Table of Contents
Open enrollment season is rapidly approaching. It gives workers an annual opportunity to review and change their health insurance. They will be able to change benefits selections for the coming year. Open enrollment for 2025 will likely run from November through January for most companies. This time presents decisions around health plans, flex spending accounts, life insurance, and other benefits. As per the International Foundation of Employee Benefit Plans (IFEBA), October or November marks the start of open enrollment for 77% of businesses. Open enrollment dates are spaced out evenly throughout the remainder of the year for the remaining minority. However, navigating open enrollment solutions and understanding changes can pose challenges for employees. This blog aims to answer top open enrollment FAQs for 2025. This aims to provide clarity around the process and choices workers will face.
The coming open enrollment period presents an excellent time for employees to review their current coverage. Comparing alternative plans, and selecting benefits that best suit their needs for the upcoming year.
What is open enrollment in the Workday?
Open enrollment in Workday refers back to the period that an enterprise permits personnel to make modifications to their advantages for the imminent year. It normally occurs once a year for a set duration, consisting of a couple of weeks. During benefits enrollment, personnel can sign up for or trade existing gain plans like medical insurance, dental insurance, imaginative and prescient insurance, lifestyles coverage, retirement plans, and structured care flexible spending debts.
Employees can also need or need to make adjustments to their blessings throughout open enrollment for diverse motives. A worker may need to enroll in a brand-new plan that is no longer formerly available. A worker’s partner or structure may additionally lose or benefit from medical health insurance which may affect the employee’s selection. An employee’s circle of relatives’ reputation may additionally exchange due to start, adoption, or marriage, necessitating the addition of dependents to a gain plan. An employee’s monetary scenario might also alternate, prompting the employee to adjust contributions to retirement plans or bendy spending bills.
What is insurance enrollment?
Insurance enrollment is the act of using or enrolling in insurance. Some of these specialist types of cover give protection against financial risk by providing health insurance, lifestyle coverage, property insurance, and automobile insurance, amongst many others.
Individuals can also enroll in insurance through multiple channels, depending on the nature of coverage in question. Some of the common channels of insurance enrollment include
- Employer-sponsored plans – The majority of employees derive insurance coverage from the employers’ benefit packages that include group health and life insurance. The employer may be subsidized with part of the premiums.
- Government programs – Citizens may enroll in the government’s schemes in insurance, like Medicare and Medicaid. Some have eligibility criteria that must be met.
- Private purchase– A person can purchase private insurance cover directly from insurance companies. Plans purchased this way are more often expensive.
- Group purchasing options : Membership groups sometimes have insurance options available for members at discounted prices.
- Insurance agents/brokers—Insurance professionals help clients compare option. Allowing them to apply for plans that provide the right coverage.
The process for enrolling in insurance typically includes filling out an application. Providing health information, choosing coverage options and beneficiaries, and determining premium payment methods.
What is the difference between open and annual enrollment?
While both open and annual enrollment provide a window of time for which employees may make changes to their benefits, there are some differences. This is usually the open enrollment, which is held annually for a certain period. It is normally two to four weeks in duration. During this time, employees have the ability to enroll in benefits previously declined, change benefit elections, and add or remove dependents from coverage. Companies may have multiple annual enrollment periods throughout a calendar year to allow new hire employees or those with qualifying life events the ability to enroll.
Another difference involves the benefits which can be changed during each enrollment period. Open enrollment for benefits typically will include changes to all company-offered benefits, however confined. Specifically to health, dental, and vision insurance; life insurance, flexible spending accounts, and retirement plans. Annual enrollment may have more restrictions in place and only allow changes related to certain benefits.
Benefit eligibility also differs for each period. Open enrollment process can be held annually only a few times, may have restrictions on the benefits that one is allowed to change, and at times can only be done by employees who have life events.
What if I miss open enrollment for health insurance through work?
When an employee misses their open enrollment to get health insurance through work, it can make all the difference in the options open to them concerning their coverage and the price of the same. Open enrollment is always the easiest opportunity each year for an employee to select or change his or her health insurance plan, unless they have a qualifying life event at some point in the 12 months. If one fails to do so at some stage in the open enrollment period, normally, he or she will be staying on the same health plan for the following year.
For instance, if an employee fails to enroll during the open enrollment period and no longer actively reinstalls into a fitness plan, he/she will likely be stuck with the same level of coverage with the same exact plan for another 12 months. That is to say, such an employee misses the chance to change to another health plan that offers better coverage, lower costs, or includes doctors and health providers they want to use.
