With the data-driven era, organizations are constantly bombarded by an increasing amount of data. From creation and storage to administration and ultimately destruction, it is an intricate process referred to as the Data Lifecycle. This is where Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) enters the scene.
In this definitive guide, we will discuss all you need to know about what is Data Lifecycle Management? ranging from its phases, deployment strategies, advantages, tools, and so much more. We will also delve into how organizations such as A3Logics can provide aid in effective DLM strategies.
Table of Contents
What is Data Lifecycle Management?

A method for managing data at every stage of its lifecycle, from data entering to data disposal, is called data lifecycle management. Data is divided into phases according to various criteria, and it progresses through these phases when it fulfills requirements or finishes certain activities. Data Lifecycle Management is crucial for organizations as data volumes continue to grow, with 90% of data being unstructured.
An effective DLM process gives a company’s data structure and organization, which supports important process objectives including data availability and security.
These objectives are essential for company performance and become more significant over time. Businesses can plan for the disastrous outcomes in the event that a company experiences data breaches, data loss, or system failure by implementing DLM policies and procedures.
Data protection and disaster recovery are given top priority in a solid DLM strategy, particularly when more dangerous actors enter the market due to the fast growth of data. This lessens some of the terrible impacts on a brand’s financial performance and reputation in the case of a disaster because an efficient data recovery plan is already in place.
Key Objectives of DLM
Now that you know what is data lifecycle management let’s take a look at the major objectives of Data Lifecycle Management are:
- Better Data Accessibility: Making data readily available and usable to authorized users.
- Data Security: Safeguarding data against breaches, loss, or unauthorized use.
- Regulatory Compliance: Complying with industry regulations for data storage, access, and destruction.
- Cost Efficiency: Minimizing storage costs by removing redundant or obsolete data.
- Data Governance: Making sure data is handled effectively and uniformly throughout the organization.
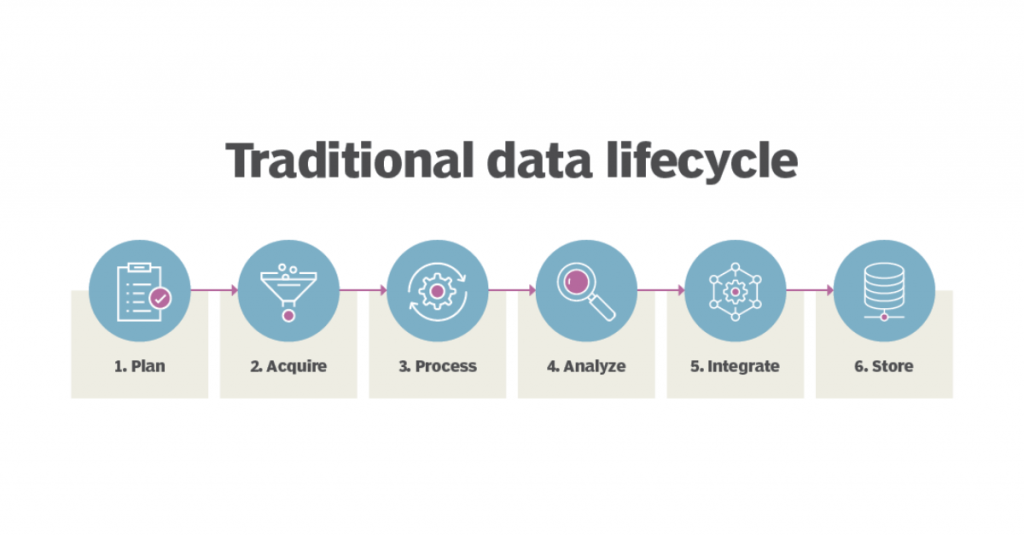
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/
The 8 Steps of Data Lifecycle Management
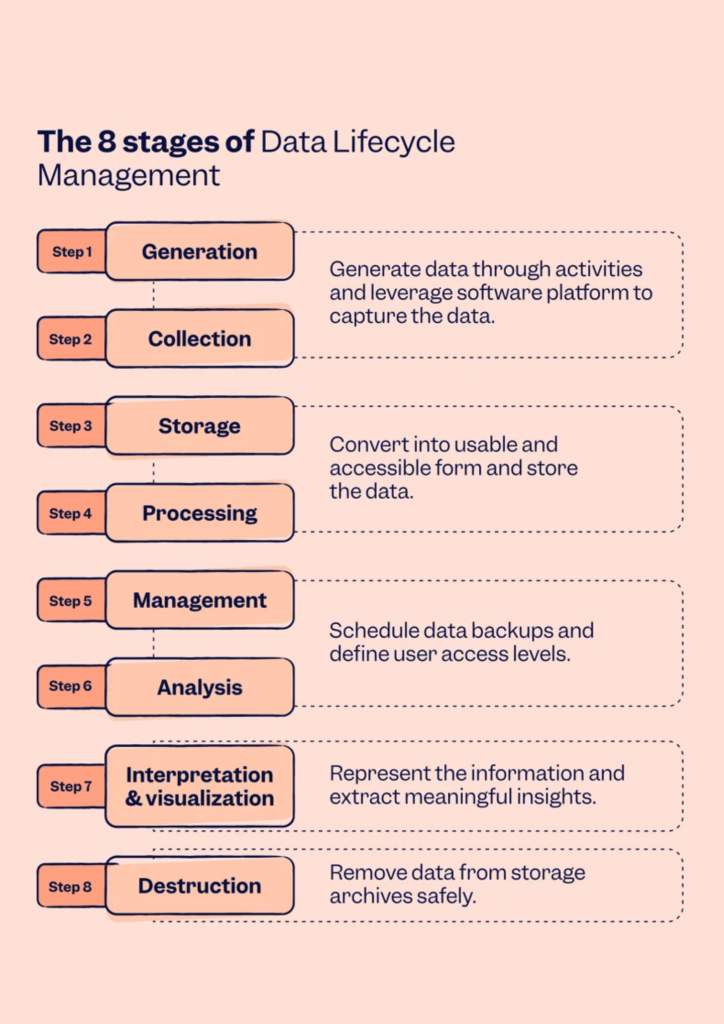
A sound Data Lifecycle Management plan encapsulates eight disparate stages, and each is fundamental to ensuring the data is treated well and safeguarded throughout its existence.
1: Data Generation
Data generation phase is where the lifecycle starts and where data gets created using several sources like transactions, sensor input, applications, social media, or business processes. It’s the phase most frequently disregarded but doing correct planning during this phase can prepare the remainder of the lifecycle. Correct data generation helps the data become structured, consistent, and worthwhile.
