Table of Contents
In an era characterized by rapid technological advancements, the landscape of the IT business in the United States has witnessed unparalleled growth and innovation. Be that as it may, with this movement comes the imperative requirement for stringent regulatory measures to safeguard businesses and safeguard sensitive data. Navigating the intricate trap of IT compliance regulations has turned into an indispensable aspect for US IT industries striving to maintain operational integrity and secure their foothold in an increasingly competitive market.
According to a report by Statista, the global expenditure on cybersecurity is projected to reach a staggering $270 billion by 2026, mirroring the escalating concerns encompassing data breaches and digital threats. Within the US, the proliferation of regulatory frameworks like the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) have added layers of complexity to the compliance landscape. Failure to adhere to these regulations can bring about extreme outcomes, including robust fines, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions.
In this dynamic climate, understanding the nuances of IT compliance regulations is paramount as far as we’re concerned IT businesses to mitigate chances and sustain their cybersecurity act. This complete aid aims to dig into the intricacies of navigating IT regulations and compliance, elucidating key ideas, challenges, best practices, and emerging trends. By equipping businesses with the knowledge and strategies necessary to navigate. This regulatory terrain effectively, organizations can safeguard their operations. As well as cultivate trust and certainty among stakeholders in a consistently developing digital environment.
What Are IT Compliance Regulations and Why Do They Matter?
IT compliance regulations include a bunch of rules, standards, and rules laid out by legislative bodies, industry affiliations, and regulatory authorities. To guarantee that associations working within the IT area comply with explicit prerequisites connected with data security, protection, and functional integrity. These regulations act as a framework to oversee the handling, storage, and transmission of sensitive data. With the general objective of mitigating risks related to cyber threats, data breaches, and regulatory non-compliance.
The meaning of IT compliance regulations couldn’t possibly be more significant in the present digital landscape. With the exponential growth of data and the proliferation of sophisticated cyber threats. Businesses face a consistently expanding chance of succumbing to security breaches and regulatory infringement. Compliance regulations by industry provide a structured approach to dealing with these risks by laying out clear rules and standards for associations to observe.
By complying with IT compliance regulations, businesses can accomplish a few urgent targets:
1. Protection of Sensitive Data
Compliance regulations mandate the execution of strong security measures to defend sensitive data from unapproved access, divulgence, or modification. This guarantees the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data, consequently limiting the gamble of data breaches that is beneficial for eLearning software development services and protecting the interests of customers, workers, and partners.
2. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Non-compliance with IT regulations can have extreme legal and monetary repercussions, including robust fines, punishments, and legal sanctions. By complying with regulatory necessities, associations can mitigate the gamble of confronting costly litigation and reputational damage. Subsequently maintaining compliance with appropriate regulations and regulations.
3. Enhanced Trust and Credibility
Compliance with IT regulations shows a commitment to moral strategic policies, straightforwardness, and accountability. This enhances the trust and certainty of customers, accomplices, and financial backers in the association’s ability to protect their sensitive data and maintain industry standards. Subsequently encouraging solid connections and supporting the association’s standing in the marketplace.
4. Competitive Advantage
In the present competitive business climate, compliance with IT regulations can act as a differentiator, recognizing consistent associations from their non-consistent partners. By exhibiting a proactive approach to cybersecurity and regulatory compliance. Businesses can gain a competitive edge, attract new customers, and hold existing ones who prioritize security in software development and compliance standards.
IT compliance regulations assume an essential part in molding the functional landscape of associations working within the IT area. By complying with these regulations, businesses can mitigate risks, protect sensitive data, maintain legal and regulatory compliance, enhance trust and credibility, and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.

How Do IT Compliance Regulations Impact the US IT Industries?
IT compliance regulations significantly affect US IT industries, forming their activities, systems, and priorities in more ways than one:
1. Regulatory Compliance Framework
IT compliance regulations lay out a framework of decisions and standards that US IT industries must comply with to guarantee the security, protection, and integrity of their tasks. These regulations direct the way that organizations handle, interact, store, and transmit sensitive data, like individual data, financial records, and protected innovation.
2. Increased Accountability
Compliance regulations force accountability on US IT industries to maintain moral and legal standards in their business rehearses. Organizations are expected to execute robust security measures, lead ordinary audits and appraisals, and keep up with far-reaching documentation to exhibit compliance with regulatory requirements.