The employee also loses the opportunity to be enrolled in any other health plans offered by their employer they were previously ineligible for. New plans are frequently added via an open enrollment as an agency’s benefits package changes. Also, if an employee misses open enrollment, he or she could pay more for medical health insurance the following year. Unless an employee actively re-enrolls in a fitness plan, they are usually rolled over to the identical plan; and employees’ rates normally rise every year.
Furthermore, employees who are not participating in open enrollment cannot benefit from provisions such as fitness savings loans or flexible spending bills, which require a person to enroll or re-enroll every twelve months.
Get ready for a Seamless Open enrollment
Reach out to the experts at A3Logics to make your process hassle-free
Can I purchase medical insurance and use it right now?
Buying medical insurance and the use of it immediately can be elaborate. While it is technically feasible to purchase a medical health insurance plan and begin using it properly, there are some matters to keep in mind.
Most important health insurance plans have an effective date of coverage, which means the date you may officially start the usage of the insurance advantages. While you could purchase a plan without delay, the date you can surely use it may be a few days or even weeks later. This is to provide the insurance employer time to technique your utility and install your coverage. Some plans additionally have waiting for durations before you can access sure benefits. For instance, a few plans require you to attend three months earlier than you may use maternity or intellectual fitness insurance. Certain offerings like bodily therapy or chiropractic care may additionally have their waiting durations.
If you have a deliberate medical rate inside the near destiny, like an optional surgical procedure or a scheduled physician’s visit, there’s a threat the insurance corporation ought to deny insurance for that expense because of it taking place before the effective date of your policy. The coverage might then most effectively cover prices for offerings acquired on or after your reliable insurance start date.
To purchase health insurance and use it as soon as viable, look for brief-time period medical health insurance plans, which are designed to start masking expenses at once upon purchase. However, those plans generally tend to have higher premiums, lower coverage limits, and exclude pre-existing conditions.
While some health plans have immediate effective dates, most major insurance require a waiting period to set up. If you have planned medical costs shortly, check the effective date and any service-specific waiting periods very carefully before purchasing a plan to ensure you will have coverage for those expenses.
How long is open enrollment for most employees?
The duration of time that is permitted for employees to take advantage of the open enrollment period varies. It is different from agency to employer but typically is no more than two to six weeks. Open enrollment solutions, including EDI solutions, refer to the time every year that all employers are required to allow employees the opportunity to enroll or change their benefit options, which will include health insurance plans and flexible spending bills. This allows them to make changes based on life events or new plans being offered.
Many companies hold open enrollment during the last weeks of October through the first weeks of November. With the changes effective on January 1 of the new year. This coincides with the timing of many new benefit years and insurance plan years. Other employers may hold an open enrollment period as short as a week or as long as six weeks.
Two to four weeks, nonetheless, remain a very typical length for employee open enrollment. The provided window length aims to be long enough to allow employees some reasonably fair time to review options, ask questions, and provide their elections while also being a defined period that does not disrupt operations for any extended period of time.
For employees, making the most of open enrollment for health benefits might involve researching options for plans, comparing costs of coverage, calling representatives for benefits and doctors, and even gathering necessary documentation to add dependents. An extended enrollment window ensures that employees have ample time to gather the necessary information for effective benefit decision-making.
What are the phases of the open enrollment process?
The open enrollment process typically consists of several key phases. This is to ensure a smooth transition of employee benefit selections for the upcoming plan year. The main phases of open enrollment are:
Communication
The benefits enrollment company communicates information about open enrollment well in advance to all eligible employees. This includes sending letters, emails, intranet posts, and distributing printed materials detailing the process, important dates, plan changes for the new year, and steps to enroll. Some companies hold benefit fairs or information sessions to explain options in person.
Employee Review
Employees review their current benefit selections, compare plan options for the new year, and determine whether changes are needed based on their situation and budget. This may involve researching plans online, speaking to benefit advisors and attorneys, and collecting information on new dependents to be added.
Enrollment
During the designated benefits enrollment period, typically lasting two to four weeks, employees make enrollment changes online or by submitting printed forms. They select new plans, add or remove dependents, make coverage level changes, and sign up for spending accounts. Benefits offices may extend hours to assist employees during this time.
Confirmation
Employees receive confirmation of their upcoming benefit selections, premium amounts and coverage start dates. A benefits enrollment company commonly sends enrollment confirmation statements via mail and email. Employees are instructed to review for accuracy and report any discrepancies.