2: Data Collection
Data gathering is the process of acquiring data from different sources and systems. In this step, organizations should make sure that they gather data in a manner that allows them to access and analyze it easily later. Data can be gathered in various formats, including structured (databases), semi-structured (JSON, XML), or unstructured (text, videos).
3: Data Storage
Once data is gathered, it should be secured with storage. The data storage phase calls for selecting the right infrastructure for storage to ensure data is securely stored and retrieved with ease whenever needed. Data can be stored in databases, cloud storage, data warehouses, or data lakes, depending on the volume, nature, and use of the data.
4: Data Processing
Data processing is the process of converting raw data into useful information. This may include cleaning, filtering, aggregating, and organizing the data. The processed data is now ready to be analyzed. Depending on the complexity and size of data, processing may be as simple as sorting or as complex as machine learning or data mining.
5: Data Management
At this point, the data is controlled to make it accurate, consistent, and usable. Data management involves activities such as defining ownership of data, ensuring data quality, and using suitable metadata. Data management practices should be in accordance with governance models and security procedures to make data available for future use.
6: Data Analysis
Data analysis is perhaps the most important phase in the data life cycle. Here, data is analyzed to reveal patterns, insights, and trends that inform business decisions. It is possible to apply advanced analytics such as predictive analytics and machine learning models to maximize the value extracted from the data.
7: Data Visualization & Interpretation
Upon analysis, the findings are usually represented via data visualization. Data visualization techniques assist in conveying complex data in a readily interpretable format, including charts, graphs, and dashboards. This phase serves to enable stakeholders to understand the findings and draw data-informed decisions.
8: Data Destruction
The last phase of the data lifecycle is destroying data. This occurs when data is no longer of any value or must be safely destroyed because of regulations. Destroying data ensures that no longer needed or redundant data is effectively erased to prevent security threats and unnecessary storage expenses.

Putting an Effective Data Management Lifecycle Strategy
> Creating Strong Data Governance Policies
A strong data governance policy is essential to making certain that data is being handled correctly through its entire lifecycle. It determines how data is going to be gathered, stored, used, and deleted. Governance policies should also include who owns data at every step and how compliance will be enforced.
> Securing Data and Being in Compliance
Compliance and data security are most critical for every organization. All necessary data protection mechanisms, like encryption, access controls, and periodical audits, must be deployed. Also, one needs to keep an eye on industry-specific regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) and be compliant.
