital identities and signatures enhance security and compliance for Know Your Customer (KYC) checks. Overall, blockchain software development services bring more resilience, accountability and opportunities for innovation to the financial system.
Key Stats: Blockchain in Finance
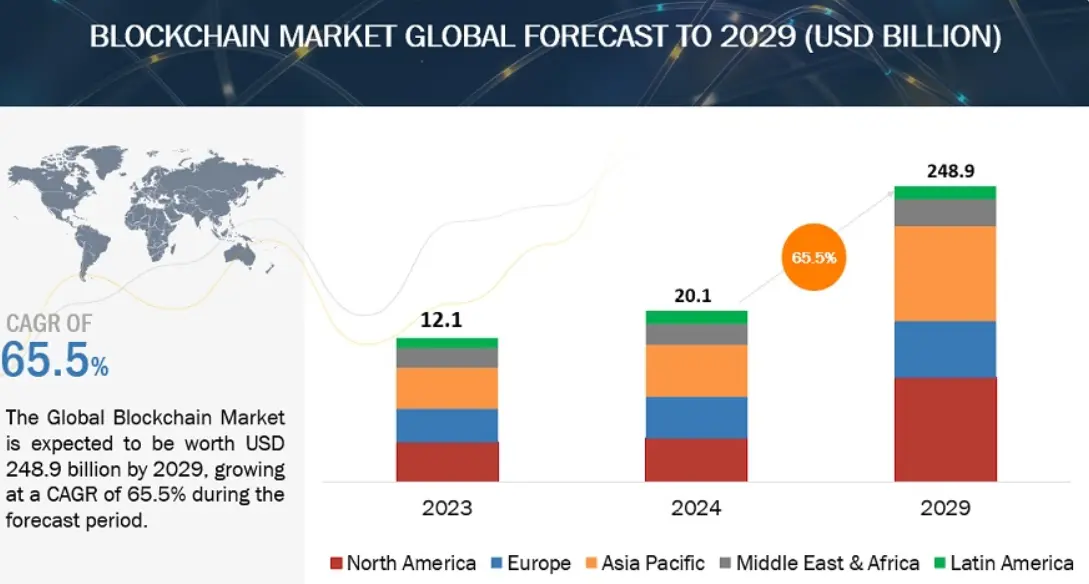
- The global blockchain market in finance is estimated to reach $248.9 billion by 2029 growing at a CAGR of 65.5% (Report by MarketsandMarkets).
- 95% of financial institutions believe blockchain investments are a high priority over the next year (Survey by FTI Consulting).
- Cross-border payments settled using blockchain can be 100x faster and 90% cheaper than traditional methods (Case studies by R3, Ripple).
- As of Q3 2022, assets invested in decentralized finance platforms surpassed $100 billion (Report by Coindesk).
- 65-80% of major banks have active blockchain projects underway and 30% of top companies will adopt blockchain by 2023 (Gartner Hype Cycle Report).
Use Cases of Blockchain in Finance that may Disrupt BFSI
Collateral Management
Collateral management involves tracking real-world assets used to secure loans. Using blockchain, lenders can more efficiently collect, store and manage digital records of collateral assets in real-time. Smart contracts facilitate automated enforcement of ownership transfer and loan payment conditions. This streamlines processes for financial institutions processing large corporate loans backed by multiple real estate properties or machinery. Blockchain ledgers ensure end-to-end visibility of collateral while eliminating inconsistencies arising from fragmented legacy databases. The immutable records also resolve disputes through transparent transaction histories.
Tokenization of Real-world Assets
Blockchain enables digitization and fractionalization of real-world assets into blockchain-based security tokens representing part-ownership. This boosts market liquidity by making previously illiquid assets easily tradable in cryptocurrency exchanges or private marketplaces. Tokenization also facilitates innovative financing structures like security token offerings enabling retail investors to fund projects previously limited to accredited individuals. Smart contracts automate asset management, distributions and regulatory requirements like KYC checks. Overall, tokenization unleashes new capital raising avenues and peer-to-peer trading models disrupting traditional private equity.