3. Resource Allocation
Compliance with IT regulations necessitates the allocation of resources, including financial, human, and technological. To execute and keep up with compliance gauges. US IT industries must put resources into cybersecurity advances, representative preparation projects, and cost of custom software development with compliance management frameworks to meet regulatory commitments and mitigate risks.
4. Risk Management
IT compliance regulations act as a critical part of risk management techniques for US IT industries. By distinguishing and tending to potential security vulnerabilities, regulatory rebelliousness, and data breaches. Organizations can mitigate risks, safeguard their resources, and shield their standing in the commercial center.
5. Competitive Advantage
Compliance with IT regulations can give a competitive advantage to US IT industries. By upgrading their credibility, trustworthiness, and reliability according to customers, accomplices, and partners. Organizations that exhibit a commitment to cybersecurity and regulatory compliance are bound to draw in and hold customers who prioritize security and software compliance standards.
6. Legal and Financial Implications
Rebelliousness with IT regulations can have extreme legal and financial implications for US IT industries. Organizations that fail to adhere to regulatory requirements may face fines, penalties, legal sanctions, and reputational damage, resulting in significant financial losses and loss of market share.
7. Innovation and Growth
While compliance with IT regulations might present difficulties and requirements for US IT industries, it can likewise produce innovation and drive growth. By putting resources into compliance advances, embracing best practices, and remaining in front of emerging threats, organizations can reinforce their cybersecurity posture. To enhance operational efficiency, and position themselves for long-term progress in the quickly developing digital landscape.
IT compliance regulations have an impressive effect on US IT industries, profoundly shaping their way of behaving, priorities, and competitiveness in the commercial center. Software development best practices such as embracing compliance as a strategic imperative, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance trust and credibility, and capitalize on opportunities for innovation and growth in the unique landscape of the IT sector.
Elevate Your Compliance Game. Click to Schedule a Personalized Compliance Consultation with Our Experts
What are The Main Components of IT Compliance Regulations in the US?
The main components of IT compliance regulations in the US typically encompass a range of requirements and standards to ensure the security, privacy, and integrity of information technology systems and data. These components may vary depending on the specific regulations applicable to an organization, but some common elements include:
1. Data Security
IT compliance regulations often mandate the implementation of robust data security measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, or alteration. This may include encryption, access controls, authentication mechanisms, and data loss prevention technologies.
2. Privacy Protection
Regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) require organizations to safeguard the privacy of individuals’ personal information. This involves obtaining consent for data collection and processing, limiting data retention periods, and implementing measures to prevent data breaches and unauthorized disclosures.
3. Risk Assessment and Management
Compliance regulations typically require enterprise software development companies to conduct regular risk assessments to identify potential security vulnerabilities, threats, and risks to their IT systems and data. Organizations must then implement risk mitigation measures and controls to address identified risks and minimize their impact on operations.
4. Compliance Reporting and Documentation
Organizations subject to information technology compliance regulations are often required to maintain comprehensive documentation of their compliance efforts, including policies, procedures, and audit trails. They may also be required to submit periodic compliance reports to regulatory authorities or undergo external audits and assessments to verify compliance.
5. Incident Response and Reporting
Compliance regulations typically mandate the implementation of incident response procedures to detect, respond to, and mitigate security incidents and data breaches. Organizations must also report significant incidents to regulatory authorities, affected individuals, and other relevant stakeholders promptly.
6. Training and Awareness
Regulations may require organizations to provide training and awareness programs for employees to ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities regarding IT regulations and compliance. This may include training on data security best practices, regulatory requirements, and incident response procedures.
7. Vendor Management
Many IT compliance regulations require organizations to assess and manage the security risks posed by third-party vendors and service providers. This may involve conducting due diligence assessments, negotiating contractual agreements, and monitoring vendor compliance with regulatory requirements.
8. Continuous Compliance Monitoring
Compliance regulations emphasize the importance of ongoing monitoring and evaluation of compliance efforts. To ensure that organizations maintain adherence to regulatory requirements over time. This may involve regular audits, assessments, and reviews of IT systems, policies, and procedures.
Overall, the main components of IT compliance regulations in the US are designed to promote the secure and responsible handling of information technology systems and data, protect individuals’ privacy rights, and mitigate risks associated with cyber threats and data breaches. By adhering to these components, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture, maintain regulatory compliance, and safeguard their operations and reputation.liance, and safeguard their operations and reputation.