> Regulatory Best Practices and Considerations
Different laws and regulations require compliance from organizations to properly manage the data. There should be the following best practices as part of a DLM strategy:
- Regular audits to evaluate compliance.
- Secure storage and transmission of data.
- Implementation of data retention policies in accordance with regulations.
- Data destruction procedures for sensitive information.
Advantages of Data Lifecycle Management
> Process improvement
An organization’s strategic efforts are mostly driven by data. DLM facilitates process optimization and boosts efficiency by assisting in the maintenance of data quality throughout its lifecycle. Businesses may optimize the value of their data by using a good DLM strategy, which guarantees that the data accessible to users is correct and dependable.
> Cost control
Data is valued throughout its existence in a DLM process. Organizations can utilize a variety of cost-cutting strategies, including data backup, replication, and archiving, after data is no longer needed for production environments. It can be transferred, for instance, to less expensive on-site, cloud, or network-attached storage.
> Data usability
IT teams can create policies and processes that guarantee all metadata is labeled consistently with a DLM approach, enhancing accessibility when necessary. Data value is guaranteed for as long as it must be kept by establishing enforceable governance principles. The agility and efficiency of business processes are increased when clean and valuable data is available.
> Governance and compliance
A strong DLM strategy aids companies in staying in compliance with the rules and regulations pertaining to data retention that are specific to each industry sector. DLM enables businesses to manage data more securely and efficiently while adhering to data protection regulations pertaining to both personal information and corporate documents.
Tools and Technologies for DLM
Technologies and tools can assist businesses in efficiently managing their data, making sure that it is accurate, safe, and easily accessible to facilitate well-informed decision-making. They support innovation and expansion, optimize data usage and storage, and simplify DLM procedures.
1. Data Management Platforms
Data management platforms (DMPs) are an integrated solution for managing, storing, and processing data throughout its life cycle. They enable organizations to automate a lot of the data management aspects, making them more efficient.
2. Data Classification and Organization Tools
Data classification and organization tools assist in ensuring that data is grouped according to its sensitivity and importance. This helps in improved data governance and easier retrieval and usage of data when required.
4. Data Monitoring and Analytics Solutions
It enables organizations to monitor data usage, performance, and integrity during the lifecycle. Data monitoring and analytics solutions guarantee that data is used effectively and as per governance policies.

Common Challenges in DLM and How to Overcome Them
Allocating resources and figuring out how to properly acquire, store, use, and manage data are common DLM difficulties. Organizations can take the following actions to resolve these issues:
> Automating Data Lifecycle Processes
Automation of data management functions is difficult but necessary for efficiency. Organizations can counter this difficulty by investing in automation tools that automate data storage, processing, and destruction.
> Adopting Strong Data Governance Procedures
The biggest challenge to DLM is making sure data governance procedures are adhered to. To counter this, organizations need to provide frequent training and establish ongoing monitoring to guarantee compliance with data governance policies.
> Enhancing Data Security Controls
With more and more cyberattacks, making data security stronger than ever before is essential. Data encryption, security audits, and access control can go a long way in minimizing the risks posed by data breaches.
DLM vs ILM: Explained
Although it is a component of data management, information lifecycle management (ILM) is not the same as data lifecycle management (DLM), despite the fact that the terms are sometimes used interchangeably.
File-level data is managed via data lifecycle management, which classifies files according to their age, size, and kind. In contrast, ILM oversees each and every piece of data in a file, guaranteeing timely refreshes and data accuracy. User data like email addresses and account balances are included in this. Let’s take a deeper look at the difference between the two.
| Aspect | Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) | Information Lifecycle Management (ILM) |
| Scope | Primarily concerned with structured and unstructured data across IT systems. | Manages business-critical information and how it is used throughout its lifecycle. |
| Primary Objective | Ensures data integrity, security, and compliance across its lifecycle. | Focuses on maximizing business value by classifying and storing information based on importance. |
| Data vs. Information | Treats all data equally, focusing on storage, security, and compliance. | Differentiates between valuable business information and general data, prioritizing key insights. |
| Storage Management | Automates storage, ensuring data is placed in the right environment (hot, warm, cold storage). | Classifies data based on business importance, reducing costs by moving less valuable data to long-term storage. |
| Security & Compliance | Strong emphasis on regulatory compliance (GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA) and security measures. | Ensures that critical business information is secured and retained based on business needs. |
| Data Governance | Implements data governance policies for structured and unstructured data. | Aligns with corporate governance to optimize information flow and decision-making. |
| Data Disposal | Focuses on secure data deletion to meet legal and compliance requirements. | Ensures that information is retained or deleted based on business importance, compliance, and legal mandates. |
| Use Case | Ideal for IT-driven data management, security, and compliance across various industries. | Best for enterprise-wide information strategy, including knowledge management and decision-making. |
The Business Success Role of DLM
A crucial component of contemporary corporate operations is data lifecycle management, which helps businesses efficiently handle their data from creation to destruction.