Crypto Staking
Crypto staking is one of the most talked about Use Cases of Blockchain in Finance. In staking, users lock up their cryptocurrency tokens to support the operations of a blockchain network and earn rewards in return. People can stake their cryptos with exchanges or companies that run validators on a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain. Unlike storing cryptos in a wallet, staking helps utilize cryptos productively and generate passive income. As per the top Cryptocurrency Wallet Development Company experts, it encourages more users to participate in validating blockchain transactions. With over $25 billion worth of cryptocurrencies staked across networks, staking is gaining popularity among retail investors.
Invoice Factoring
Invoice factoring is the process of selling unpaid invoices to a third party known as a factor at a discounted price. The factor immediately pays the supplier for the invoices and takes care of collection when the customer pays later. It helps suppliers get quick access to operating capital. Blockchain can streamline invoice factoring by enabling suppliers to tokenize invoices as digital assets on a distributed ledger. Factors can browse invoices online, verify their authenticity using smart contracts, and purchase the tokens. The invoice token is sent to the factor once payment is received, reducing manual intervention and delays. This Use Case of Blockchain in Finance improves transparency and turnaround time for invoice factoring.
Paper Currency Replacement
Paper currency needs frequent reissuing due to wear and tear. It is also prone to forgery. Blockchain offers a solution by enabling central banks to issue digital currencies as a replacement for physical cash. Countries like China and Sweden are testing central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) on permissioned blockchain networks. CBDCs can potentially address counterfeiting while digitizing the popular functions of cash such as direct peer-to-peer transfer and offline use. Countries realize that a fully-digital currency system ensures financial inclusion, aids commerce, and even collects transaction taxes automatically. This can perhaps force a massive disruption to paper currencies in the long run.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platforms
DeFi signifies blockchain technology in finance similar to how the internet is used today for various online financial services. It involves peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries using smart contracts. Popular DeFi Use Cases include platforms for lending, trading, asset management, insurance, and more. For instance, Aave is a major DeFi lending protocol allowing crypto depositors to earn interest on their assets. Similarly, Compound enables crypto loans while Uniswap is the dominant platform for decentralized exchange of ERC-20 tokens. With over $100 billion worth of value locked in the overall DeFi development company ecosystem, it is gradually changing how people access and interact with financial services worldwide.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs are the digital form of fiat currencies issued and governed by a country’s central bank. They combine the attributes of physical cash with digital payment systems. Central banks across the world are exploring potential CBDC models to modernize their monetary systems. China’s Digital Currency Electronic Payment (DC/EP) pilot is the largest example to date with over $5 billion worth of digital Yuan distributed. The key motivation is to reduce reliance on private forms of digital money, stay relevant in the future monetary landscape, and make domestic currency transactions more cost-effective. CBDCs are believed to redefine the role of central banks and challenge the existing financial order in the long run.
Blockchain-Based Derivatives Trading
Derivatives trading involves contracts whose value is derived from underlying assets like equities, commodities, currencies, etc. Examples include futures, options, and swaps. Blockchain makes it possible to automate cumbersome trading, clearing, and settlement activities for derivatives. Smart contracts can encode trading terms, execute matched trades, automate collateral and margin transfers, and settle obligations payouts – all without any central counterparty or exchange. Firms like Digital Asset and Constellation are working to digitize over-the-counter derivatives on distributed ledgers. This Use Case of Blockchain in Finance industry promises significant cost savings, near-instant settlements versus days/weeks, and elimination of non-intentional errors from manual interventions.
Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
International payments go through multiple intermediaries spanning different geographies and often take days to complete. This involves high fees, foreign exchange spreads, complications in compliance, and lack of transparency for users. Blockchain networks help reduce the intermediation through their peer-to-peer nature and smart contracts. Remit Tech firms like Ripple, Stellar, and Telegram Open Network (TON) are building payment corridors on distributed ledgers to accelerate cross-border money transfers significantly while lowering costs to almost zero. Initiatives like the Marco Polo bridge between major trade finance banks integrate trade finance activities within remittance corridors. This is disrupting the centuries-old correspondent banking model for international value exchange.
Securities Tokenization
Securities tokenization involves digitally representing real-world assets like equity shares, bonds or derivatives on a distributed ledger as crypto tokens. It provides an open platform for fractional ownership of assets using smart contracts. Transactions become automated, round-the-clock, transparent and verifiable. The issuer benefits from streamlined capital raising while investors obtain direct asset exposure. Companies raising capital through initial coin offerings as well as platforms securitizing real estate, fine art, and VC funds using blockchain are leading examples of this innovative Use Case of Blockchain in Finance. Regulators are also recognizing the potential to deepen markets through such token-based financing models.