How Can Businesses Ensure Compliance with IT Regulations?
Businesses can ensure compliance with IT regulations by implementing a robust framework of policies, procedures, and controls that align with regulatory requirements. According to a report by PwC, 68% of organizations consider compliance with IT regulations a top priority due to the increasing frequency and severity of cyber threats. To begin, companies must conduct a comprehensive assessment of relevant regulations applicable to their industry and operational context. For instance, the Global Cybersecurity Index (GCI) 2023 highlights that 57% of countries have established national strategies for cybersecurity, emphasizing the global significance of regulatory compliance in the digital age.
Subsequently, custom software development services should develop tailored compliance programs addressing specific regulatory obligations, such as data security and privacy protection. The IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 reveals that the average total cost of a data breach in the United States is $8.64 million, underscoring the financial implications of non-compliance. Therefore, investing in robust policies and procedures governing data handling, access controls, and risk management is imperative. Moreover, organizations should prioritize employee training and awareness initiatives to foster a culture of compliance. According to a study, 64% of data breaches involve human error, highlighting the importance of educating staff on cybersecurity best practices.
Regular audits, assessments, and reviews are essential to monitor compliance efforts and identify areas for improvement. The Ponemon Institute’s Cost of Compliance Study 2022 found that organizations spend an average of $5.47 million annually on compliance-related activities, demonstrating the significant resource investment required. Leveraging technology solutions, such as compliance management software and security in software development tools, can streamline compliance processes and enhance monitoring capabilities. By adopting a proactive and systematic approach to compliance management. Businesses can mitigate risks, protect sensitive information, and maintain regulatory adherence in an increasingly complex and challenging cybersecurity landscape.
What Challenges Do US IT Industries Face in Achieving Compliance?
Amidst stringent regulations and rapidly evolving cybersecurity threats, businesses grapple with the complexities of maintaining adherence. To regulatory frameworks while striving to innovate and remain competitive. Balancing the need for robust security measures with the pressures of operational efficiency presents a formidable challenge. Often compounded by the dynamic nature of compliance standards. The intricacies of implementing comprehensive risk management strategies. In this intricate dance between security and innovation, US IT compliance regulations navigate a landscape fraught with challenges, seeking to safeguard sensitive data, uphold consumer trust, and meet the rigorous demands of regulatory compliance.
1. Complexity of Regulations
- According to a survey by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), 53% of organizations cite the complexity of IT compliance regulations as a significant challenge.
- The average organization must comply with multiple regulations simultaneously, such as GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and PCI DSS, each with its own set of requirements and standards.
- Keeping pace with regulatory updates and changes can be daunting, with the number of data protection laws worldwide reaching over 140, as reported by TrustArc’s Global Privacy Laws Handbook.
2. Resource Constraints
- A study by Ernst & Young found that 42% of organizations struggle with limited resources when it comes to compliance efforts.
- Compliance requires significant financial investment, with the Ponemon Institute reporting an average annual expenditure of $5.47 million on compliance-related activities for organizations.
- Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) may face particular challenges due to limited budgets and IT resources. Making it difficult to implement and maintain compliance measures effectively.
3. Rapidly Evolving Threat Landscape
- The cybersecurity threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new and sophisticated threats emerging regularly.
- A survey highlights that data breaches are becoming more frequent and costly, with the average total cost of a breach in the United States reaching $8.64 million.
- Compliance regulations must adapt to address emerging threats, which can pose challenges for organizations. In terms of keeping up with evolving regulatory requirements and implementing effective security measures.
4. Lack of Skilled Personnel
- There is a growing shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals capable of understanding and implementing complex compliance requirements.
- According to a report by (ISC)², the global cybersecurity workforce gap surpassed 3.12 million professionals in 2023, underscoring the challenge of finding qualified personnel.
- Recruiting and retaining skilled cybersecurity professionals for enterprise software development companies can be difficult, particularly in highly competitive industries where the demand for talent is high.
5. Vendor and Supply Chain Risks
- Organizations often rely on third-party vendors and suppliers for information technology compliance and services, introducing additional compliance risks.
- Ensuring compliance throughout the supply chain requires robust vendor management processes. Including due diligence assessments, contractual agreements, and ongoing monitoring of vendor compliance with regulatory requirements.
How Technology Can Aid in Managing IT Compliance?
