Table of Contents
Electronic Data Interchange is changing the way businesses exchange information. It allows firms and organizations to transmit and receive documents. These documents include invoices, purchase orders, payment updates, and others electronically, rather than on paper. This helps in reducing errors, decreasing costs, and smoothening supply chain operations.
While the core concept of electronic document exchange remains unchanged, EDI systems must evolve with technology to stay relevant. The underlying technologies supporting EDI have significantly advanced in recent years. Modern technologies applied in EDI networks will bring considerable performance, capacity, and benefit improvements. The market for Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) software was estimated to be worth USD 1.78 billion in 2022 and is expected to expand at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.5% from USD 1.98 billion in 2023 to USD 4.52 billion by 2030. This blog explains how the full potential of EDI can be leveraged by businesses through integration with the power of technologies such as cloud computing, application programming interfaces, blockchain, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, and data analytics to gain strategic advantages.
What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
Electronic Data Interchange means the electronic exchange of business documents. Including invoices, purchase orders, and payment advice between organizations. It provides an electronic way for sending and receiving standard information between businesses rather than using paper documents.
EDI involves the direct transfer of data from one computer system to another computer system in an established data format. This minimizes the need for re-keying information, reducing errors. EDI transactions follow predefined data formats that could otherwise be referred to as EDI formats or even EDI schemas. These formats define certain data elements that organizations agree to exchange. EDI supports businesses in numerous ways compared to the traditional paper-based process. It accommodates quick document processing, automatic entry into a computer system, and real-time visibility of transactions. This eliminates paper and mail costs. Transaction volumes could be easily scaled up without adding more staff.
This information, typically exchanged through EDI, includes quantity and description of orders, unit prices, dates by which delivery is requested, shipping instructions, invoice number, tax amounts, and payment details. The payment instructions may then automatically initiate transfers of funds from business bank accounts. While EDI was initially between large corporations and their suppliers, today, medium and small business enterprises engage in it too. Cheaper EDI software, coupled with cloud-based services and the standard EDI formats, has made this technology more accessible
Importance of Adopting New Technologies in EDI
EDI allows one business to transfer data electronically to another, instead of sending paper documents. For EDI to be most effective and efficient, it should adapt to new ways of exchanging and processing data as they emerge.
Adapting new technologies in EDI speeds up, makes secure, and makes reliable each business’s transactions. Faster data transfers mean that documents and updates will be transmitted in real-time, and the times of response to changes in orders, shipments, and payments will be quicker as well. This way, new methods of encryption and authentication enhance EDI data security, which is thus more secure when it is exchanged over public networks. The risk of possible breaches of information and unauthorized access decreases. Next, technological advancements in EDI lead to the development of more robust and resilient EDI solutions. Errors and interruptions during data exchange are less common. Depending on the nature of a transaction failure, it may be retried automatically or an alert can be sent out to reconnect the connections.
New integration technologies make it easier and quicker to link business applications to EDI solutions. This would help a business shift between different EDI software options with less disruption. Cloud-based EDI Services have their advantages, which involve scalability, location independence, and less upfront cost. Businesses can scale up transaction volumes easily in the cloud.
EDI standards are also changing continuously in light of new data types and transaction formats. The adoption of the latest EDI standards ensures that the system is compatible with business partners.
Evolution of EDI
Electronic Data Interchange has undergone tremendous evolution in these years. It has been making transactions faster, more secure, and more user-friendly. However, the basic concept of EDI has remained the same. electronically exchanging business documents like orders, invoices, and payments. The technologies nevertheless, backing EDI have evolved at a very fast pace.
In the 1980s, EDI was based on point-to-point, direct transmission between organizations over dedicated networks with proprietary formats. Large corporations and their major suppliers were earlier adopters of this technology. During the 1990s, standard EDI formats developed, like EDIFACT and ANSI X.12, which let organizations exchange data regardless of their internal systems. This brought wider adoption, especially to many suppliers and retailers.
