Table of Contents
In the medical field, a doctor’s performance is directly related to the health and sometimes the life of the patient. Nowadays, machines are superior to humans in many of these duties since they never get tired or experience pressure during even the most difficult operations. Medical professionals now have superpowers like unwavering focus and unceasing observation because of advancements in computer vision in healthcare, particularly in the area of object detection. For instance, a machine’s error rate is about 3.5%, while a human’s is 5%. In short, these tasks can be performed more effectively by computer vision object detection and recognition.
The most recent advancements in object recognition technology are attributed to deep learning or the use of multi-layer neural networks in machine learning solutions. The accuracy of object detection on both public and private data sets has greatly increased thanks to deep learning. AI and ML capabilities are the foundation for computer vision applications in the medical imaging sector.
What is Computer Vision in Healthcare?
An area under the general phrase “artificial intelligence” is computer vision. It works with the examination of still photos or video feeds to conclude and take appropriate action. Thanks to deep learning, the accuracy of computer vision services—which are driven by extremely intricate mathematical algorithms called neural networks—has significantly increased. These systems analyze datasets, which are collections of photos or videos of a particular topic. A neural network performs more accurately the more of these photos or videos it processes.
Computer vision technology has been transformed by deep learning, a kind of machine learning. Increases in processing power, privacy-preserving technology, and more effective training frameworks are to blame for its growing popularity. In contrast to conventional machine learning, which mostly depends on feature extractors designed by humans, deep learning makes use of several layers of representations to automatically identify patterns in unprocessed data. Due to this change, computer vision technology has advanced significantly, allowing machines to perform picture identification tasks with great accuracy.
