Table of Contents
Since company operations are continually changing, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has emerged as a critical technology that facilitates data communication between trading partners. EDI is being used by organizations more and more to speed transactions; therefore, to ensure that integration projects succeed, it is essential to understand the essential elements of EDI testing and validation.
Recent industry reviews that highlight the growing utilization of EDI systems predict that the worldwide EDI software market will grow from $1.98 billion in 2022 to $4.52 billion in 2030. The importance of EDI in enhancing real-time communication in the supply chain, reducing errors, and boosting operational effectiveness is demonstrated by this.
However, there are several challenges associated with using EDI integration effectively. Serious problems might arise during electronic transactions from data errors, compliance faults, and communication breakdowns. This emphasizes the requirement for a comprehensive testing and validation plan to lower risks and ensure a smooth and error-free EDI integration process.
EDI testing is critical for identifying issues and addressing them before they compromise critical business processes. By implementing comprehensive testing procedures to ensure data conforms with EDI standards, the likelihood of mistakes is reduced and the dependability of electronic transactions is enhanced. For businesses trying to boost automation and efficiency, an efficient EDI testing strategy is crucial.
The ins and outs of EDI testing and validation will be covered in this blog, along with tips on common issues, recommended procedures, and methods to ensure seamless EDI system integration.
From understanding the importance of compliance testing to researching data validation techniques, our thorough help will guarantee the success of your EDI integration endeavors. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced EDI specialist, this comprehensive text will give you the tools and knowledge you need to optimize your EDI processes and reap the full rewards of seamless data interchange.
Maximise Efficiency and Minimize Errors With Our EDI Solutions
Understanding EDI and Its Significance in Business
EDI is the virtual trade of business data or records between exchanging partners through an electronic format mainly including EDI 834 and other file formats offering diverse functions. The cycle involves moving solicitations, installments, buy orders, transporting visits, and other required archives electronically, subsequently eradicating any documentation.
EDI looks to upgrade virtual trades and work on functional effectiveness with your exchange partners. With EDI, any business can successfully speak with another organization globally without having nothing to do and assessing future activities.
EDI considers better and more proficient cooperation with your providers. It likewise pushes costs out of the supply chain by eliminating inefficiency and manual inclusion. Regardless of who you are exchanging with, an enormous or modest number of SME providers found locally or universally, EDI can help with any business and specialized necessities while offering help and assets to make due.
Whether your business requires an EDI Section to trade figures, solicitations, orders, or other related business archives , with EDI provider options 100 percent reconciliation can be accomplished without a lot of pressure.
According to Jeff Douglas, solutions manager at Babelway, smaller-sized businesses may continue to engage in the aforementioned outsourcing of EDI processing: “I think what we’re seeing now is a burst of new iPaaS [Integration Platform as a Service] vendors that are saying that this technology can be put back into the hands of the companies.
They’re saying that it’s not complicated and you can empower your business by doing this yourself without a third party. And you kind of beat some of the extra cost and frustrations … Seeing that trend of SaaS in the EDI world gives companies more power and more control which I think is good for their business.”
10 Advantages of EDI
Implementing EDI to your business structure can increase the value of your organization’s interaction with programmed data handling, lessen executive responsibilities, and eliminate data passage errors. The advantages of EDI for the start-to-finish exchanges all through the business cycle bring about better utilization of time and assets.
1. Better Speed:
EDI diminishes the time it takes for a representative to make solicitations and handle purchase orders physically. Timing is significant in the handling of a request. With EDI, organizations can accelerate their cycles by 61%, making a stipend for a more mechanization process that fundamentally lessens, on the off chance that not wipe out, time postpones connected with manual cycles that expect you to think about, enter, and record data.
Records management is redesigned and made more successful with synchronous data refreshes. Moving archives electronically further develops exchange speed and detectable quality while decreasing the expense associated with a manual approach. Stock levels are additionally kept routinely refreshed and noticeable.
2. Business Proficiency
For the explanation that human mistake is decreased, organizations can benefit from further developed degrees of capability. Instead of zeroing in on regular and tedious exercises, staff can dedicate their thoughtfulness regarding more worth adding assignments.