Implementation
The benefit changes selected during the open enrollment process take effect on the first day of the new plan or policy year. Coverage, claims, and premium payments are administered according to employees’ new elections. Employees receive ID cards for new health plans and information about using their benefits.
Follow-Up
After open enrollment, companies may conduct surveys or audits to identify areas for improvement in the next enrollment cycle. Employees can provide feedback to ensure a smooth process in the future. Any issues with benefit changes are addressed and resolved.
These key phases work together to transition employees to their new benefit selections for the upcoming plan year through open enrollment .
What are enrollment types?
Employee benefits talk over with the non-salary repayment supplied to personnel similarly to their wages. Benefits can consist of healthcare, retirement plans, paid time off, lessons repayment, and more. They are an important part of a worker’s total reimbursement package deal.
The foremost sorts of benefits corporations provide are medical health insurance advantages, retirement benefits, and time-off blessings.
For medical insurance benefits
Employers generally provide medical health insurance plans that cover employee medical institution and health practitioner visits. Plans range in phrases of deductibles, co-can pay, and insurance. Dental and vision coverage alternatives will also be presented.
Retirement benefits
Help employees save and plan for their future years. Common alternatives encompass 401k plans, pensions, and retirement financial savings accounts. Employers may get a sure percentage of employee contributions to these plans.
Time-off benefits
Allow employees to take time far away from work whilst wanted. Paid holiday and unwell leave are standard, offering a hard and fast range of paid days off every 12 months. Short-time period and lengthy-time period incapacity insurance can shield a part of employee income if they’re not able to paint due to illness or injury. Paid holidays and floating vacations may be allowed to the firms throughout the year.
Other benefits
May provide for life insurance, tuition reimbursement, and flexible spending accounts. This includes employee discounts, wellness programs, maternity/paternity leave. Employee stock purchase plans, on-site clinics, or gyms are also included.
Benefits are very different from one employer to another and from one industry to another. Small business owners provide fewer benefits, while large corporations offer numerous benefit packages. The benefit is one of the most significant factors and incentives that really attracts good people to an organization, motivates them to be more productive, and retains them for a long time. It enhances productivity and creates more interest in the nature of their work.
What is the enrollment process?
Basically, the open enrollment process is a process in which workers are mandated to participate in registering or signing up for all the benefits offered by their employers. The enrollment usually takes place during hire and annually during the open enrollment periods.
Onboarding:
When first coming onboard, employees generally have the information on the benefits offered and how to enroll. A human resource or benefits enrollment company takes them through the options in detail in a meeting. They go through summary plan descriptions and booklets for each benefit. Employees are asked to fill out enrollment forms that indicate benefits they desire. They choose benefit options such as medical plans, dental plans, vision plans, retirement plans, etc. They may enroll eligible dependents in the plans and provide dependents’ information.
Choosing the plan
On the medical plans, they choose from HMO, PPO, and high-deductible plans. In addition to that, employees select levels of coverage: employee only, employee plus spouse, or family. Employees would refer to lists of in-network providers. It also includes the facilities to make sure their doctors will be covered.
For 401k and other retirement plans, employees select contribution percentages and investment options. These include stocks, bonds, or target date funds. Beneficiaries are provided with life insurance and other plans.
Document submission
After filling out the enrolment forms, employees submit supportive documents like social security cards and birth certificates for their dependents. The employee also fills any health questionnaire as shall be required. After the employees have been enrolled, they are issued with ID cards for their health coverage and all other relevant package documents.
Orientations
Orientations are provided whereby the employees get educated on how to use their benefits. Employees can, at the beginning of each year, make changes to their benefits and coverage levels during the open enrollment process. They will review plans and their respective costs to determine whether any changes need to be made. Then, the employee enrolls again with updated forms and documents. The enrollment process assures that employees select proper benefits packages, which fit their needs in adherence to plan requirements. Human resources and benefits staff also provide guidance, assistance, and answers along the way.
Can I waive health plan coverage?
Yes, in most circumstances employees are able to waive, or decline their company’s health plan insurance. There are a number of reasons because employees may want to waive medical health insurance, the most popular amongst which are:
- You have coverage under a spouse’s plan. If your spouse’s employer offers a health plan and you are satisfied with that coverage, waiving your coverage will save your employer money on premiums.
- Individual coverage: If you already have your own personal health care plan, then opting to waive your enterprise’s insurance may indeed be a great choice.