Blockchain-Based Identity Verification (KYC/AML)
Due to stricter KYC (Know Your Customer) and AML (Anti-Money Laundering) norms, regulated financial institutions spend millions annually complying with Customer Identity Verification processes. Blockchain provides a solution by enabling customers to own, control and share their verified identity attributes as digital credentials across supported organizations. Decentralized identity networks like Sovrin Foundation allow login with self-sovereign identities complying with KYC. Users only share required attributes as claims validated by issuers on-chain. Firms can access verified customer profiles through consent-based database lookups and smart contract integrations. This brings significant efficiencies compared to redundant, paper-based KYC among financial services providers and other industries subject to KYC requirements.
Blockchain in Syndicated Loans
Loan syndication involves several banks jointly providing credit to a single borrower and sharing the risk. This requires complex administrative tasks including credit assessment, deal structuring, fund allocation, and interest collection. On blockchain, smart contracts can govern collaboration between banks to automate syndicated lending workflows. Participants get transparency into loan documentation, capital call schedules, payment receipts through the shared ledger. Audit trails improve compliance while pre-coded debt covenants help enforce timely payment recovery automatically. Companies like Nivaura, Circus and Barclays are researching this promising Use Case of Blockchain in Finance industry to streamline multi-party lending arrangements.
Blockchain for Trade Finance
Trade finance encompasses initiatives by banks, export credit agencies, insurers to facilitate global commerce through letters of credit, guarantees, insurance, and other instruments. However, documentary processes involving paperwork transfer between geographically distributed banks inflict time lags and costs. Blockchain offers a way to digitize physical trade documents and finances on distributed ledgers. Pilots show bills of lading, certificates of origin, invoices and SWIFT messages can be transferred simultaneously over borders through tagged smart contracts. Trade finance consortiums are leveraging this to reduce paper dependency, eliminate fraud and fulfill bilateral trade obligations automatically. Firms foresee savings between 20-40% of trade finance costs if blockchain adoption scales.
Blockchain in Asset Management
Investment funds and asset managers spend a lot on resource-intensive operations like trade settlement, regulatory reporting, and asset servicing. Blockchain tech increases efficiency across these functions through shared ledgers, tokenization, and distributed storage systems. For instance, fund subscription and redemption activities can utilize smart contracts avoiding multiple intermediaries. Custody and reconciliation headaches reduce as ownership records, transactions remain immutable on-chain. RegTech angle eases regulators’ work extracting real-time portfolio disclosures directly. Industry consortiums like FPAs are actively applying Use Cases of Blockchain in Finance like digital securities, analytics platforms between stakeholders to optimize operations and cost for asset managers.
Decentralized Insurance Markets
Incumbent insurers face complex fulfillment processes due to involvement of policyholders, agents, claims adjusters leading to high frictional expenses. Whereas customers seek personalized coverage, quick payouts. Blockchain enables “smart insurance” addressing both challenges through on-chain programmable policies powered by distributed consensus and financial cryptography. For example, Etherisc allows users to receive and pay claims without intermediaries using if-this-then-that smart contracts and pooling mechanisms. Today, when you hire blockchain developers, you get parametric insurance protocols settling payouts on pre-defined external conditions such as weather patterns, inflation rates. In future, direct peer-to-peer model between individuals and businesses may even disintermediate traditional underwriters.
Blockchain-Enabled Microfinance
Microfinance aims to provide small credit and other financial services to low-income clients who lack collateral. However, traditional models involve lengthy paperwork, centralized databases prone to errors and high operating costs. Blockchain offers a decentralized alternative, reducing costs by 30-50% according to studies. By recording lending history on distributed ledgers, clients can build verifiable credit profiles, bypassing collateral needs. Smart contracts automate loan disbursement and repayments. This empowers rural poor with access to formal credit. Startups like Bitspark and Cogo leverage Ethereum for attribution of identity, credit assessment and micro-lending in developing nations. Such initiatives have disbursed millions of dollars in loans. Overall, blockchain heralds financial inclusion by streamlining microfinance and opening access to global capital pools.