EDI move ensures immediate handling and eliminates waste of time connected with manual entering, getting, and sending orders.
3. Aggregate Efficiency
The innovations in EDI allows more organizations to take on additional tasks with less human resource. Business groups can deal with projects with cutting-edge extra worth. With EDI solution providers, the entire cycle is finished in practically no time.
4. Cost Reserve funds and Improving Monetary Proportions
This is among the most well-known advantages of EDI. With EDI, the expenses for handling business reports get no less than a 35% cut, however, it very well may be substantially more exceptional on account of electronic solicitations, with 90% reserve funds a chance. Of course, this super monetary saving is because of computerization and, likewise, the less connection of paper use.
EDI diminishes your working expenses by eliminating the expenses of record recovery, documenting, mailing, paper, postage, printing, reusing, propagation, and capacity. EDI fundamentally lessens regulatory, support, and asset costs.
With EDI implementation, moving and getting e-solicitations happens immediately. EDI additionally adds programmed confirmation and checking methodology, which empower quick agreement at the endpoint, supporting assessing cash necessities. In appreciation of this prescience, clients can exploit fast installment refunds, and the vendor’s liquidity is upgraded.
5. Economical
The development from paper-based management to electronic exchanges accessible on EDI diminishes CO2 emissions. Consequently, the utilization of EDI empowers corporate social responsibility and assists the association with accomplishing economical supply chain management.
6. Data Accessibility on Cycle Status
Replacing paper with e-reports makes it simple to keep up with and track data. EDI protects discernibility and exchange integrability like changes to buy orders, solicitations, forthcoming installment status, receipt affirmation, and other comparable occasions. Also, sending data through confidential organizations makes ait ccessible enduring command over message status about handling, perusing, receipt, and so forth.
7. Further developed Precision
Aside from insufficiency, the manual approach is additionally profoundly vulnerable to mistakes, typically coming about because of entering and once again targeting errors, incredible writing, and poor report management. EDI significantly further develops your business data quality and eliminates the issue of reworking requests by bringing a 30% to 40% drop in exchange errors. The utilization of morals recognized by the two players (collector and shipper) ensures the right translation of data, regardless of action areas or identities.
8. Task Automation
The advantages of EDI devices significantly ease up the management trouble. A few projects, such as encompassing, franking, enlisting, and printing out business records, would blur totally. EDI’s flexibility modernizes the communication stream and improves ordinary business relations with other exchange partners.
9. Refining Services to Partners and End Clients
Execution of EDI implies the application of ideal work processes and reaction time. Carrying out EDI in particular, as assembling plans and distributions become considerably more exact. EDI likewise expands its client base and oversees exchange partner connections because of its speedier labor and product distribution.
10. Security
EDI helps the degree of insurance for any exchanges by unequivocally distributing data across a greater variety of imparting conventions and safety standards, thus, lessening supply chain errors. Your exchanging partner would benefit from the consistent development of data and openness to innovation makes possibilities for renewed business gaps.
Ensure An error Free Supply Chain With Our EDI Testing Services
What is EDI Testing and How Is It Done?
In basic words, EDI testing is a course of checking the EDI records stream from start to finish among organizations and inside frameworks to guarantee smooth data trade before the genuine EDI execution. It’s quite possibly the main move toward the general EDI execution process.
It’s a general practice certified, followed, and ordered by most exchange partners to check that suppliers have the fundamental software and equipment to send, get, and interpret standardized business reports and ensure there are no glitches during production. EDI testing, from the exchanging partner’s side, is put either in-house or is outsourced to an EDI supplier or an outsider tech organization. Normally, the same is the situation with their suppliers as well.
Top 5 things to remember during EDI testing:
- Testing should be done from start to finish which implies through your EDI portal and to and from your back-end ERP. It is critical to guarantee there are no glitches with your inner back-end ERP when you are in production or live with your exchanging partner
- For, assuming you are trying an EDI 850 (purchase request) and you have a bookkeeping software where you store every one of your POs/deals orders, you need to ensure that it gets through your EDI portal as well as goes straightforwardly into your bookkeeping software.