Technology plays a crucial role in aiding organizations to effectively manage IT compliance by providing tools and solutions. However, that streamlines processes, automates tasks, and enhances visibility into compliance efforts. Here’s how technology can facilitate compliance management:
1. Compliance Management Software
- Specialized compliance management software enables organizations to centralize and automate various compliance-related tasks. Such as policy management, risk assessments, and audit tracking.
- These platforms provide a centralized repository for storing compliance documentation, policies, and procedures. Making it easier to track and demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements.
- Advanced features, such as workflow automation and notification alerts, help organizations. To streamline compliance processes, improve efficiency, and ensure timely completion of compliance activities.
2. Risk Assessment and Monitoring Tools
- Technology solutions for risk assessment and monitoring enable organizations to identify, assess, and prioritize potential compliance risks more effectively.
- These tools leverage data analytics, machine learning, and artificial intelligence in software development to analyze vast amounts of data and identify patterns indicative of potential risks or compliance violations.
- Real-time monitoring capabilities provide organizations with actionable insights into compliance status. Enabling them to proactively address issues and mitigate risks before they escalate.
3. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems
- SIEM systems collect, analyze, and correlate security event data from various sources, such as network devices, servers, and applications. To detect and respond to security threats and compliance breaches.
- By integrating compliance-specific rules and regulations into SIEM platforms, organizations can automate compliance monitoring and reporting. However, reducing the burden on manual efforts.
- SIEM systems provide centralized visibility into security and compliance posture. Enabling organizations to identify deviations from established policies and take corrective actions promptly.
4. Continuous Compliance Monitoring
- Continuous compliance monitoring solutions enable organizations to continuously assess and validate compliance status in real-time, rather than relying on periodic audits and assessments.
- These solutions automate the collection and analysis of compliance-related data. Such as system configurations, access controls, and user activities, to identify deviations from regulatory requirements.
- By continuously monitoring compliance posture, organizations can detect and address compliance issues promptly. Subsequently, reducing the risk of non-compliance and potential regulatory penalties.
5. Cloud-Based Compliance Solutions
- Cloud-based compliance solutions offer flexibility, scalability, and accessibility, allowing organizations to manage compliance efforts from anywhere, at any time.
- These solutions provide centralized platforms for collaboration, communication, and documentation sharing, facilitating collaboration among distributed teams and stakeholders.
- Cloud-based compliance solutions often come with built-in security features and controls. Helping organizations adhere to regulatory requirements while leveraging the benefits of cloud computing.
Overall, technology plays a critical role in enabling organizations to effectively manage IT compliance by automating processes, improving visibility, and enhancing efficiency. By leveraging technology solutions tailored to their specific compliance needs, organizations can streamline compliance management. Reduce the risk of non-compliance, and demonstrate adherence to regulatory requirements effectively.
Why Consider Outsourcing Solutions for IT Compliance?
Organizations should consider outsourcing solutions for IT compliance to leverage specialized expertise, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency in managing complex regulatory requirements. According to a survey, 72% of organizations outsource at least one aspect of their compliance activities, highlighting the widespread adoption of outsourcing as a strategic approach to compliance management. Custom software development outsourcing companies allow them to tap into the knowledge and experience of third-party compliance experts who possess a deep understanding and proficiency in navigating intricate regulatory landscapes.
Moreover, outsourcing solutions for IT compliance can yield significant cost savings for organizations. A study by Everest Group found that outsourcing compliance activities can result in cost savings of up to 25-40% compared to in-house compliance efforts. Outsourcing eliminates the need for organizations to invest in hiring and training internal compliance personnel. However, the overhead costs associated with maintaining compliance infrastructure and resources. Additionally, outsourcing providers often operate at scale, allowing them to spread costs across multiple clients. However, this also helps economies of scale, resulting in lower overall costs for each client.
Furthermore, outsourcing solutions for IT compliance can improve efficiency and scalability in managing compliance activities. Outsourcing providers leverage advanced technologies, automation tools, and best practices to streamline compliance processes, reducing manual efforts and enhancing productivity. This enables organizations to focus their internal resources on core business activities while outsourcing non-core compliance tasks to external experts.
Outsourcing solutions for IT compliance offers organizations a strategic approach to effectively manage regulatory requirements. However, realizing benefits such as specialized expertise, cost savings, efficiency improvements, and scalability. Moreover, by partnering with trusted outsourcing providers, organizations can navigate the complexities of IT regulations and compliance more effectively, mitigate risks, and achieve greater compliance success in an increasingly challenging regulatory environment.y environment.