- You receive government coverage: In some cases, certain employees will be eligible for Medicaid or Medicare because of age or disability, which would make them eligible to waive the coverage made by an employer.
- You cannot afford the premiums. For employees who cannot afford to pay for health insurance coverage, waiver may be necessary. On the other hand, waiver can result in better out-of-pocket expenses if an emergency occurs.
- Waiving coverage policies vary from one employer to another. Some employers require employees to waive only under the condition they have other qualifying coverage. Other employers even allow their employees to go uninsured if they so wish.
- Employees who opt out of the coverage, therefore, should assess the risks they may be exposed to as a result of a lack of insurance, such as high medical care costs, declined claims to pre-existing conditions, and penalties under the Affordable Care Act individual mandate (if relevant).
Employees may generally waive the health plan coverage during the open enrollment process each year or within the first 30—60 days of working depending on the employer. They may do this by completing a specific waiver form. They have to state reasons for such a waiver and, further to that, sign the form acknowledging the presence of other health coverage that’s reckoned with. Also,They have to inform their employer about changing this situation; for instance, in case of losing their other health coverage, they might have to enroll into the employer plan during a special enrollment period.
How are salary-based payroll premiums calculated?
With some employee benefits, the premiums are a percentage of an employee’s salary. One common instance is long-term disability insurance. Here is how the premiums typically will work out:
Premium rates are assessed as a percentage of an employee’s base salary.
For example, an employer may provide long-term disability coverage that is rated at 0.5% of the employee’s salary.
Employee premium cost automatically increases as they get an increase or a promotion. The employer will automatically adjust the payrolls’ deductions to a higher salary that is equivalent to the new premium. This equally works in the opposite direction: premium cost will equally automatically reduce in the event an employee takes a pay cut for any reason. The employer will make downward adjustments to payroll deductions.
The salary-based premium model is designed to ensure that the amount of an employee’s insurance corresponds to the level of income he or she earns. Because higher-income-earning employees have the willingness and capacity to have larger potential claims, they pay higher premiums.
Designed simply and equitably, under the same levels of protection, each employee pays a premium directly proportional to their salary.
Let’s Simplify Open Enrollment Together!
Save Time and Stress by partnering with us
What if I want to change my benefits after I’ve made my enrollment choices?
There may be times when you have made your elections for the annual open enrollment process. Afterwards, feel that you really do need to make changes for next year. You will find that you are able to make these changes after the fact. First, talk to your company’s human resources or benefits department. Inform them of the changes you would like to make. They should be able to advise you on whether changes can be made outside the open enrollment.
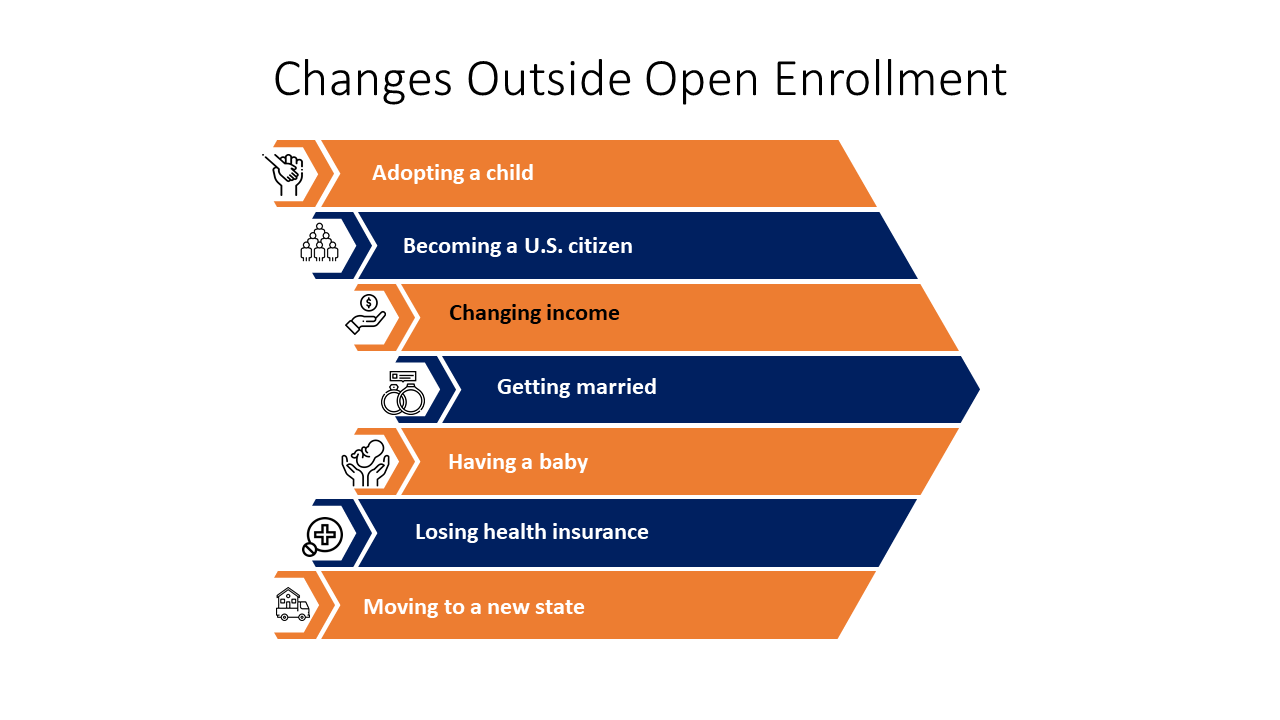
In many cases, the open enrollment process extends for people who experience a qualifying life event. A qualifying life event could include:
- Marriage or divorce
- Birth, death, or adoption of a child
- A change in your spouse’s employment or benefits
In case of a qualifying event in your life, your employer may permit changes outside the open enrollment time. You will generally need to show documentation of this event, such as a marriage certificate.