- Essentially, on the off chance that you are trying an EDI 810 (invoice), the invoice needs to go from your bookkeeping software to your exchange partner through your EDI portal.
- You will require everybody remotely to close down once a record is handled from start to finish
- Understand that there are many complex components in the general cycle and here you find any defects in the data stream and have the amazing chance to fix them without getting chargebacks or fines.
- EDI project groups (both inward and outer) and account groups need to ensure they impart appropriately so no data is lost concerning the exchanging partner necessities. Monitoring after testing is finished is important to ensure little astonishments can stay away from immediate response and amendment of any issues whenever found.
Step-by-Step Process on How to Create an EDI Project or Test Plan
Select the sort of EDI service you need to go with
Select the EDI software for your business thinking about your ongoing foundation, assets, and long-term needs. To figure out how to choose the right EDI service provider for your business, A3Logics has got you covered.
Get the EDI exchanging partner contact
By and large, if you are exchanging with any enormous box organizations, you will be given a rolling aide or unit which will have every one of the contacts (telephone, email, and so forth) to their EDI/Backing group who will assist you with testing the EDI records. If not, you can acquire the contact data from the purchaser group you are managing.
Assemble EDI execution rules for EDI Archives to be traded
In a similar way, you ought to have a web connection that will give you access to the EDI records/codes and their details.
Assemble EDI availability data for the delivery of EDI reports
The specialized technique used by your exchanging partner ought to likewise be referenced in the pack. If not, kindly reach out to their EDI connection.
Frame EDI record stream
Significantly, you resolve how your archives will move from your ERP, WMS, TMS, or bookkeeping software (if you have one) to your EDI portal and to your exchange partner as well as the other way around.
Test all Interior record streams
Before you contact your exchange partner to set up a date for testing, test the progression of records from your ERP to your EDI portal. For example, you could need to send out a deals request in the CSV design from your bookkeeping software, convert it into an EDI configuration and afterwards consider sending it to your exchange partner through the portal.
Likewise, there could be numerous back-end frameworks you may be utilizing that need to cooperate with your EDI portal. This is one of the main phases of testing that most organizations miss and are hit with shocks in production that can demonstrate to break your execution.
Set up, plan a testing date, and test the network
When you have the above fundamental requirements sorted out, you can reach out to the exchange partner’s EDI and set up a testing date. From that point onward, the initial step will be to test the association.
EDI document processing with internal user testing and trading Partner document approval
The subsequent step will be to test individual EDI records individually between your business and the exchanging partner all the while. The aide will let you know what amount of time the testing system will normally require and what is generally expected of you as a supplier.
EDI mistake monitoring
Check the finished services after testing and ensure every one of the issues (if present) is tended to and amended. Nonstop monitoring is expected for a couple of days after testing to ensure you are prepared for production/go-live.
Types of EDI Testing
EDI testing includes different sorts to guarantee powerful integration. Sentence structure Testing approves the format, while Useful Testing surveys exchange usefulness. Interoperability Testing looks at similarity with partner systems, and Performance Testing assesses system effectiveness under load. Compliance testing guarantees adherence to industry standards. These sorts by and large assure a consistent and solid Electronic Data Interchange process.
The following are probably the most well-known sorts of EDI Testing utilized by an organization-
1. Unit testing
Unit testing checks individual software parts or modules that handle EDI exchanges and transformations. It guarantees every unit works appropriately all alone before integration.
2. Integration testing
Integration testing joins individual units and checks how they cooperate. It approves interfaces, mappings, approvals, and transformations between various systems and applications engaged with EDI processes.
3. Regression testing
Regression testing re-runs past tests to affirm existing usefulness isn’t upset by any changes, for example, software refreshes. It keeps up with reverse similarity and guarantees old bugs are not once again introduced.
4. System or end-to-end testing
System or end-to-end testing assesses the general EDI services across the supply chain. It affirms EDI messages can stream consistently between all exchanging partners and applications from sending to getting and handling. It distinguishes any bottlenecks or integration issues.
5. Mock testing
Mock testing utilizes reenacted conditions to prior the EDI format before the live organization. It reproduces situations under controlled conditions to work out specialized issues and limit risks. Mock testing checks that all parts will work together as intended in genuine utilization.