Real-Time Regulatory Reporting (RegTech)
Banks face immense technical and operational challenges in meeting global compliance burdens. Regulatory reporting consumes huge costs as data must be reconciled across multiple siloed legacy systems. Blockchain allows immutable recording of audit trails for transactions and customer data directly on distributed ledgers. Its cryptographic timestamping reveals authentic sources, preventing data tampering. Smart contracts program compliance rules and automate reporting. This significantly reduces costs while ensuring accuracy. Firms like QED-it have developed RegTech solutions where financial transactions are recorded privately on permissioned blockchains. Queries reveal necessary data for regulators with enterprises retaining full control. Startups are also exploring public blockchain use for instant cross-border surveillance. Overall, RegTech facilitates seamless supervisory oversight while minimizing compliance friction.
Blockchain for Peer-to-Peer Lending
P2P lending circumvents traditional banks by connecting individuals directly as lenders and borrowers via online platforms. However, these platforms still involve centralized databases and require intermediaries. Blockchain provides a distributed solution matching lenders directly with qualified borrowers globally based on their risk profiles. Smart contracts automate loan agreements, disbursement and repayments through tokenized assets. This reduces costs associated with banking commissions and infrastructure. Prominent projects like Salt Lending, Ethlend and Bitbond integrate identity checks and credit scores on distributed ledgers then match profiled borrowers and lenders. Other startups are exploring decentralized reputation and credit scoring on public blockchains to eliminate credibility issues associated with centralized credit agencies. In future, P2P lending may disrupt financing with blockchain removing intermediation costs and opening financing pools across borders.
Programmable Money
Cryptocurrencies are increasingly getting associated with additional functions beyond just serving as a medium of exchange. Programmable money involves blockchain-based digital assets whose core functions can be redefined through embedded computer programs known as smart contracts. For example, stablecoins aim to maintain price stability relative to real-world currencies and commodities through automated mechanisms like collateralization and arbitrage built via smart contracts. Others experiment with central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) whose money supply and interest rates could potentially be programmed to adjust dynamically based on economic indicators. Smart contracts may also define conditions for money transformers that alter an amount’s spendability or characteristics based on certain triggers. In future, as digital ledger infrastructure matures, programmable money functionalities could encompass automated taxation, social welfare disbursement, invoice financing and salary payments among other use cases through rules codified in distributed applications.
Blockchain for Real-Time Tax Settlements
Tax collection traditionally relies on slow, inefficient paper-driven processes prone to errors and corruption. Tax payers also endure arduous compliance requirements involving multiple intermediaries. Blockchain enables digitally recorded taxation streams through smart contracts which can automate tax calculations, filings, audit trails and dispute resolution. Its pseudonymous addresses prevent misuse of personal data while ensuring identities. Payment settlements in the form of fiat-pegged stablecoins or CBDC tokens can occur instantly. This does away with opaque bureaucratic oversight while minimizing revenue leakages. Jurisdictions like Ohio and Georgia are conducting pilots leveraging Hyperledger to modernize tax processes. Startups are also exploring how tokenized micro-economies involving utility tokens may automatically extract and remit consensus-based taxes in real-time. Overall, blockchain presents another disruptive way to remedy antiquated tax systems worldwide through ushering greater efficiencies, trust and cost optimization.
Ready for the Future of Finance? Explore Blockchain Solutions Today!
Benefits of Use Cases of Blockchain in Finance Industry
Blockchain offers significant benefits that are disrupting the traditional financial system. Some of the key benefits include:
Improved security and transparency: Being distributed, encrypted and immutable, blockchain eliminates single points of failure and the need for intermediaries, providing higher security levels than centralized databases. All transactions recorded on the shared ledger bring more transparency.
Reduced Costs: Blockchain minimizes infrastructure costs by removing layers of intermediaries. Automated processes reduce compliance, reconciliation and labor costs. As per Santander, blockchain can potentially reduce $20 billion costs annually for banks.
Faster Transactions: Without intermediaries, blockchain transactions process instantly, allowing near real-time asset transfers and settlements. Cross-border payments can be settled 100x faster using blockchain.
Greater Financial Inclusion: Cryptocurrencies and open finance platforms improve accessibility of financial services for the underbanked. Fractional ownership of assets also boosts participation.
Enhanced Traceability: The ability to trace digital assets and transactions end-to-end boosts auditability and check financial crime. Blockchain resolves disputes through transparent transaction histories.