The complexity and optimization of deep learning algorithms over the last ten years have increased average accuracy from roughly 50% to 99%. Additionally, deep learning neural networks have benefited greatly from the fast-growing amount of datasets, especially digital photographs available on the internet.
Because computer vision in healthcare can identify an illness at its earliest stages, it is very valuable in the healthcare industry when it comes to delivering care services for patients in medical environments. According to recent research, artificial intelligence helps physicians provide value-based care while also improving their speed. A doctor does not have to spend a lot of time performing labor-intensive, manual tasks. Most crucially, because machines never weary, the error rate drops when the neural network serves as the doctor’s advisor.
How Healthcare Computer Vision Is Operated?
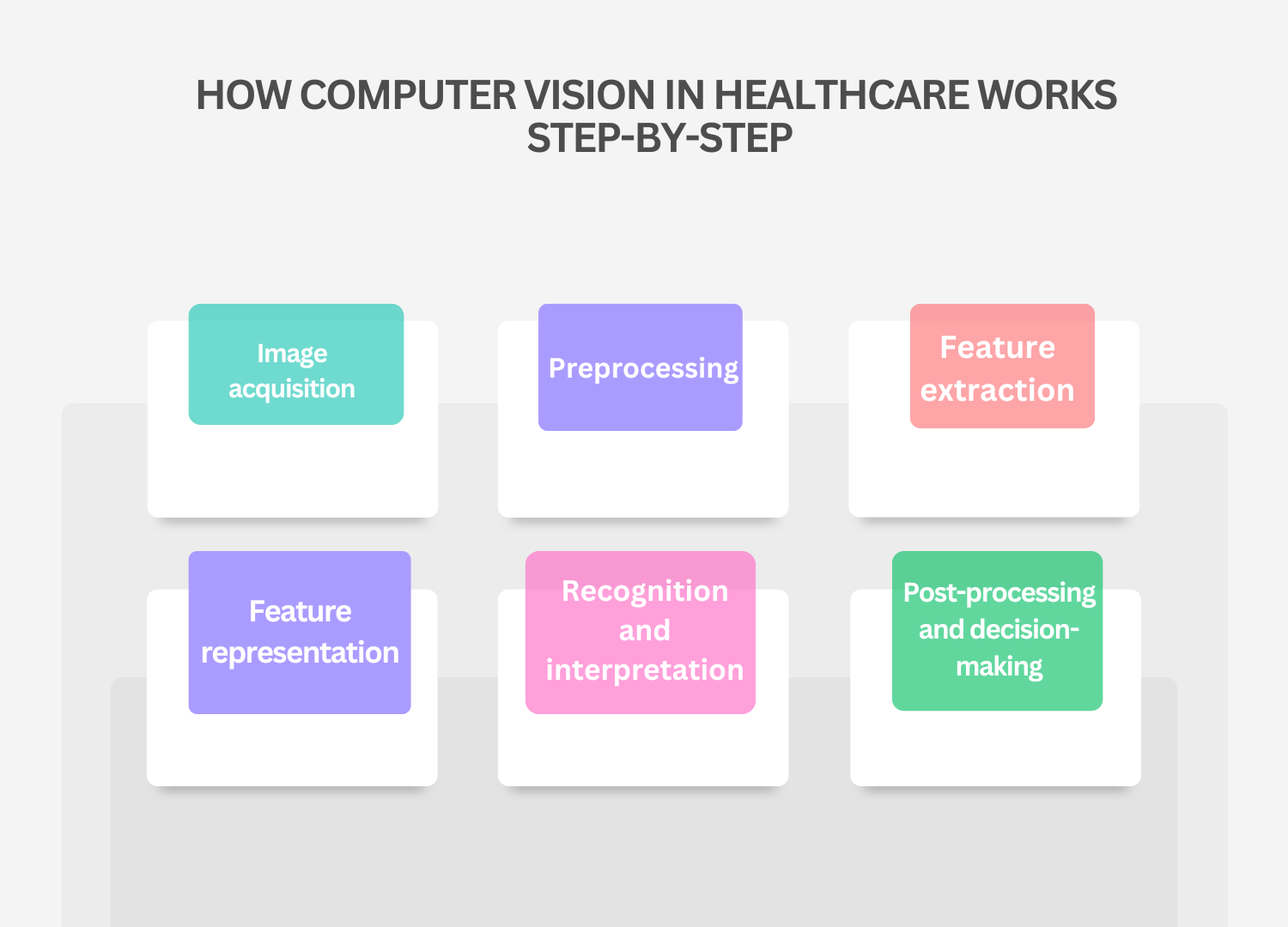
The development of AI computer vision has already greatly benefited the healthcare industry. Healthcare computer vision is now advancing quickly to provide life-saving interventions. Physicians can diagnose patients more quickly and in the early stages of the illness. They can then recommend the most effective course of action and keep an eye on the disease’s development.
It saves medical professionals a significant amount of time that would otherwise be required to diagnose the illness based on its varied symptoms. The application of computer vision in healthcare is starting to show up in several fields. Predictive analysis, health monitoring, and medical imaging analysis are a few of them.
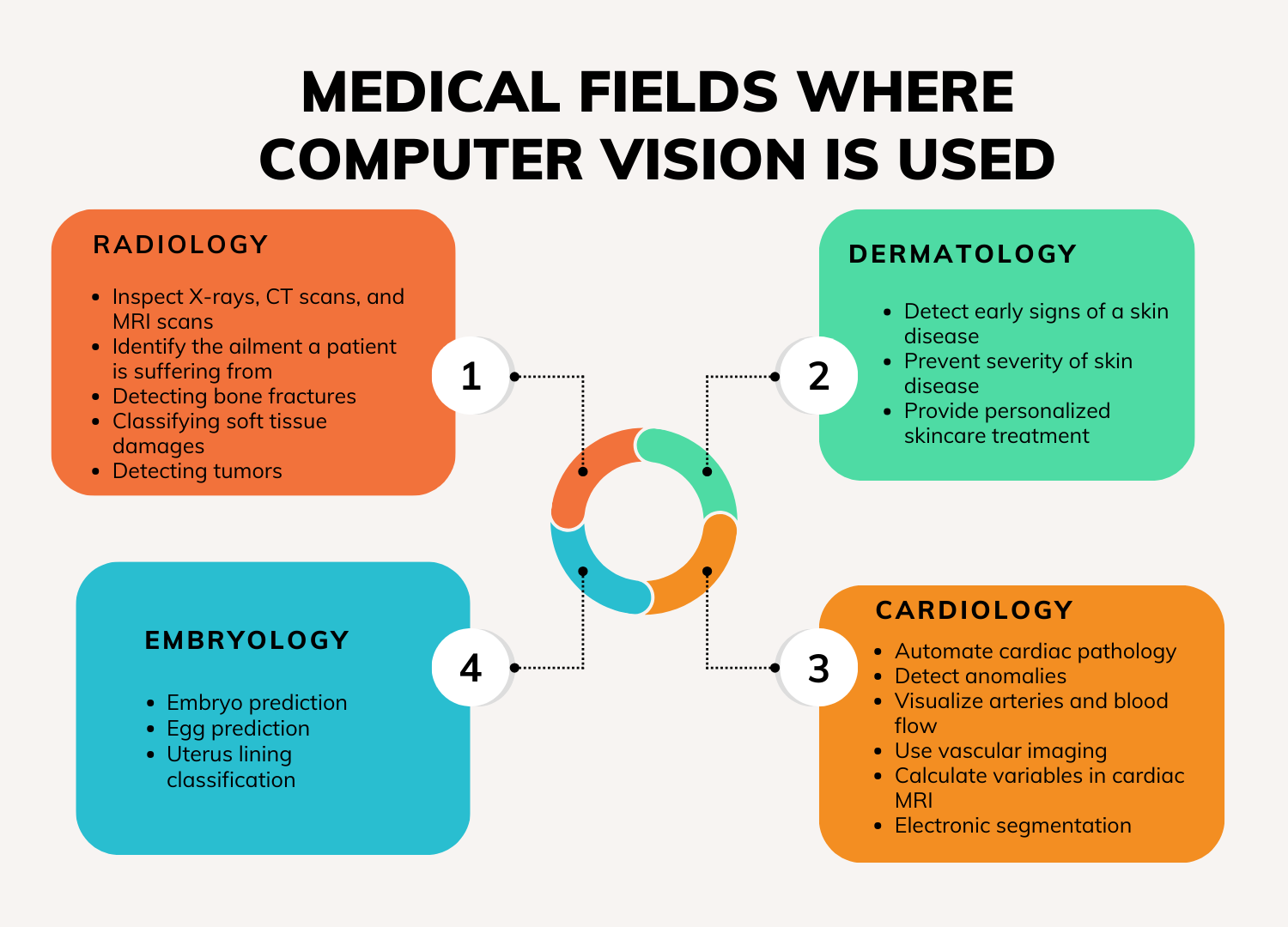
The interpretation of pictures and videos is the focus of computer vision. Among the tasks are segmentation, object identification, and picture categorization. Medical imaging can benefit greatly from recent advances in object recognition and picture classification. Numerous studies in pathology, radiology, and dermatology have demonstrated positive results in difficult medical diagnostic tasks. By offering second opinions and identifying trouble spots in images, computer vision in healthcare may be able to assist medical professionals.