In the 2000s, with the growth of the Internet and e-commerce networks, EDI was able to shift the proprietary network to public networks. Companies could easily connect to trading partners over the Internet for data exchange.
Today, very common among EDI consulting services are outsourced offerings, like scalability, accessibility, and decreased costs. They make running EDI systems easier for small and mid-sized businesses.
The technology has added the latest technologies to blockchain so that it can provide innovative offerings in terms of the security, transparency, and traceability of transactions. This shall be powered by Artificial Intelligence and machine learning, working out the simplicity of setup, error detection, and automated exception handling.
Latest Technologies in EDI
Electronic Data Interchange uses electronic ways of communication to exchange business documents between different organizations. With evolving technologies, newer methods are constantly being adopted into EDI systems to enhance their efficiency.
Some of the latest technologies in use with electronic data interchange include:
Cloud-based EDI: The majority of the solutions that are offered by EDI companies are now cloud services where data gets stored and processed over the internet. The advantages are, therefore, scalability, anywhere accessibility, and lower up-front costs. In addition, there are APIs or web services and Application Programming Interfaces that provide EDI systems with the means to integrate with other applications easily. This allows for real-time data exchange between business systems and automates workflows.
Blockchain: Blockchain is this distributed ledger technology which has conceived a secure and transparent way of recording EDI transactions. It allows tracing documents from the beginning down the whole supply chain in an immutable record.
Artificial Intelligence: AI technologies like machine learning are being used to automate the routine tasks of EDI, error detection, handling exceptions, and generation of reports. This reduces the need for manual intervention.
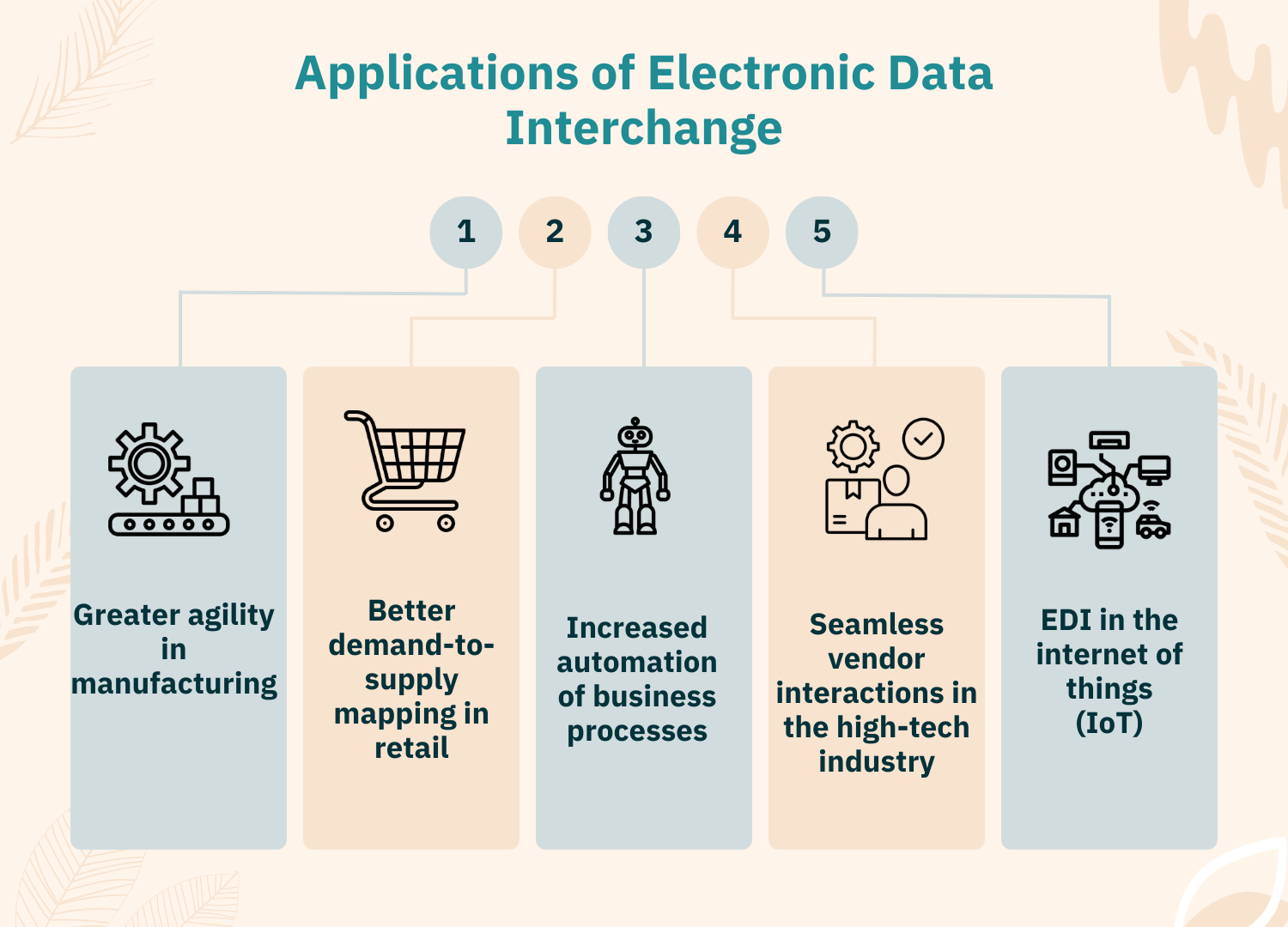
Internet of Things – IoT sensors can automatically generate and transmit EDI documents based on real-time data. This enables track and trace capabilities as well as automatic replenishments.
5G networks – The high-speed 5G cellular networks will further accelerate data transfers in EDI systems. Near real-time exchange of documents will become possible.
