Table of Contents
Every business deal with confidential information, like customer data, financials, and trade secrets. Protecting this sensitive data is crucial for your operations and reputation. Electronic data interchange or EDI provide an easy way to share information with trading partners securely. EDI solutions allows you to electronically send standard business documents, like purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices. By exchanging these documents digitally with EDI, you gain more control and visibility over your information. Jan Arendtsz, founder and CEO of Celigo, explains:
“It’s an annual ritual to predict the demise of EDI. Competing standards, web services and modern APIs — all have been forecast to end EDI at one time or another. But EDI is here to stay for now as it still works well for many users.”
EDI minimizes errors and ensures on-time delivery of all your data exchanges. It also creates an auditable trail so you know exactly where your information goes. Using EDI improves security, reduces costs, and streamlines processes. It future-proofs your systems and adapts to changing needs. Whether just starting with EDI or enhancing existing practices, this guide shows how EDI protects confidential information. EDI covers threats like fraud and data breaches. It ensures compliance with industry security standards. It gives you more power and oversight into sensitive data sharing between partners.
Read on for practical advice on implementing robust EDI security. Learn how to classify your critical documents by sensitivity. Discover endpoint security and encryption best practices. Understand partner, platform, and choose the EDI solutions supporting your security strategy.
What is EDI?
Electronic data interchange or EDI refers to the electronic transfer of business documents between companies. EDI allows businesses to share standard business transaction documents electronically in a standardized and secure format.
Some of the most common EDI documents include purchase orders, invoices, advance shipping notices, shipping manifests, bills of lading, and remittance advice. Companies can use EDI to send and receive these standardized documents electronically instead of on paper.
Benefits of EDI
There are several benefits to using EDI. First, EDI reduces errors by automating data entry and validation. Second, EDI speeds up the exchange of documents by ensuring on-time delivery. It also provides an auditable trail of all transactions for accountability and compliance.
- Low Cost
EDI lowers costs by streamlining paper-based processes and reducing manual labor. It simplifies integration with other systems, allowing an effortless data flow between trading partners. EDI also enables straight-through processing so documents can move from one partner’s system to another without rekeying or reformatting.
- Security
EDI provides secure and encrypted transmission of sensitive business documents. It uses secure protocols to ensure that only authorized parties can access, view, or modify EDI messages and documents. It protects business information from threats like fraud, theft, or data breaches.
The EDI standards ensure documents are formatted consistently, contain the same structured data fields, and have standard identifiers for trading partners, product codes, transportation services, etc. It allows for greater interoperability between trading partners using EDI. Independent standard committees under the United Nations set standards.
Trading partners agree on the types of EDI documents and standards to use. It includes details like naming conventions, data formats, links between EDI documents, and the required authentication or encryption tools. Proper setup and testing help align EDI implementation between partners before deploying for live production processes.
Use Cases of EDI in Different Industries
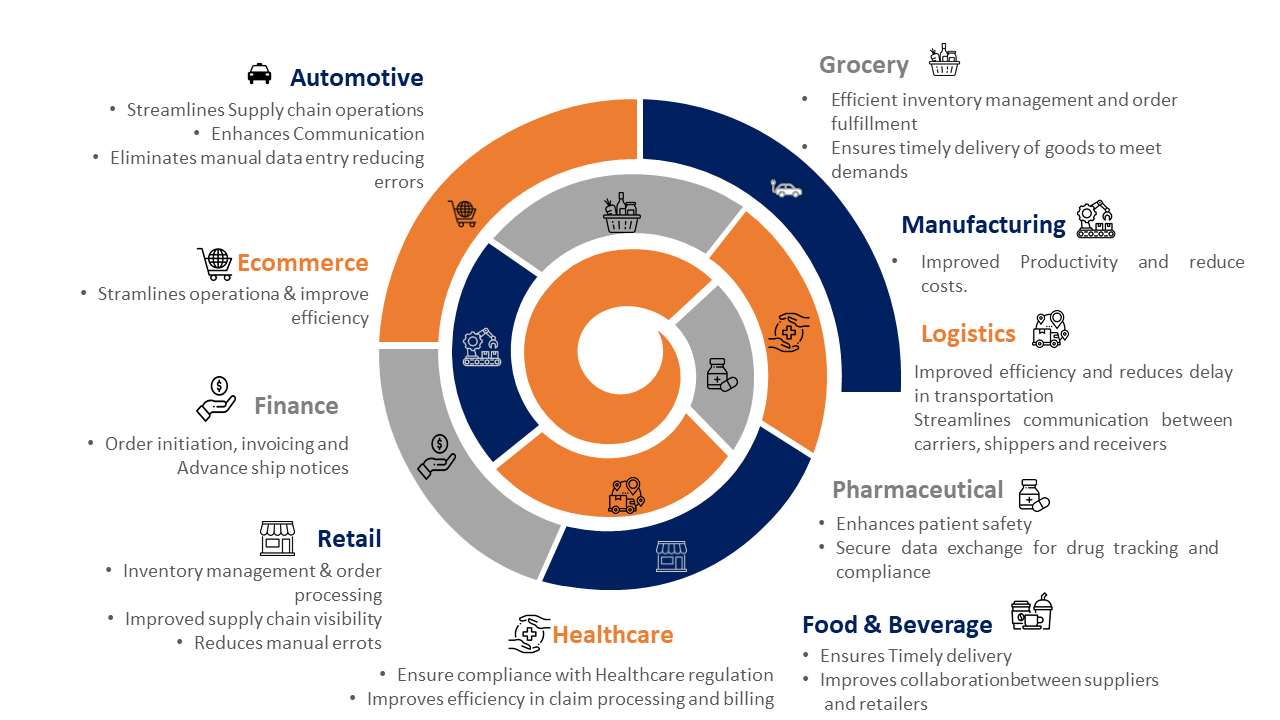
EDI is used across many industries for secure and efficient data exchange between trading partners. Some of the significant industries leveraging EDI and critical use cases include:
Retail
Retailers use EDI to send purchase orders electronically, inventory tracking info, invoices, and supplier payments. Suppliers use EDI to send advance shipping notices to notify of pending product shipments. EDI streamlines the supply chain and ensures on-time delivery of goods.