In object classification tasks, where a neural network learns to classify the object in an image, Convolutional Neural Networks have surpassed humans. Convolutional neural networks have demonstrated impressive results in transfer learning. In transfer learning, a CNN is trained on a sizable dataset (such as ImageNet) unrelated to the task at hand, and then it applies the learned information to a new task.
The fundamentals of computer vision
Computer vision in healthcare, like any other AI and ML-enabled technology, is made possible by several clever behind-the-scenes methods. However, despite being opaque, computer vision algorithms are not magical. To identify a range of objects and situations, they require training data that is high-quality and diverse.
Deep learning and machine learning
The fundamental technologies at the center of any computer vision technology are these two. While deep learning enables computer vision models to interpret visual data in a human-like fashion, machine learning methods allow robots to become more proficient with time and reliably recognize unknown images.
Recognition of images
Computer vision technology serves as a fundamental task that is frequently integrated with picture categorization and object identification. They enable machines to identify objects, properties, and other variables in images or movies.
Object recognition
This particular branch of computer vision finds, recognizes, and delineates things in an image by tracing a bounding box around each object. For medical imaging applications of computer vision in healthcare such as image-guided therapy and surgical planning, object detection is the method of choice.
Division
Segmentation is the process of dividing a picture into several segments or pixels to make it easier to represent and analyze later. This method is essential for jobs involving tracking, object recognition, and medical picture analysis.
Identification of patterns
To find recurring or consistent patterns in visual information, pattern recognition is used. By giving computers recognition intelligence similar to that of humans, this computer vision in AI method provides crucial capabilities for activities related to healthcare analytics.
Extraction of features
From unprocessed data, feature extraction finds and extracts pertinent characteristics and significant patterns. Additionally, it prepares visual input for tasks like categorization, prediction, and grouping and lowers the complexity of the data.
