Table of Contents
EDI Security has long been filled in as a fundamental piece of business tasks, considering the quick and effective exchange of significant business reports. Businesses now recognize this progressive innovation more than ever as a necessity for digital transformation. Its impact on processes involving electronic data is indescribable. Leveraging latest technologies for EDI like AI and ML integration also strengthens the security of transactions. As an idea, EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is certainly not a new one. It tends to be followed as far as possible back to the Berlin Airlift in 1948. Set forth plainly, EDI frameworks automate and work on the most common way of trading key business reports -, for example, solicitations, buy requests, and delivery views – chiefly with partners, EDI services, and customers.
Introduction to EDI
The most reliable EDI definition is the computer-to-computer trade of business records in a standard EDI report design between business partners. By moving from a paper-based trade of business records to EDI reports, businesses have significant advantages of EDI, like
- decreased cost,
- sped up,
- diminished mistakes, and
- further developed relationships with business partners.
EDI exchanges are handled a lot quicker and with less human intercession. What’s more, all EDI software and services can coordinate into back-end frameworks, for example, integration with ERP and accounting platforms to empower the start-to-finish handling of key business archives.
Why Secure EDI Matters?
Since its broad reception in business during the 1980s, EDI has turned into a centerpiece of the IT infrastructure for businesses across an extensive variety of industry sectors. It keeps on developing today. The latest evaluations suggest that the EDI market in the healthcare business alone will reach a value of $9.18 billion by 2030, with an annual growth rate of 9.6%.
Moreover, EDI services go past the trading of organized data to permit associations to profit from EDI exchanges across their inventory network. EDI-managed services likewise consider secure document sharing – including Oversaw Record Move – that can help offices like designing to trade huge computer-aided design or Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) records.
Our Cutting Edge Technologies Will Keep Your Data Secure
Risks associated with EDI
EDI has many risks and difficulties that make it rather a headache for companies depending on it. Thus, we chose to list the most widely recognized difficulties companies can experience while starting with EDI. Likewise, this article talks about how to manage those difficulties and issues.
Consequently, this will be a heads-up for the people who are going to plunge their toes into EDI and a suggestion for the people who are as of now in the snare of EDI and need to build the effectiveness of its b2b mix with compelling reason need to roll out critical improvements to the current IT arrangement.
1. You have a complex B2B organization
As businesses have globalized, many found themselves in a situation where their partner companies and ecosystems have become more complex, involving collaboration with more partners than ever before. Among those are, producers, cargo forwarders, and some more, it is likely endless to make a list.
This implies that everyone of ought to have the option to associate with every single vital partner and send them data electronically, ideally progressively, to remain effective and productive.
2. The volumes are EDI are developing
More exchange and more partners will lead to a developing volume of data that you create and data that you want to impart to your environment.
You should consider how to associate with explicit frameworks, how to work on the nature of the data, how to impart data to your partners, and whether you have the assets to deal with all EDI-related projects in-house.
3. There are mistakes and missing fields in EDI
Staying away from EDI challenges and missing fields in the EDI is difficult, particularly when you begin to manage greater volumes.
A few more established configurations of EDI (EDIFACT) weren’t designed for people to view and understand, making the process of identifying and fixing errors challenging. In any event, when it’s possible to view the data, manually identifying mistakes in tedious and costly. Also , it bring errors. Automating mistake identification can fundamentally expand productivity and increment gross edges.
4. The expense of EDI is soaring
Possessing software and equipment for EDI requires significant monetary assets. Additionally, it is important to understand the importance of in-house EDI services. Thus it is essential to align the team to get a clear understanding of EDI to carry it in-house.
To lessen the expenses, you might need to identify the top EDI solution providers for taking care of your EDI transactions. For instance, outsourcing EDI to a vendor that can run the businesses in the cloud will fundamentally bring down your expenses.
5. EDI exchanges should occur continuously with more transparency
The speed of getting data is basic for transparency. It can impact your productivity, effectiveness of cycles, expenses, and customer fulfillment.