Innovation with Smart Contracts: Smart contracts facilitate new products, decentralized applications and automated processes beyond capabilities of legacy systems.
Programmable Digital Assets: Cryptocurrencies, security tokens and virtual assets issued on blockchain inherit powerful programmed capabilities for different uses.
Improved Risk Management: Trustless peer-to-peer transactions minimize risks of defaults or technological complications. Insurance claims are verifiable through digitally recorded transactions.
Regulatory Compliance: Audit trails and oversight over transaction data help meet global compliance and avoid financial market abuses and money laundering.
In summary, blockchain introduction has the potential to revolutionize the finance industry with disintermediation, higher efficiencies and inclusion.
Navigating the Challenges – Implementing Use Cases of Blockchain in Finance
While blockchain brings multiple advantages, its adoption also faces challenges that need to be addressed carefully. Some key challenges in implementing blockchain in the financial ecosystem include:
Regulatory Uncertainty: With blockchain disrupting traditional models, regulations are evolving. Financial companies need clear regulatory and legal guidelines for activities like crypto trading, stablecoins and decentralized operations.
Technological Immaturity: Blockchain is still in a nascent stage, with scalability, security and operational issues to be resolved for large-scale enterprise use. Technical problems can stall wholesale adoption.
Resistance to Change: Legacy systems of banks make changeovers costly and difficult. Overcoming organizational inertia requires top management buy-in plus retraining employees.
Interoperability Challenges: Blockchain networks currently operate in silos, but various protocols must connect to realize the vision of an interconnected global financial system.
Data Privacy and Ownership: Financial data privacy on public chains raises concerns. Private/consortium chains involve trust-related tradeoffs vs public blockchains.
Volatility Risks: Crypto prices are highly volatile presently for use as currencies. Stablecoins still face risks around asset backing and centralization.
Skill Shortages: There is a severe shortage of experienced blockchain talents, undermining chain infrastructural development and customization needs.
To address these hurdles, financial organizations can focus on building education, explore private/hybrid approaches, collaborate with fintech startups, engage regulators proactively, undertake cautious pilots and adopt a stepwise integration plan with existing infrastructure. Overall, blockchain’s potential as a core finance platform will be realized through progressive standardization and with solutions to socio-technical challenges.
Blockchain Trends in Finance to Watch in 2025
The next few years will be transformative for blockchain adoption in the financial industry. Here are some key trends to watch:
Rising Digital Asset Markets: With developments in decentralized finance, the market capitalization and volumes of cryptocurrencies and digital assets are projected to multiply further.
Widespread CBDC Adoption: Most large economies will roll out initial versions of CBDCs by 2025. Interoperable CBDCs and their global infrastructure will start taking shape.
Tokenized Assets Boom: Fractional ownership of real assets will become more common through security tokens issued on public/private chains with standardized protocols.
BFSI Going Blockchain-native: Major banks will create independent blockchain subsidiaries. New blockchain-based neobanks will directly compete with incumbents for retail clients.
Institutional Crypto Embrace: As regulations stabilize, institutional crypto trading platforms will help mainstream adoption while mitigating risks/volatility.
DeFi Disruption of Traditional Services: Decentralized lending, trading, asset management and insurance will mature as attractive crypto-based alternatives challenging incumbent business models.
Job marketplace Tokens: Blockchain-based professional platforms may tokenize job opportunities and reputation through participation and performance tokens.
Real-time Clearing and Settlements: Inter-bank financial networks and cross-border payment solutions will transition to real-time blockchain settlement rails, minimizing float periods.
Global KYC Utilities: Shared KYC networks leveraging self-sovereign digital identities will facilitate seamless onboarding while strengthening AML checks on public and private chains.
Supply Chain Financing Platforms: Cryptocurrency-powered lending marketplaces will disrupt legacy invoice financing through smart contracts on permissioned chains.
Regulatory Tech (RegTech) Solutions: Blockchain-powered regulatory reporting and compliance-as-a-service offerings will emerge, aided by the increased use of programmable rulesets, data privacy as well as analytics on distributed ledgers.
Expanded Blockchain Consortia: Large industry associations and standardization bodies will help test, support development of commonly acceptable blockchain frameworks and form global alliances among network participants.
A3Logics is a Leading Blockchain Consultant for Finance Industry
A3Logics is a prominent blockchain consulting services company that designs and implements custom blockchain solutions for the finance industry. With a global team of blockchain experts, A3Logics has successfully delivered several blockchain projects across different industry verticals.