Edge recognition
Edge detection is a technique used in image processing that locates the borders of objects that are highlighted. This facilitates data extraction and image segmentation, speeds up computer vision operations, and reduces the amount of data needed.
Three-dimensional vision
By permitting the perception of depth and three-dimensional structure from 2D images, 3D vision improves AI computer vision by addressing issues with spatial understanding and lighting fluctuations.
Unlock The Power of Visual Data. Let’s See What Computer Vision Can Do For You?
Computer Vision’s Advantages for Healthcare
The following are a few of the benefits of computer vision in healthcare:
Reliable Image Interpretation
Accuracy and speed are necessary for medical picture analysis. Both sides benefit from computer vision since it can identify patterns that aid in more accurate disease diagnosis. In the medical field, computer vision in healthcare also lessens the potential for human error. Machine learning-based image recognition algorithms are proficient in detecting breast cancer by examining mammograms. Additionally, they make quick analysis possible, which is essential for early disease diagnosis.
Modern Operating Rooms
Using Electronic Health Record (EHR) systems can be laborious, particularly when recording surgery. It involves a lot of human input, which frequently results in mistakes and delays. This issue is solved by computer vision technology, which records and observes the entire process without the need for human involvement. This technology allows medical professionals to reduce labor-intensive physical labor and devote more time to patient care.
Enhanced Recognition of Patients
Healthcare institutions frequently deal with instances of incorrect patient identity. Even while the majority of these cases are typically detected early on, there is still a risk. Patients may die if it is not discovered because they may be given the incorrect medication and treatment. Their health may deteriorate, and other problems may arise.
These mistakes may also result in lawsuits for millions of dollars worth of damages against hospitals, along with the reputational harm that follows. Computer vision in healthcare software development services helps solve all of these issues.
Improved Healthcare Safety
Compared to other private sector industries, hospitals experience a higher number of work-related illnesses and injuries. The majority of injuries frequently result from medical personnel malpractice. They might not adhere to the established procedures for safe work or employ safety equipment.
Accidents may occasionally occur, but they can be avoided with the right application of computer vision in healthcare. When an accident occurs, responsible authorities are notified by computer vision and other AI-based visual systems. Thus, computer vision in healthcare aids in lowering reaction times.
Accelerated Medical Research
Rapid medical research is necessary for improved disease detection and treatment. It typically takes a long time and is still biased, which can produce inaccurate results. Computer vision in medicine is the procedure impartially.
Thus, diseases can be identified by researchers much more quickly. They can then better formulate medication to achieve the desired effects.
Applications of Computer Vision in Healthcare
The fast-developing field of computer vision has the potential to completely transform healthcare. The technique combines optical sensors and cameras with potent artificial intelligence algorithms. Consequently, computer vision in medicine can assist physicians and other healthcare providers in promptly recognizing illnesses, giving precise diagnoses, customizing patient care, keeping track of medicine administration, and even forecasting health consequences. Let’s examine the numerous applications of computer vision in healthcare:
1. Tumor detection powered by AI
Applications of deep learning and computer vision technology have shown to be extremely beneficial in the medical profession, particularly in the precise diagnosis of brain tumors. Early identification is critical to the patient’s survival since untreated brain tumors spread swiftly to other areas of the brain and spinal cord. Medical practitioners can reduce the time and effort involved in the detection process by using computer vision software.
Computer vision methods such as Mask-R Convolutional Neural Networks (Mask R-CNN) have the potential to significantly reduce human error in brain tumor diagnosis in the healthcare industry.
2. Computer Vision for Compliance with Hospital Hygiene
A highly useful technology for guaranteeing hospital hygiene compliance is computer vision. Computer vision can assist in the detection of dirt, dust, and other types of contamination that may be dangerous to patients and staff by enabling automated examination of patient rooms and surfaces. With the use of surface analysis, filth accumulation detection, and disinfection process detection, AI and ML in healthcare can keep an eye on a room’s cleanliness.
Clinical personnel can detect places that require more regular cleaning by using computer vision to enable real-time surveillance of high-touch areas including patient beds, door knobs, and handrails. Furthermore, AI computer vision can offer insightful data on patient usage trends, allowing building administrators to assess personnel movement and pinpoint areas that may require more resources or cleaning. Managers of hygiene can use this to streamline procedures and lower the chance of contamination.