Healthcare
Healthcare providers use EDI to bill insurance companies for claims and process payments electronically. They also use EDI to verify insurance coverage and check patient eligibility before medical procedures. EDI reduces administrative overhead and speeds up claims and payments.
Transportation
Shipping companies use EDI to send electronic notifications about incoming cargo shipments, customs paperwork, vessel manifests, bills of lading, and drop-offs. They also use EDI to coordinate shipment details with freight forwarders, airlines, railways and trucking companies. EDI provides real-time visibility into cargo and optimizes delivery timelines.
Finance
Banks and financial institutions rely on EDI to securely share transaction data and clients. They use EDI for electronic funds transfers, remittances, and transferring mortgages/loans between institutions. EDI reduces processing times, speeds access to funds, and ensures seamless transition of portfolios between financial partners.
Automotive
Automakers use EDI to electronically send and receive purchase orders, advance shipping notices, invoices, shipping manifests, and quality/compliance reports with suppliers. Suppliers use EDI to notify automakers about upcoming shipments, defects, or delays. EDI streamlines just-in-time manufacturing by minimizing delays and ensuring complete visibility into supply chain operations.
Government
Governments use EDI to share data and documents with citizens, contractors/suppliers, non-profits, and federal/state agencies in a secure and standardized manner. EDI is used to send, and process benefit claims, reimbursements, licenses, certifications, permits, audit/compliance data, and emergency alerts. EDI automates paperwork, speeds up service, and ensures transparency between governments and stakeholders.
In summary, EDI services deliver significant value by automating data exchange and streamlining business processes across critical industries. EDI continues gaining new use cases as industries digitize, but its primary benefit remains – efficient, effective, and secure information sharing.
Benefits of Using EDI Solutions to Organizations
There are several key benefits to implementing EDI solutions for your business. EDI delivers value through automation, integration, visibility, and secure data exchange with trading partners.
- Automation – EDI automates the manual entry, processing, and exchange of repetitive business documents like purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and payments. It reduces errors, ensures compliance, and streamlines paperwork. Employees can focus on higher priorities rather than data entry and administration.
- Integration – EDI easily integrates with your business systems to enable a seamless data flow between partners. It facilitates straight-through processing so documents can move automatically from one partner’s system to another without rekeying information. It provides an end-to-end, optimized flow of business information across your supply chain.
- Visibility – EDI provides real-time visibility into all your partner data exchanges and transactions. It creates an auditable trail, so you know exactly where your information is and who can access it. It allows for greater accountability, compliance monitoring, and risk management across your trading partners and suppliers network.
- Security – EDI transmits sensitive business documents over secure networks using encrypted protocols and digital certificates. Only authorized users and systems have access to documents and messages. It prevents threats like fraud, theft, hacking, or data breaches from compromising your confidential information shared with partners. EDI helps ensure information security and compliance with industry standards.
- Lower costs – EDI reduces costs by minimizing paper use, manual labor, postage fees, and supplier management time. Employees can focus on higher-value work rather than data entry clerks. Partners incur fewer administration expenses so lower prices may be passed on to you. Overall, EDI frees up funding to invest in business growth.
- Speed – EDI accelerates the exchange of time-sensitive business documents by ensuring faster delivery between trading partners. Real-time visibility into all exchanges allows for quicker response to delays or issues. EDI streamlines synchronization across your supply chain so products and information move as efficiently as possible with minimal bottlenecks or holdups. Faster document transmission improves cash flow by speeding up invoicing, delivery, and payment cycles.
- Better quality – By automating repetitive tasks, EDI reduces errors and provides more consistent, accurate document exchange. Employees have more time to focus on quality control and exception handling. Standard EDI formats and identifiers prevent mix-ups between partners. Fewer manual keying and rekeying steps minimize typos or selecting incorrect options. EDI delivers higher-quality information in a shorter period to meet business needs.