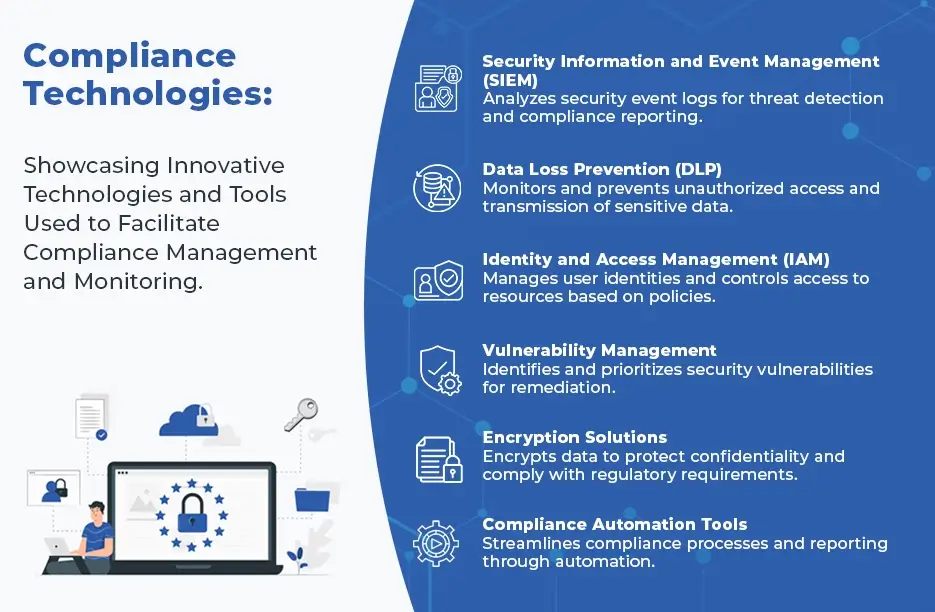
What are The Consequences of Non-Compliance with IT Regulations?
Non-compliance with IT regulations can have severe consequences for organizations, ranging from financial penalties and legal sanctions to reputational damage and loss of customer trust. According to a study by the Ponemon Institute, the average cost of non-compliance for organizations in the United States reached $14.8 million in 2023, representing a 30% increase compared to the previous year. Regulatory authorities have the authority to impose hefty fines and penalties on organizations found to violate IT regulations. Similarly, violations of the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) can lead to fines ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, with a maximum penalty of $1.5 million per year for each violation category. The cost of custom software development can have a significant impact on an organization’s bottom line, potentially leading to financial distress or bankruptcy in extreme cases.
In addition to financial penalties, non-compliance with IT regulations can also result in legal consequences, including lawsuits, litigation, and legal settlements. Organizations may face lawsuits from affected individuals, customers, or regulatory authorities seeking compensation for damages resulting from data breaches or privacy violations. For example, in 2023, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC) reached a $5 billion settlement with Facebook over the company’s mishandling of user data, highlighting the legal ramifications of non-compliance with privacy regulations. According to a survey by Edelman, 81% of consumers say that trust in a brand influences their purchasing decisions, underscoring the importance of maintaining a strong reputation for trust and integrity.
Furthermore, non-compliance with IT regulations can have broader implications for organizations beyond financial and legal consequences. Overall, the consequences of non-compliance with IT regulations are multifaceted and far-reaching. Therefore, digital transformation service providers must prioritize compliance efforts and invest in robust compliance management strategies to mitigate these risks effectively.
How to Implement Best Practices for IT Compliance in US Industries?
In the dynamic landscape of US industries, ensuring compliance with IT regulations is paramount for organizations. Moreover, it safeguards their operations, protects sensitive data, and maintains trust among stakeholders. Implementing best practices for IT compliance is crucial for navigating the complex regulatory environment effectively. Here’s how US industries can implement these best practices:
1. Conduct Comprehensive Risk Assessments
Start by conducting thorough risk assessments to identify potential compliance risks, vulnerabilities, and threats to IT systems and data. Custom software development outsourcing companies that regularly assess risks are better equipped to mitigate compliance risks effectively, as evidenced by research from the Ponemon Institute.