To make sure that all safety procedures are followed, computer vision can also be utilized to keep an eye on what hospital employees and visitors are doing. It can detect when someone enters a room without wearing protective gear or when a medical professional enters a patient’s room without first washing their hands. Computer vision algorithms can assist hospitals in promptly identifying and resolving any possible safety hazards by automating this monitoring process.
3. Computer Vision-Based Cancer Detection
Surprisingly, deep-learning computer vision algorithms have completed diagnostic tasks including distinguishing melanomas from moles with accuracy comparable to that of a clinician. For example, it might be challenging to identify skin cancer early on since its symptoms frequently mimic those of common skin conditions. As a cure, researchers have successfully distinguished between cancerous and non-cancerous skin lesions with the aid of computer vision software.
The many benefits of employing computer vision and deep learning technologies for breast cancer diagnosis have also been recognized by AI research. It can assist in automating the identification process and lowering the possibility of human error because it was trained using a vast collection of pictures that included both healthy and malignant tissue.
Shortly, healthcare computer vision solutions may be utilized to diagnose cancers other than lung and bone cancer because of the rapid advancements in technology.
4. Astute Medical Education
Medical skill training and diagnostics both make extensive use of computer vision. Surgeons today rely on more than just the old-fashioned method. Especially when it comes to learning skills through hands-on experience in the operating room. On the other hand, simulation-based surgical platforms have become a useful tool for surgical skill assessment and training.
Before going into the operating room, trainees can practice their surgical abilities with surgical simulation. Before operating on patients, they can better grasp patient care and safety thanks to the thorough feedback and performance evaluation they receive.
Computer vision in healthcare can also be used to measure activity levels, identify frantic movement, and examine how long patients spend in particular places (called regions of interest) to evaluate the quality of the procedure.
5. Astute Illness and Contamination Avoidance
Global healthcare saw enormous challenges during the Covid-19 outbreak. Computer vision technology can play a big role in helping countries throughout the world tackle the difficulty of fighting the disease.
Computer vision applications can help in COVID-19 diagnosis, control, treatment, and prevention thanks to the rapid improvements in technology. Patients can have the disease easily detected when digital chest X-ray radiography images are used in conjunction with computer vision technologies such as COVID-19. The prototype program, created by Darwin AI in Canada, has demonstrated results in COVID-19 diagnosis accuracy of about 92.4%.
Masked face detection, which is frequently used to enforce and monitor policies preventing the transmission of pandemic diseases, is performed via computer vision.
6. Automated Health Monitoring and Vital Signs
Medical personnel can more accurately assess and measure their patients’ fitness and overall health with the aid of automated health monitoring. By using these analytics, medical professionals—such as surgeons and doctors—can decide when to do surgery or prioritize emergency care more quickly and effectively.
In a different application of computer vision in healthcare, blood loss during surgery was measured using computer vision models to assess if the patient had reached a critical state. As a result, a software program calculates how much blood the patient will require either during or following the operation.
7. AI-based medical diagnostics
Medical diagnostics and imaging have grown in significance in today’s healthcare system. This is because they offer information that aids in the detection and diagnosis of illnesses by medical professionals. Recent developments in computer vision technology have made diagnostics in the medical field quicker and more precise.
Medical photographs can be rapidly examined for disease indicators using computer vision algorithms, allowing for more precise diagnoses to be made in a fraction of the time and money compared to more traditional techniques. By avoiding needless treatments, assisted or automated diagnostics contribute to a decrease in healthcare expenses overall.
Computer vision algorithms that recognize patterns in images have demonstrated remarkable success in identifying diseases; for instance, they have assisted doctors in detecting subtle alterations in tumors that may indicate cancer.
8. Monitoring of Patient Rehabilitation at Home
After a medical condition, many patients would rather recover at home than in a hospital. Medical professionals can visually monitor their patients’ progress and administer the required physical therapy to them with the use of computer vision solutions. Such home training is more cost-effective in addition to being more convenient.
Furthermore, non-intrusive remote patient or senior monitoring can be facilitated by computer vision technologies. Deep learning-based human fall detection systems, which use computer vision to detect falls, are a popular area of research that aims to lower care costs and dependency in the senior population.