Businesses can unleash the full potential of their data assets and propel innovation, growth, and success in today’s competitive world by putting in place a strong DLM strategy that incorporates data governance principles, data security measures, and regulatory compliance.
Building a strong DLM will be essential to ensure long-term success and sustainability for businesses of all sizes and sectors as the world grows increasingly data-driven. Effective Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is crucial for ensuring data integrity, security, and compliance throughout its entire journey—from collection to disposal. A3logics offers comprehensive end-to-end data analytics services tailored to meet the unique needs of businesses across industries.
1. Data Collection & Ingestion
A3logics simplifies data ingestion and collection by allowing companies to ingest data from various sources—be it enterprise applications, IoT devices, cloud platforms, or third-party APIs.
2. Data Storage & Organization
Appropriate data storage and organization are key to scalability, accessibility, and security. A3logics is an expert in cloud-native data storage solutions that guarantee high-performance optimization, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. Our solutions are:
- Data Warehousing for storing structured data
- Data Lakes for processing enormous unstructured data sets
- Hybrid and Multi-cloud Storage solutions for accessible data access
Through advanced data classification, indexing, and metadata management, businesses can retrieve and process information quickly when required.
3. Data Security & Compliance
In a world with growing cyber attacks and strict regulatory demands, A3logics focuses on data security and compliance by:
- Encryption and Secure Access Controls to ensure unauthorized access is blocked
- Role-based Permissions & Authentication to safeguard data confidentiality
- Regulatory Compliance Frameworks (HIPAA, GDPR, CCPA, SOC 2) for industry-specific regulation
- Regular Security Audits & Risk Assessments to limit vulnerabilities
With the use of AI-driven threat detection and anomaly monitoring, your data is safe throughout its entire lifecycle.
4. Data Analysis & Processing
Raw data is of very high value, but only if processed efficiently. A3logics equips companies with:
- Advanced Analytics & Business Intelligence (BI) for informed decision-making
- Machine Learning (ML) & AI-based Predictive Analytics for better decision-making
- Data Processing Pipelines that preprocess, transform, and format data for real-time and batch analytics
Organizations are able to extract rich insights with our cloud-based big data processing frameworks, fueling efficiency, innovation, and growth.
5. Data Archiving & Retention
Appropriate data retention and archiving policies are required to maximize storage expenses while guaranteeing compliance with regulations. A3logics offers:
- Automated Data Archiving Solutions for the secure storage of historical data
- Compliant Data Retention Policies tailored to compliance needs
- Cold Storage & Backup Mechanisms to guarantee long-term access
With the use of tiered storage strategies, companies are able to weigh performance against cost savings while maintaining vital data in easy access.
6. Data Governance & Disposal
Once data has reached the end of its lifecycle, good governance and disposal are imperative. A3logics guarantees secure and compliant data destruction via:
- Data Anonymization & Masking to secure sensitive data
- Blockchain-backed Audit Trails for transparent tracking of data disposal
Secure Data Wiping & Deletion Protocols to avoid unauthorized recovery.
With a clearly established data governance framework, organizations can ensure accountability, avoid breaches, and satisfy compliance mandates.
Why Choose A3logics for Data Lifecycle Management?
A3logics is a reliable partner in Data Lifecycle Management because of our:
Cloud-native Data Solutions Expertise – Scalable and future-proof data storage, processing, and analytics architectures.
AI & Automation-driven Data Management – Sophisticated tools for automated data classification, anomaly detection, and predictive analytics.
Strategic Focus on Security & Compliance – Compliant with international data privacy laws and cybersecurity best practices.
Complete End-to-End DLM Solutions – Strategically customized solutions that suit your business goals and industry-specific needs.

Conclusion – Data Lifecycle Management
In a data-driven world, successful Data Lifecycle Management (DLM) is paramount to maximize operational effectiveness, maintain security, and uphold compliance. Organizations that adopt best practices, utilize the appropriate tools, and partner with seasoned DLM experts such as A3logics can extract the utmost value from their data while avoiding risks. Choose our data analytics consulting services for the smooth data lifecycle management solution.


![10 Top Internet of Things (IoT) Consulting Companies in the USA [2025]](https://www.a3logics.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/10-Top-IoT-consulting-companies-in-USA-2024.webp)