Data Analytics – Advanced analytics of EDI transactions help identify patterns, predict issues, and optimize supply chain operations.
Are you looking to manage your EDI system with the latest technologies?
A3Logics is your partner in managing EDI solutions by using cutting-edge technologies
Benefits of Adopting Modern Technologies
Electronic Data Interchange allows a company to transfer structured documents. These include invoices, orders, or payments, between enterprises over an electronic network. The new-age EDI technologies can leverage multiple benefits for enterprises.
Migration of EDI systems to the cloud provides numerous advantages in terms of scalability, mobility, reliability, and security. When volumes increase, it is easy for businesses to scale up transaction volumes without being hindered by any high-cost on-premise infrastructure.
APIs—Application Programming Interfaces—are used to facilitate the integration of EDI systems with other applications that enable workflow automation, real-time data exchange, and quick ‘onboarding’ to another EDI vendor if required.
Blockchain technology ensures that there is an irreversible, transparent record of all EDI transactions. It enhances the document flow across the supply chain in terms of better visibility, traceability, and audit. While artificial intelligence technologies help in automating routine EDI tasks, machine learning detects errors and handles exceptions, generating reports with very little human intervention to increase efficiency.
The Internet of Things enables the integration of EDI services with smart sensors and devices. Real-time data from devices can trigger EDI document generation and automatic replenishments. 5G networks will allow for near real-time data transfers in EDI. Documents can be exchanged and processed within seconds. Businesses can respond much faster to changes.
Advanced analytics of EDI data gives insights into issues, inefficiencies, and opportunities for improving supply chain operations. Performance and compliance can be optimized.
Cloud-based EDI Solutions
Cloud-based EDI solutions allow businesses to exchange electronic data interchange documents via hosted systems across the internet. This means that instead of an on-premise EDI software installation and management, a company will subscribe to the EDI Services available in the cloud.
The key benefits of cloud-based EDI include:
- Scalability: Cloud EDI Services can easily scale up to handle increased transaction volumes. Businesses do not have to overprovision for peak loads when deploying on-premise systems.