6. Load testing
Load testing decides how the EDI system handles expanded load volumes, assessing performance, reaction times, throughput, accessibility, and adaptability. It decides on framework necessities to support high volumes and maintains a strategic distance from breaks during occupied periods.
7. Stress testing
Stress testing deliberately initiates system overloads, tensions, and disappointments to recognize weaknesses or flimsy parts. It pushes the EDI solutions past normal cutoff points to decide limits and guarantee vigor. Any issues distinguished can then be tended to before wide-scale services.
8. EDI pilot testing
EDI pilot testing includes restricted live sending with select exchanging partners. It empowers true testing under close monitoring before wide EDI implementation services. Pilots practice the services, work out any excess issues, and construct trust in the EDI system before full-scale rollout.
9. Parallel testing
During change, parallel testing runs the current legacy system(s) together with the new EDI services. It empowers the correlation of results to guarantee precision and limit disturbance. Parallel testing goes on until the inheritance system(s) can be redesigned, and the EDI solutions work independently.
10. Post-implementation monitoring
Post-implementation monitoring notices the EDI services in live production to distinguish and correct any issues not recognized during testing. It gives oversight and empowers quick issue goals by continually exploring basic measurements, logs, reports, and criticism.
Thorough EDI testing from units to systems to pilots guarantees top-caliber, secure, consistent, and ideal EDI software solutions. An organized testing approach constructs trust in EDI and makes it ready for consistent electronic data interchange across the supply chain.
Step-by-Step Guide to EDI Testing and Validation Process
Executing fruitful EDI testing and approval includes following an organized series of steps. When done correctly, these lead to top-notch EDI services, upgraded supply chains, key advantages, and limited risks.
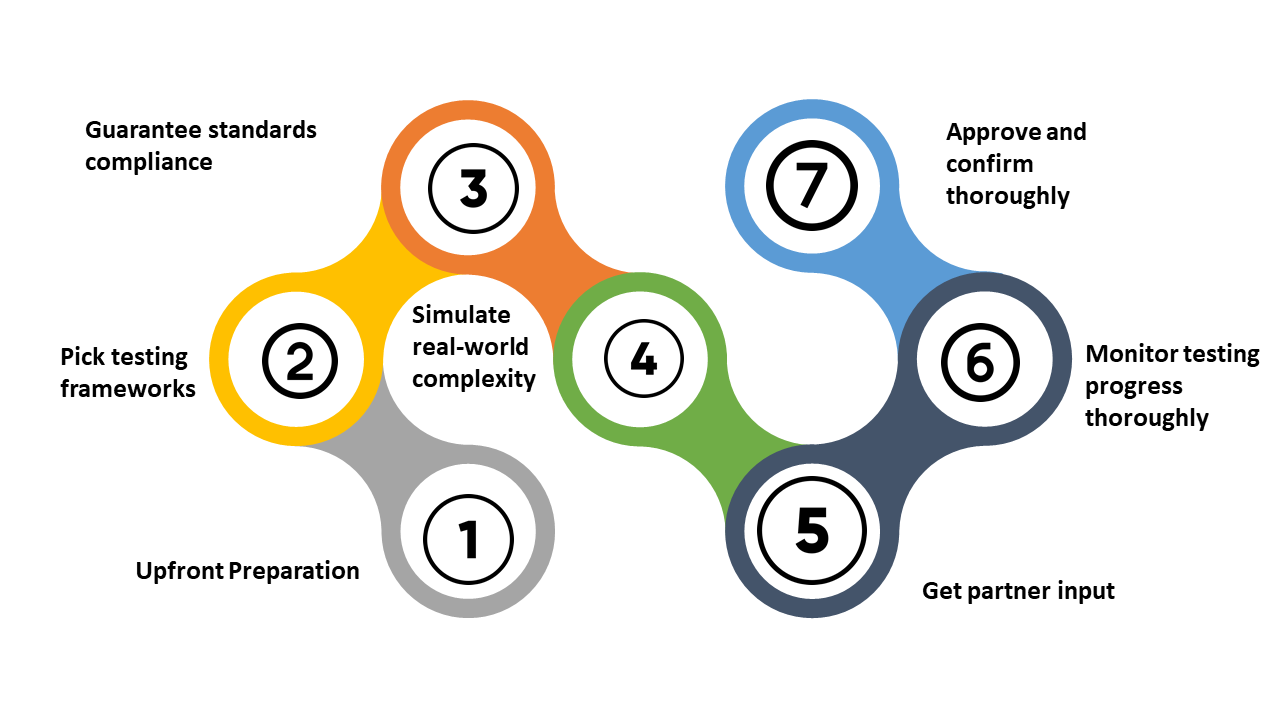
Stage 1- Upfront preparation
Right off the bat in the task, decide the testing extension, approach (dexterous versus cascade), standards, frameworks, assets, and spending plan. Guarantee satisfactory financing and time are assigned before development starts. Lacking upfront arranging brings about hurrying testing or exorbitant cuts later on.