The use of computer vision for video-assisted analysis of standardized medical exams, like the Timed Up and Go test (TUG test), is another technique for patient monitoring. The computer vision technology calculates how long it takes to complete a quick evaluation test to gauge functional mobility. The TUG test is a useful tool for determining a person’s walking balance and fall risk.
9. Medication Management with Computer Vision
A cutting-edge technology called computer vision for medicine management seeks to completely transform the dispensing and administration of medications. This device tracks the entire pharmaceutical distribution and administration process by scanning medication labels using cameras, sensors, and computer vision algorithms. To guarantee precision in the dosing and administration of medications, the system also makes communication between doctors, nurses, and pharmacists easier.
Erroneous or missing prescriptions, dose problems, or even forgetting to take a drug are among the medical errors that might be significantly decreased by the computer vision-driven medication management system.
Additionally, making sure that drugs are taken on schedule, can lower the possibility of drug interactions and other negative consequences. In addition, the system may notify doctors and nurses in real-time when dosage adjustments are needed or the wrong medication is supplied.
Patient safety is increased when computer vision in drug discovery and management. Consequently, less work will be placed on medical personnel, and time and money will be saved over time.
10. Individualized Care for Patients
In the medical field, the pursuit of AI models for Personalized Treatments for Patients has been continuous. It comprises applying technology to more fully comprehend and identify specific diseases and ailments. As well as to develop individualized, case-by-case more effective therapies.
AI analysis of medical imaging technologies, such as MRI and CT, aids in the individual diagnosis and assessment of diseases, recommending customized treatments based on each patient’s specific medical requirements.
Computer Vision’s Challenges in Healthcare
There are unique obstacles to computer vision applications in the healthcare industry. An expert artificial intelligence development company can help overcome them.
Caliber and Availability of data:
The high-quality, annotated medical images required for efficient algorithm training are frequently in low supply. Furthermore, the procedure is made more complex by the diversity in image-capturing methods resulting from variations in patient populations, equipment, and approaches.
2. Integration With Other Systems
Another challenging aspect is computer vision integration with current healthcare systems. A major pain to make sure these solutions work well with legacy IT infrastructure is similar to trying to fit a new puzzle piece into an old jigsaw. Workforces used to traditional procedures may resist new technologies because they can upset them. Not to mention that AI applications might be costly and time-consuming to go through this integration procedure.
3. Data Security & Privacy:
Then there are the enduring worries about data security and privacy. Safeguarding confidential patient data and preventing system intrusions and data leaks are critical tasks. Another layer of complication to the equation is the non-negotiable nature of compliance with rules such as HIPAA.
4. Regulatory Compliances
Adherence to regulations is also very important. It can take a while to get the required clearances for medical devices that use computer vision from organizations like the FDA. The issue of liability is a major one: who bears responsibility for accidents? What about moral issues like justice and algorithmic bias? Answers to these questions are required.
5. Resistant to Adopt to New Technologies
It’s common knowledge that the healthcare sector resists change. It might be difficult to get medical practitioners to adopt new technologies. Establishing confidence in AI applications and resolving worries about job displacement is essential.
6. Expert Availability
It takes qualified professionals to apply computer vision in healthcare in an efficient manner. To use computer vision systems efficiently in their daily work, they must learn how to understand the system’s outputs. To fully utilize computer vision in healthcare, ongoing support via training and efficient change management to adjust to new processes are essential.
Accelerate medical diagnostics with AI-assisted imaging
In summary
The fast development of computer vision healthcare companies has benefited and pioneered the healthcare sector. Numerous medical specialties have benefited from computer vision in healthcare, saving thousands of lives through improved diagnosis, early identification of health conditions, and more effective treatment strategies.
Computer vision in healthcare has benefited medical practitioners as well as their patients. Computer vision aids in lowering the number of diagnostic errors made by physicians. Picking up on even the smallest irregularities and variances that doctors would miss during manual exams, can also reduce false negatives. Additionally, surgical medical staff can benefit greatly from computer vision in healthcare. It can aid with pre-operative planning, instrument tracking (by identifying items in the video), and even training of future surgeons.
The various forms of computer vision in medicine provide patients with self-service kiosks, quicker admissions, scenarios for remote health monitoring, and much more. Above all, computer vision in medicine saves lives and reduces the severity, trauma, and cost of treatments.
FAQs