2. Develop Tailored Compliance Policies and Procedures
Develop customized policies and procedures aligned with regulatory requirements and tailored to address specific compliance obligations relevant to your industry and operational environment. Well-defined compliance policies and procedures contribute to compliance success and risk mitigation, according to Gartner.
3. Implement Robust Access Controls and Data Security Measures
Implement robust access controls and data security measures to safeguard sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, or alteration. Effective access controls in healthcare digital transformation companies can correlate with lower total costs of data breaches, as indicated by the IBM Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023.
4. Provide Ongoing Employee Training and Awareness
Offer regular training and awareness programs to employees to ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities regarding IT compliance. Educating staff on compliance best practices is essential for reducing human error, a significant contributor to data breaches, according to Verizon.
5. Conduct Regular Compliance Audits and Assessments
Conduct regular compliance audits and assessments to evaluate the effectiveness of compliance measures and identify areas for improvement. Organizations that conduct regular audits experience lower compliance costs and fewer compliance-related incidents, according to the Ponemon Institute’s Cost of Compliance Study 2022.
6. Leverage Technology Solutions for Compliance Management
Invest in compliance management software and technology solutions to automate compliance processes, streamline workflows, and enhance visibility into compliance efforts. Leveraging technology for compliance management leads to greater efficiency and cost savings.
7. Foster a Culture of Compliance and Accountability
Foster a culture of compliance and accountability by promoting ethical behavior, transparency, and adherence to regulatory requirements. Custom software development consulting companies with strong compliance cultures are better equipped to detect and prevent compliance violations, according to EY.
8. Establish Clear Incident Response and Reporting Procedures
Establish a clear incident response and reporting procedures to promptly detect, respond to, and mitigate compliance breaches of security incidents. Effective incident response plans are associated with lower total costs of data breaches.
9. Stay Abreast of Regulatory Updates and Changes
Stay informed about regulatory updates and changes relevant to your industry and jurisdiction to ensure ongoing compliance with evolving requirements. Keeping pace with regulatory changes is a top challenge in compliance management, according to Compliance Week’s survey.
By implementing these best practices, US industries can enhance their cybersecurity posture, mitigate risks, and demonstrate a commitment. For ethical and legal standards, thereby ensuring compliance with IT regulations effectively.
What are The Future Trends in IT Compliance for US Businesses?
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the landscape of IT compliance for US businesses is undergoing significant transformations. Keeping abreast of emerging trends in IT compliance is crucial for organizations. However, to adapt to evolving regulatory requirements, mitigate risks, and maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace. In this context, exploring the future trends and compliance regulations by industry provides insights into the potential challenges and opportunities for US businesses.
Future Trends in IT Compliance for US Businesses:
1. Adoption of AI and Automation
- Organizations are increasingly leveraging automation and artificial intelligence in software development with technologies to streamline compliance processes, enhance efficiency, and reduce manual efforts.
- According to a report by Gartner, by 2025, 80% of organizations will use AI for IT compliance tasks, such as risk assessment, anomaly detection, and compliance monitoring.
2. Focus on Privacy Regulations
- Organizations are placing greater emphasis on privacy compliance with the proliferation of data privacy regulations. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- A survey by TrustArc found that 88% of organizations consider compliance with global privacy regulations a top priority for their business.
3. Rise of Cybersecurity Frameworks
- Cybersecurity frameworks, such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework and the Center for Internet Security (CIS) Controls, are becoming integral to information technology compliance efforts.
- The Ponemon Institute’s Cost of Compliance Study 2022 revealed that 67% of organizations use cybersecurity frameworks to guide their compliance initiatives.
4. Embrace Continuous Monitoring
- Continuous monitoring technologies enable organizations to detect and respond to compliance issues in real-time, rather than relying on periodic assessments.
- According to a study by IDC, spending on continuous compliance monitoring solutions is expected to reach $6.8 billion by 2025, driven by the need for real-time risk management and compliance insights.
5. Integration of ESG Criteria
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria are increasingly being integrated into IT compliance frameworks to address broader societal and ethical concerns.
- A survey found that 73% of executives believe that ESG considerations for healthcare digital transformation companies will become more important in shaping compliance requirements in the future.
6. Enhanced Data Governance Practices
- Data governance practices are evolving to address the growing volume, variety, and velocity of data. As well as regulatory requirements related to data protection and privacy.