Stage 2- Pick testing frameworks
Select integration testing, end-to-end testing, unit testing, or a blend based on EDI services and undertaking needs. The picked frameworks guide testing strategies, inclusion, reporting, and monitoring. They should give exhaustive inclusion across all pieces of the EDI services, from units to end-to-end.
Stage 3- Guarantee standards compliance
Approve that all standards (ANSI X12, XML, EDIFACT, and so on), outlines, language structure, semantics, code sets, and protocols are correctly stuck to for consistent interoperability with exchanging partners and their systems. EDI compliance testing constructs trust in exact data sharing and interchange. Rebellious services Face integration issues, dismissed exchanges, debates, and legitimate indictments.
Stage 4- Simulate real-world complexity
Testing ought to go past straightforward, routine models and edge cases to uncover issues in stressful, outstanding circumstances and high-volume situations tracked down in production conditions. Genuine intricacy frequently presents issues missed with fundamental checks alone. Chances arise while scaling from a basic test suite to a completely conveyed service.
Stage 5- Get partner input
During testing at each stage, including entrepreneurs, clients, well-informed authorities, and exchanging partners intently. Their input figures out what’s required as opposed to fixing some unacceptable issues. Close inclusion likewise keeps away from protests and opposition by tending to huge worries before the services are launched. Without partner input, tending to their priorities becomes conceivable through exorbitant changes and rework post-services.
Stage 6- Monitor testing progress thoroughly
Use reports, reviews, measurements, logs, agendas, and quality checks to direct testing and guarantee satisfactory inclusion and quality. Monitor to improve the testing timetable and degree against imperatives while augmenting thoroughness. Lacking monitoring might complete the process of testing rashly, miss significant regions, or take too lengthy, deferring the project unnecessarily.
Stage 7- Approve and confirm thoroughly
Dissect results to approve testing that meets necessities and confirms business needs. Additionally, confirm specialized details are met enough. Issues found ought to be fixed and once again tried before proceeding to the following testing level.
Conclusion
The meticulous course of EDI testing and validation is principal to ensuring the progress of EDI integration. Utilizing a mix of syntax validation, data mapping, functional, interoperability, and security testing, among others, forms a strong technique.
Organizations can embrace EDI integration by sticking to industry standards, guaranteeing consistent data trade, and resolving likely issues through extensive testing. The obligation to non-stop improvement, incorporating client acknowledgment testing and regression testing, guarantees that EDI systems stay strong while advancing business prerequisites. Eventually, a very much tried and approved EDI integration is the way to open the maximum capacity of electronic data interchange, cultivating effectiveness, exactness, and unwavering quality in deals.
Get Expert EDI Testing and Validation for Error Free Processes With A3Logics
A3Logics remains the zenith in EDI greatness, giving unparalleled skill in EDI testing and validation. Partner with us to guarantee sans-error processes, consistent data trade, and compliance with industry standards. Hire EDI experts from our dedicated group to utilize progressed testing approaches, including syntax validation, data mapping, and security testing, ensuring the outcome of your EDI integration.
Drive Effectiveness and Efficiency in Your Deals By Partnering With EDI Experts