6. Your partner can’t comprehend the format you are utilizing
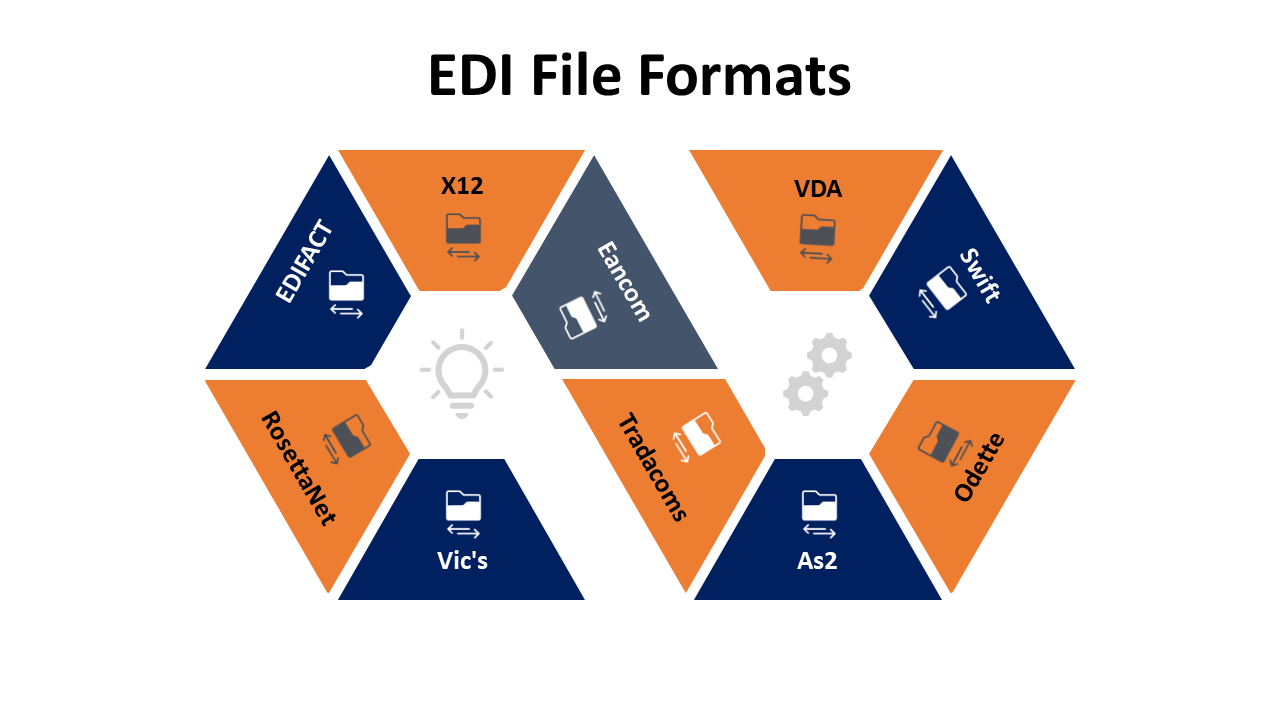
Many organizations use various standards, such as EDIFACT, ANSI, X12, TRADACOMS, XML, JSON, Pixie, CSV, ODETTE, VDA, VICS, HIPAA, EANCOM, ebXML, UBL, and RosettaNet, as well as in-house configurations and public guidelines, to name a few. There is a high possibility that some of your partners may use a EDI format which is not compatible to your system.
7. Security Concerns
EDI is deep-rooted and utilized across numerous associations and enterprises. In any case, there are still worries regarding data sharing to partners.
Such worries are the absence of trust, the risk of the data being taken advantage of because of security breaks, as well as the, are potential legitimate issues too because of authoritative or administrative guidelines.
Best Practices for Ensuring EDI Security
Electronic data interchange (EDI) is a normalized approach to trading business records and exchanges between various groups, like providers, customers, banks, and regulators. Electronic data interchange consultant can further develop proficiency, exactness, and speed of business processes. It likewise presents security chances, for example, data breaks, altering extortion, and unapproved access.
How would you guarantee EDI security across businesses and markets? Here are a few prescribed procedures and tips to follow.
Utilize secure protocols and encryption
One of the main parts of EDI security is to utilize secure protocols and encryption techniques to safeguard the data on the way and very still. Secure protocols, like HTTPS, FTPS, SFTP, AS2, and AS4, guarantee that the data is communicated over a protected association that checks the character of the shipper and the collector, and forestalls snooping, interference, or change.
Encryption techniques, like AES, RSA, and PGP, guarantee that the data is encoded such that main approved gatherings can unravel it, and forestall unapproved access or revelation.
Implement strong authentication and authorization
One crucial part of ensuring EDI security is to govern the access and utilization of the EDI framework and data. Validation checks the character of the client or framework that solicitations access, while approval decides the degree of access and consent allowed. Solid confirmation and approval can be accomplished by utilizing techniques like passwords, tokens, declarations, biometrics, or multifaceted validation. Also, it is critical to uphold approaches and rules for secret word management, client jobs, access privileges, and review logs.
Conform to norms and guidelines
EDI security likewise relies upon conforming to significant guidelines which apply to the business and market of EDI members. Principles and guidelines give rules and prerequisites to data security, protection, quality, and honesty, and guarantee that the EDI framework and data measure up to the assumptions and requirements of the partners. A few instances of guidelines are EDIFACT, X12, ISO, HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, and NIST.
Monitor and test the EDI framework and data
EDI requires steady monitoring and testing of the framework and data to distinguish and forestall any likely dangers, weaknesses, or inconsistencies. Monitoring and testing can help distinguish and determine any issues or mistakes in the EDI framework or data, like framework disappointments, data defilement, data misfortune, or data breaks.
Monitoring and testing can likewise help assess and work on the presentation, dependability, and productivity of the EDI framework and data. A few instances of monitoring and testing tools and techniques are dashboards, cautions, reports, reinforcements, firewalls, antivirus, encryption tests, and infiltration tests.