- Mobility: Employees can access cloud EDI solutions from anywhere using internet-enabled devices. There is no need for a VPN.
- Reliability: Cloud EDI Solution Providers maintain high uptime through redundancy, backups, and disaster recovery plans. On-premise systems require in-house IT expertise for this.
- Lower costs: Cloud EDI solutions have lower upfront costs as no hardware or software needs to be purchased. Businesses only pay a subscription fee.
- Maintenance free: Cloud Solution Providers handle all maintenance, upgrades, and bug fixes of EDI systems. Businesses do not have to allocate IT resources for this.
- Security: EDI consultancy providers employ advanced security measures like encryption, firewalls, and access controls. Data is also replicated across multiple servers and locations.
- Compatibility: Cloud EDI solutions easily integrate with other business applications regardless of their location. Systems do not have to be physically connected.
API Integration in EDI
Application Programming Interfaces or APIs have become a crucial part of modern Electronic Data Interchange systems. APIs allow consulting services to integrate and exchange data with a wide range of external applications.
API integration helps EDI systems in many ways:
- Flexibility: APIs provide a flexible and modular approach to integrating electronic data interchange with various business applications. This simplifies adding new connections and partners.
- Automation: API-connected applications can automate workflows and trigger actions based on EDI document exchanges. This improves efficiency.
- Real-time data: Software Providers enable real-time two-way exchange of data between EDI and other systems. Documents can be processed as soon as they are generated.
- Scalability: APIs scale easily to accommodate increased transaction volumes without integration issues. EDI partners can be onboarded quickly.
- Interoperability: APIs rely on open protocols and standards, enabling seamless data exchange between different platforms.
- Troubleshooting: Detailed API logs and reports provide visibility into issues during document exchanges. Errors can be resolved quickly.
- Cost savings: APIs provide a cost-effective alternative to custom integrations which require more development and maintenance efforts.
- Consumer-driven: APIs act as the middle layer between EDI and external applications. They expose only relevant data to consumers through a secure interface.
Blockchain in EDI
EDI implies the interchange of structured documents, such as purchase orders and invoices, between two businesses over an electronic medium. Integrating blockchain into it can bring many benefits to EDI systems. Blockchain provides a shared and transparent record of every document exchange that happens between trading partners. The same updated information is accessible to all partners in real-time. This improves visibility. The permanent nature of blockchain records also enables full traceability of EDI documents across the entire supply chain. This improves audibility.
Data stored on a blockchain network is secured through cryptography and access controls. This prevents unauthorized changes to EDI documents and transactions, improving security. Since blockchain data is replicated across multiple nodes, any errors in one record are automatically resolved through the network consensus mechanism. This reduces errors in EDI document exchanges.
Blockchains using permissioned networks allow for faster processing of transactions. This enables near real-time EDI document exchanges and faster response times. Blockchain-based EDI solutions can also be more cost-effective due to their distributed nature and automation.
Smart contracts embedded in the blockchain can automate EDI consultancy document exchanges and payments based on pre-defined business rules. This streamlines and optimizes supply chain processes. Public blockchains can easily scale to accommodate a large number of users and transactions, allowing for ecosystem-wide EDI implementations.
AI and ML in EDI
Electronic Data Interchange is the paperless electronic exchange of documents between two businesses. These documents could be invoices, purchase orders, and many others. The inclusion of AI and ML technologies enhances the efficiency and performance of EDI systems.
AI technologies, of which machine learning is one, can be trained against large volumes of EDI transaction data to identify patterns and thereby automatically detect errors, reducing the need for manual error checking. Similarly, AI can process exceptions and anomalies to EDI document exchanges without human intervention.
Machine learning algorithms identify trends from EDI historical data, predict problems, and recommend the best course of action to enable the optimization of supply chain operations. They also detect fraudulent transactions and data that do not comply with EDI standards. This helps reduce inefficiencies.