For the finance segment, A3Logics’ services include blockchain advisory, DApp development, smart contract audits and managed blockchain services. Some prominent solutions developed by A3Logics include:
- A decentralized settlement network for a global investment bank to process USD daily trades using Hyperledger Fabric.
- A credit scoring platform on Ethereum for a leading credit card issuer evaluating credit profiles of over 120 million customers.
- A cross-border remittance network based on Stellar Blockchain handling daily transactions between international bank branches.
- A security token issuance platform leveraging ERC-20 standard that has helped tokenize real estate assets for institutional clients.
- An insurance claim settlement system built with Hyperledger Besu facilitating instant verification and auto-approval of several life insurance claims annually.
- A commodity trading platform on Corda Enterprise facilitating weekly trading of agricultural produce among global farmers and retailers.
Leveraging its pool of Blockchain Security Experts, Smart Contract Auditors and Infrastructure Consultants, A3Logics adopts a comprehensive approach to address finance challenges around security, scalability and compliance through blockchain advisory and managed blockchain-as-a-service models. It helps clients craft innovation strategies around blockchain Use Cases like stablecoins, CBDCs and tokenized investments.
Transform Your Software Vision into Reality – Book A 30 Minutes Free Consultation!
Final Take
In conclusion, blockchain has emerged as a disruptive technology accelerating the digital transformation of the finance industry. It offers promising solutions to address long-standing problems around costs, trust and efficiencies through decentralized networks, programmable assets and smart contracts. While the technology still has limitations to overcome, early Proof-of-Concepts and implementations show immense potential across all sectors within the BFSI domain.
Going forward, the continued maturation of the underlying blockchain platforms will strengthen protocols enabling faster, cheaper and more inclusive financial services. Regulatory clarity around digital assets will support the responsible growth of both public and private chain markets and applications. Standardization efforts will tie together fragmented ecosystem participants. Resolution of technical roadblocks will expand the capacity of blockchain networks.
Financial firms are rightly experimenting with blockchain at an accelerating pace to evaluate its overall commercial viability and specific Use Cases for modernization. Given its cross-industry relevance, prudent investments in human capital and blockchain skills will remain vital. Careful piloting integrated within existing infrastructure can help contain risks while capturing early benefits.
When successful technical, regulatory and organizational challenges are overcome methodically, blockchain is positioned to change the business logic of the entire financial landscape – from remolding retail banking to transforming B2B capital markets. As use cases of blockchain in finance market continue to mature, exciting times lie ahead for both financial modernization and widespread financial inclusion at a global scale.
FAQ’s
How is blockchain used in finance?
Blockchain facilitates decentralized, transparent and secure financial transactions without intermediaries. It digitizes assets, automates processes using smart contracts and issues programmable digital currencies. Blockchain also boosts auditability, compliance and opportunities for innovation.
How has blockchain revolutionized the finance industry?
Blockchain addresses long-standing problems of costs, trust and efficiencies in finance through disintermediation, peer-to-peer networks and programmable assets. It facilitates real-time, global transactions at lower costs while enhancing security, transparency and financial inclusion.
How do smart contracts work in finance?
Smart contracts automate execution of financial agreements through coded conditional rules. They self-verify and self-execute transactions like funds transfer based on predefined criteria like timely payments, thus removing manual oversight and disputes.
What is the role of blockchain in central bank digital currencies?
Blockchain facilitates issuance, distribution and transaction verification of CBDCs – which are fiat currency claims represented in digital token format on distributed ledgers. It ensures auditability, security and real-time settlement of tokenized fiat currencies.
How does blockchain improve transparency?
All transactions recorded immutably on distributed ledgers bring transparency as anyone can view transaction flows without intermediaries. This allows traceability, easy dispute resolution and heightens trust in financial processes.
How does blockchain impact securities trading?
Blockchain facilitates seamless issuance and exchange of security tokens representing equity or debt portions. Automated peer-to-peer trading lowers costs for investors while enhancing liquidity, traceability and opportunities in capital markets.
Can blockchain reduce transaction costs?
Studies show blockchain adoption may reduce up to $20 billion intermediation costs for banks annually through disintermediation, reconciliation optimization and automated processes bringing savings on infrastructure, labor and compliance.