EDI security is a fundamental part of any EDI execution and activity. By following these accepted procedures and tips, you can guarantee that your EDI framework and data are secure, agreeable, and dependable across businesses and markets.
You Can Trust Us To Ensure the Security of Your EDI Transactions
How to choose the right encryption solution for EDI
Electronic data interchange (EDI) is a technique for trading business reports and exchanges electronically between various gatherings, like providers, customers, and banks. EDI can further develop effectiveness, precision, and speed of business processes, yet it additionally represents some security chances. If the data is blocked, altered, or lost, it can cause significant monetary and reputational harm.
Accordingly, the use of encryption must safeguard the classification, uprightness, and accessibility of EDI data. Encryption is the most common way of changing data into an indiscernible configuration utilizing a mystery key so that main approved gatherings can unscramble it with the equivalent or a related key. In any case, how would you choose the most secure EDI encryption for your business? Here are a few factors to consider.
1. Encryption norms
Different encryption norms and calculations can be utilized for EDI encryption, for example, symmetric, lopsided, or crossover encryption. Symmetric encryption involves a similar key for encryption and unscrambling, which is quicker and easier, yet requires a solid approach to trading and storing the key.
Deviated encryption utilizes a couple of keys, one public and one private, which are numerically related, yet entirely not indistinguishable. The public key can be shared openly, while the confidential key is kept in mystery. upside-down encryption is safer and adaptable, yet in addition more perplexing and slower.
Hybrid encryption joins the two techniques, utilizing deviated encryption to trade a symmetric key, and afterward utilizing symmetric encryption to scramble the data. Mixture encryption is the most widely recognized and suggested choice for EDI encryption, as it offers the best harmony between security and execution.
2. Encryption strength
The strength of encryption relies upon the length and intricacy of the key, as well as the calculation utilized. The more extended and more intricate the key, the harder it is to break it.
Notwithstanding, longer keys additionally require serious figuring power and time to scramble and decode the data.
For instance,
- AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) is generally utilized and confided in symmetric encryption calculation
- RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) is a well-known and dependable upside-down encryption calculation.
The suggested least key length for EDI encryption is 128 pieces for symmetric encryption and 2048 pieces for asymmetric encryption.
3. Encryption protocols
Encryption protocols are the principles and strategies that oversee how encryption is applied and overseen in a communication framework. For EDI encryption, various protocols can be utilized relying upon the sort and organization of the EDI data, the vehicle system, and the security prerequisites.
For instance,
- AS2 (Materialness Explanation 2) is a protocol that supports secure and solid EDI over the web, utilizing HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and Digitized marks.
- SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) is a protocol that empowers secure and encoded record move over SSH (Secure Shell).
- FTPS (File Transfer Protocol) is a protocol that adds security layers to FTP (Record Move Protocol) utilizing SSL (Secure Attachments Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer Security).
Every protocol enjoys its benefits and hindrances, and you ought to pick the one that best suits your EDI needs and capacities.
4. Encryption compliance
One more factor to consider while choosing EDI encryption is the EDI compliance with the pertinent regulations, guidelines, and norms that apply to your industry, district, or customers. For instance, for healthcare data you might have to agree with HIPAA , GDPR , or different data assurance regulations that command specific degrees of encryption and security. Also, assuming that you work with monetary or installment data, you might have to conform to PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard.), which determines encryption prerequisites for cardholder data.
It would be ideal for you to likewise check assuming your EDI partner has particular encryption inclinations or assumptions that you want to follow.
5. Encryption testing
Finally, before you execute any EDI encryption arrangement, you ought to test it completely to guarantee that it fills in as expected. You ought to test the
- encryption and decoding processes,
- the critical management and
- appropriation strategies,
- the similarity and interoperability with your EDI partner and frameworks,
- the exhibition and adaptability of the encryption arrangement,
- the versatility and recuperation of the encryption arrangement in the event of blunders or disturbances.
You ought to likewise monitor and review your EDI encryption routinely to distinguish and determine any issues or episodes.
Secure Your Business Data Against Cyber Threats and Attacks With Our Trusted EDI Solutions
Conclusion
Overall, mastering the complexities of EDI security and encryption is central to shielding the uprightness, privacy, and accessibility of basic business data. The comprehensive guide features the how Electronic Data Interchange frameworks could be strengthened. It underlines the significance of encryption, secure transmission protocols, access controls, and normal reviews.
By embracing powerful measures associations can invigorate their protections against advancing digital dangers. The measures includes:
- firewall assurance,
- secure document move protocols,
- occurrence reaction plan,
Joint efforts with exchanging partners, worker preparation, and adherence to design management add to making a far-reaching security structure. Furthermore, to keep a strong EDI climate it highlights the importance of data veiling, secure document maintenance, and routine security evaluations.
As innovation develops, so do the difficulties of getting electronic data interchange. Hiring EDI experts should remain cautious, consistently refreshing frameworks, and adjusting practices to remain one stride in front of likely dangers. With the experiences given in this guide, businesses can explore the complicated scene of EDI security. As a result, it help in cultivating trust, consistency, and dependability in their digitized co-operations.