- According to Forrester, organizations are investing in data governance solutions to improve data quality, ensure regulatory compliance, and support data-driven decision-making.
By anticipating and adapting to these future trends in IT compliance, US businesses can strengthen their compliance posture, mitigate risks, and leverage opportunities for innovation and growth in the evolving regulatory landscape..

Conclusion
It is fundamental as far as US IT industries to explore IT compliance regulations to defend their business operations, protect sensitive data, and keep up with trust and credibility in an undeniably perplexing and dynamic digital landscape. Software development best practices like discussion, and compliance with IT regulations aren’t just a legal necessity but also an essential basis for associations to mitigate risks, keep away from expensive punishments, and maintain moral standards. As indicated by a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, cybercrime is supposed to cost the world $6 trillion every year by 2030, highlighting the earnestness of prioritizing compliance efforts to mitigate cyber risks and protect against data breaches.
US IT industries can use best practices, technology solutions, and industry standards by embracing a proactive and orderly way to deal with IT compliance. However, to explore administrative complexities as proven by various examinations and reports, associations put resources into compliance management solutions. Moreover, employee training programs and continuous monitoring technologies are better prepared to make compliance progress and mitigate risks related to non-compliance. For example, the Global State of Information Security Survey led by PwC found that associations with a devoted cybersecurity budget are stronger due to cyber dangers and administrative difficulties.
Looking forward, US businesses must remain cautious and versatile to arising patterns and administrative changes in the IT compliance landscape. The reception of technologies like artificial intelligence, continuous monitoring, and cybersecurity systems. However, it will assume an urgent part in improving compliance capabilities and strength against developing dangers. Exploring IT compliance regulations is a continuous excursion that requires joint effort, development, and commitment from all stakeholders within US IT industries. By embracing compliance as an essential goal and putting resources into proactive measures to address administrative prerequisites. Subsequently, associations can defend their business operations, and protect sensitive data.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQs)
1. What are The Most Common IT Compliance Regulations That US IT Industries Need to Navigate?
The most well-known IT compliance regulations that US IT industries need to explore incorporate the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). These regulations force explicit prerequisites connected with data security, privacy protection, and functional integrity, which US IT custom software development consulting companies must comply with to avoid punishments and keep up with compliance.
2. How Do IT Compliance Regulations Impact The Operational and Financial Aspects of US IT Businesses?
IT compliance regulations altogether affect the functional and monetary parts of US IT businesses. Compliance efforts require committed assets, remembering monetary speculations for technology solutions, employee training programs, and compliance management frameworks. Non-compliance can bring about weighty fines, legitimate authorizations, reputational harm, and loss of customer trust. All of which can antagonistically affect business operations and profitability.
3. What Are The Key Challenges Faced by US IT Industries in Achieving Compliance with IT Regulations?
US IT industries face a few vital difficulties in accomplishing compliance with IT regulations. These difficulties incorporate the complexity of regulations, asset requirements, quickly advancing danger landscapes, absence of talented faculty, and vendor and supply chain risks. Addressing these moves expects associations to embrace a proactive and efficient way to deal with compliance management, leveraging technology solutions. Best practices, and joint efforts with administrative authorities and industry accomplices.
4. How can Technology Solutions Aid US IT Businesses in Managing and Maintaining Compliance with IT Regulations?
Technology solutions can help US IT businesses in overseeing and keeping up with compliance with IT regulations. By smoothing out processes, computerizing undertakings, and improving visibility into compliance efforts. However, compliance management programming, risk appraisal instruments, security in software development information and event management (SIEM) frameworks, and continuous monitoring solutions empower associations to distinguish, survey, and mitigate compliance risks. Leveraging technology solutions additionally assists associations with further developing productivity, reducing expenses, and keeping up to date with administrative updates and changes.
5. What are The Potential Consequences for US IT Industries in Case of Non-compliance with IT Regulations?
The possible consequences for US IT industries in the event of non-compliance with IT regulations can be serious. These outcomes might incorporate monetary punishments, legitimate authorizations, lawsuits, litigation, administrative investigation, reputational harm, and loss of business opportunities. Associations viewed as infringing upon IT regulations might confront fines going from thousands to millions of dollars. Contingent upon the severity and extent of the infringement, non-compliance can bring about loss of customer trust, damage to brand reputation, and disruptions to business operations. Additionally, all of these can have long-term implications for the success and viability of the organization.