AI and ML can automate routine tasks in EDI software providers like report generation, report distribution, and scheduling of document exchanges. They can also automate tasks like setting up new EDI connections and onboarding trading partners based on their requirements. This reduces the workload for EDI administrators. AI chatbots and virtual assistants can assist EDI users in troubleshooting issues, answering queries, and providing guidance. They can offer 24/7 support at lower costs compared to human agents.
Overall, adopting AI and ML technologies for EDI systems can improve their performance, reliability, and intelligence. Machine learning algorithms become more accurate over time as they have access to growing volumes of EDI transaction data. However, human oversight is still required to validate AI decisions and model outputs.
Implementation Considerations
EDI allows companies to conduct business while exchanging electronic documents that include purchase orders, for example, and invoices instead of written paper. However, the implementation of an EDI system is subject to an in-depth investigation of a few factors.
First, businesses need to identify their EDI requirements and goals. What documents need to be exchanged? With whom? How frequently? Clarifying these aspects helps determine the right EDI solution. Businesses also need to research and compare different EDI software options like on-premise, cloud-based, or legacy systems. Each has pros and cons in terms of costs, risks, scalability, and capabilities.
Data mapping and integration with existing ERP or accounting systems is another important factor for electronic data interchange providers. Businesses need to identify data elements to be exchanged in EDI documents and how they map to their internal systems. This ensures accurate data transfer. EDI standards also need to be evaluated and selected. Most businesses opt for XML, EDIFACT, or ANSI X12 standards to ensure compatibility. Security is a key concern as EDI involves exchanging sensitive transaction data. Proper authentication, encryption, and access controls are required.
Businesses also need to find and connect with EDI trading partners. Establishing EDI connections may require additional setup, testing, and validation. Finally, ongoing maintenance and support need to be considered. EDI systems require regular monitoring, upgrades, and support for users.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Here are some best practices for a successful EDI implementation:
- Define clear objectives and requirements: Know exactly what documents need to be exchanged, with whom, and how frequently. Understand the business pain points EDI aims to solve.
- Conduct research and evaluate options: Compare different EDI solutions, vendors, and technologies based on your needs. Consider integration requirements, standards support, scalability, and costs.
- Create a pilot program: Start with a small number of trading partners and document types to test and refine the system before full implementation. This reduces risks.
- Map data elements accurately: Ensure data from EDI documents maps correctly to your internal systems to avoid issues at integration. Test mappings thoroughly.
- Establish test accounts: Set up test connections with trading partners to validate data exchange, document flows, and error handling before going live.
- Create a data dictionary: Document data elements, formats, codes, and protocols to be used. Share this with trading partners for reference.
- Put security measures in place: Use encryption, authentication, access controls, and firewalls. Also, conduct risk assessments.
- Provide training and education: Train users on the new EDI system and processes. Also, educate trading partners.
- Monitor performance closely: Track key metrics like document exchange failures, processing times, and error rates. Make improvements through electronic data interchange providers.
- Have a support plan: Have resources to assist EDI consulting, resolve issues quickly, and make upgrades. Stay up to date on EDI standards.
Future Trends in EDI
- Increased cloud adoption: More and more EDI solutions will move to the cloud to gain advantages. The advantages include scalability, flexibility, and lower costs. EDI support teams will become the default option for EDI.
- Greater use of APIs: APIs will be further integrated into EDI systems to enable seamless data exchange with a wide range of applications. This will improve interconnectivity and automation.
- More blockchain implementations: Blockchain will be adopted widely to bring benefits like transparency, traceability, security, and automation to EDI networks. Smart contracts will also become more common.
- Higher AI and IoT integration: AI technologies developed by EDI service providers in the USA like machine learning will be leveraged more to optimize EDI processes, detect errors, and recommend actions. IoT devices will generate EDI documents in real-time.
- Automation of manual tasks: More mundane and repetitive tasks in EDI will be automated through AI and robotics. This will improve efficiency and reduce human errors.
- Standards evolution: EDI support teams will continue to develop to incorporate new data types, enable real-time communication, and accommodate emerging technologies.