If you just want to make changes, not related to a qualifying event, you will probably have to wait until open enrollment to make any desired changes. Until then, your original selections will still apply.
So, reach out to your benefits team to have a conversation. They will help you determine if you can make changes.
How can I decide which health plan option is best for me?
The best choice in a health plan is based on your needs and preferences. Consider this:
- Cost: What premium, deductible, and out-of-pocket costs can you afford? Generally speaking, the higher your premium, the lower your deductible and out-of-pocket costs for care will be.
- Network: Are your favorite doctors and your community’s best hospitals part of the plan’s provider network? You often pay several times more for care outside a plan’s network.
- Benefits: what does the plan cover? Will it pay for one’s necessary prescription drugs and procedures? Plans do vary in what they cover.
- Deductible: what is the annual deductible that you must meet before the plan pays a percentage? Depending on one’s health needs a lower deductible might be worth a higher premium.
- Maximum Out-of-Pocket: What is the most, one will pay in a year before 100% is paid on the plan?
If you have a medical condition that’s chronic or pricey to treat, focus the attention to buy coverage, despite pricey. Otherwise, compare costs to the provider network and benefits which fit the need.
Can I waive all health care or dental options completely?
That is, do not enroll in any health coverage. An employee of some organizations may choose to waive all the way from participation in the health care plans, be it medical, dental, or vision, being given by an employer. On the other hand, some employers are quite exceptional when it comes to this requirement. Those that require one plan to be enrolled, others may even leave the employee to decide whether to forgo all plans offered.
There are potentially hazardous downsides to waiving all the health coverage. You would be paying out of your own pocket for any and all medical, dental, and vision care needs—possibly thousands of dollars for specific drug purchases, procedures, and hospital stays. Other downsides include you not being able to apply for individual plans in the future without the risk of being denied for pre-existing conditions.
Some employers even give an incentive to waive coverage. The offer might be to pay part of the savings right into your paycheck. The catch—that payment is often not equal to the value of the coverage being waived, or it’s very small and won’t counteract the risks of not being insured.
To decline coverage, in general, you should meet with the human resources or the benefits department of your employer. You should ask about their policy on declining all healthcare. While some employers will require you to have other qualifying coverage for healthcare to decline, others will only require you to sign a waiver form that you will be foregoing such coverage.
Should I assess health care needs for the coming year before Open Enrollment?
You can’t always predict your future health care needs. But you may know that you need knee surgery next year. Maybe you are starting a family, or maybe you’re on medication that costs several hundred dollars every month. All of those things could impact how much you pay for health insurance.
The amount of healthcare you might require next year may influence the plan you choose. If you are expecting a healthy year and you have very limited issues related to healthcare, an HDHP might be the proper choice. On the other hand, if you are having a baby or anticipating other healthcare needs, then a plan having higher premiums with a lower deductible may be more appropriate.
While bronze and silver plans cost less in premium but come with higher deductibles, gold and platinum plans bear higher premiums with lower deductibles. Be sure to understand just how these costs differ for the bronze, silver, gold, and platinum health insurance.