- Integrations ecosystem: EDI solutions will evolve into open platforms that easily integrate with a wide range of enterprise applications through APIs.
Challenges and Mitigation Strategies
Here are some challenges in EDI and mitigation strategies:
| Challenges | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|
| Data mapping issues | Accurate data mapping and thorough testing |
| Slow adoption | Education and incentives for trading partners |
| High costs | Cloud-based EDI for better scalability and lower costs |
| Limited scalability | Cloud-based EDI for better scalability |
| Security threats | Regular security audits, encryption, and access controls |
| Lack of standards | Use of universal EDI standards |
| System failures | Reliable infrastructure with redundancy |
| Disruptions and outages | Disaster recovery and business continuity plans |
| Monitoring and performance issues | Monitoring key performance metrics |
| Obsolete technology | Timely upgrades and software updates |
| Complex implementation | Support from EDI experts |
Conclusion
EDI allows firms to exchange data electronically instead of using paper documents. Nevertheless, to be efficient for the sake of remaining, EDI systems should adapt to the newer technologies to improve speed, security, and reliability. Integrating technologies like cloud computing, APIs, blockchain, AI, IoT, and analytics can transform rigid EDI software into an intelligent and interconnected platform. This enables faster data exchange, end-to-end visibility, automated workflows, real-time decision-making, and optimized supply chain operations.
Advanced technologies also simplify EDI implementations and reduce costs. As EDI networks evolve through the integration of the latest technologies, they will transform supply chains and enable new levels of connectivity, intelligence, and efficiency. Therefore, leveraging the appropriate technologies is key for businesses to realize the full benefits of Electronic Data Interchange.
FAQs
What different technologies are used for EDI?
Various technologies are enabling Electronic Data Interchange between organizations. Cloud computing services are increasingly being used for Outsourced EDI Services that offer advantages like scalability, lower costs, and mobility. EDI systems can be easily integrated with other applications because of their application-programming interfaces, allowing automation and real-time exchange of data. Blockchain can offer an open, transparent, and secure method for recording transactions.
Technologies like machine learning are being used to automate tasks in EDI like error detection and report generation. IoT devices can generate EDI documents automatically based on sensor data and trigger replenishment. 5G networks will further accelerate data transfers for near real-time EDI exchanges. Advanced analytics of EDI transactions helps identify issues and optimize operations.
What is the future of EDI?
The future of Electronic Data Interchange looks promising with the integration of newer technologies that improve its performance, capabilities, and benefits. An increasing number of Outsourced EDI Services will move to the cloud to gain advantages like scalability and lower costs. More technologies like APIs, AI, blockchain, IoT, and analytics will become part of EDI systems enabling faster data exchange, end-to-end visibility, automated workflows, and optimized supply chain operations.
EDI standards will also evolve continuously to incorporate new data types and accommodate emerging technologies. All these technological developments will be the triggers that will make EDI networks transform and interconnect in new ways, thereby infusing intelligence and efficiency into supply chains.
What are the 4 major components of EDI?
The four major components of any Electronic Data Interchange system are:
- EDI software – Manages the exchange of documents between trading partners.
- EDI translator – Converts EDI documents into the format understood by internal systems and vice versa.
- EDI network – Carries data between trading partners, and can be a public or private network.
- EDI terminals – Allow users to access the EDI system to transmit and receive documents.
What is a modern application of EDI?
Modern Electronic Data Interchange solutions leverage various technologies to provide businesses with a wide range of benefits. Cloud-based EDI Services offer advantages like scalability, lower costs, and mobility. API integration allows an amalgamation of different applications for automation and real-time data exchange.
It can enhance transaction security, transparency, and traceability by implementing blockchain integration. Integration of EDI with IoT devices allows for automatic document generation based on sensor data. All these emerging technologies are enabling faster data transfers, end-to-end visibility, automated workflows, and other strategic benefits for businesses when implemented in modern EDI solutions by EDI solution providers.