Implementing EDI solutions within your business provides significant benefits. EDI continues expanding use cases and value as companies digitize supply chain operations. These benefits show why EDI has become essential for secure, streamlined information exchange in an increasingly global and electronic world. For seamless yet controlled data sharing, EDI delivers.
Why is Security Important in EDI?
Security is crucial for electronic data interchange. EDI allows businesses to share sensitive documents electronically with trading partners, so protecting this information is imperative. EDI exposes you to severe threats like fraud, hacking, theft, and data breaches without solid security. Malicious actors can gain unauthorized access to trade secrets, financials, customer data, or intellectual property shared over your EDI network. Once information is compromised, it is difficult to recover from the damage. Following are the risk factors that can be faced by an organization in the absence of EDI-
Confidentiality at risk
EDI transmits business-critical documents electronically between partners. If security is lacking, malicious actors can intercept, view, or modify these documents. Sensitive details could be revealed or manipulated for illegal purposes like fraud, identity theft or blackmail. Robust encryption and secure networks are needed to prevent information leakage during EDI transmission.
Integrity at risk
Weak security allows threats to alter EDI documents or tamper with business systems unnoticed. Fraudsters could modify figures on invoices, shipping notices, or payments to siphon funds without detection. Hacking or malware could also corrupt system data, crash servers, or lock you out of accessing EDI information. Strong authentication and access control ensure that only authorized changes are made to information and systems.
Accountability lost
Without security, it is difficult to determine who accessed what information or made unapproved changes within an EDI network. Audits and compliance oversight become nearly impossible, as no verifiable access record or trail exists. Digital evidence needed for the investigation, fraud, or legal disputes would not exist in the event of unauthorized access. Security provides accountability and an auditable chain of custody for all EDI exchanges and modifications.
Legal and compliance risk
Many regulations mandate data security, privacy, integrity, and accountability requirements that electronic data interchange consultants must meet. Failure to comply could result in legal penalties, loss of business partners, damage to reputation, or inability to continue EDI operations. Security aligns EDI with standards, laws, and best practices so you can ensure adherence and minimize compliance risks.
Security should not be an afterthought when setting up EDI. Robust security at every stage helps prevent threats, ensures confidentiality and accountability, maintains integrity, and enables ongoing compliance. Purposeful security integration provides trust in your EDI network and allows continued secure exchange of sensitive data with minimal risks.
For EDI to deliver value, strong security is essential. With a solid security foundation, EDI can save costs, speed processes, improve quality and provide visibility while stopping threats. When sharing information electronically, security must come first. Security is why EDI solutions are essential for your business.
How EDI Solutions Ensure Security
In the lightning-fast business world, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) reigns superbly. It’s the virtual handshake making sure seamless exchange of vital statistics between agencies. But with extremely good performance comes awesome responsibility – the responsibility to guard sensitive information traversing the digital landscape.
Enter EDI security and encryption – the guardians of your virtual fort. Imagine a high-security vault protecting your economic statistics, product details, and client records. That’s the essence of EDI protection!
Why is EDI Security Crucial?
Breaches and leaks can be devastating. An available protection lapse can disclose hypersensitive statistics, leading to:
1. Financial Loss:
Hackers can make the most stolen financial facts for fraudulent activities.
2. Reputational Damage:
Data breaches erode customer agreements and may critically damage logo popularity.
3. Compliance Issues:
Violations of records privacy policies can result in hefty fines and criminal repercussions.
Encryption: Your Digital Shield
Encryption rearranges data into an encrypted layout, making it hard to read for each person without the decryption key. It’s like locking your statistics in a chest, available simplest with the right code. Common encryption techniques used in EDI consist of:
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI):
Utilizes a couple of cryptographic keys – a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption – making sure only authorized parties can get entry to the records.
- Symmetric Encryption:
Employs a single key for both encryption and decryption, imparting a less difficult yet equally stable choice for precise situations.
Beyond Encryption: Building a Security Fortress
Encryption is a cornerstone, however, robust EDI protection requires a multi-layered technique:
- Access Control:
Restrict entry to sensitive facts based on personal roles and permissions.
- Data Integrity:
Employ mechanisms to make certain statistics stay unaltered throughout transmission.
- Authentication:
Verify the identities of buying and selling companions before information trade.
- Regular Security Audits:
Conduct periodic assessments to perceive and deal with capacity vulnerabilities.
Investing in EDI protection isn’t pretty much compliant; it is approximately safeguarding your enterprise’s destiny:
Partnering with reliable EDI carriers who prioritize safety is paramount. Look for agencies that offer strong encryption answers, implement stringent get right of entry to controls, and adhere to enterprise best practices.
By strengthening your EDI infrastructure with robust safety features, you could with a bit of luck navigate the digital panorama, enable acceptance as accurate along with your companions, and ensure the smooth drift of important commercial enterprise records. Remember, in the age of data, protection is not an option – it’s a necessity.
Ensure Data Privacy and Security With Our EDI Solutions
The Role of EDI Solutions in Compliance
EDI services provider are essential in ensuring compliance with security standards, regulations, laws and industry best practices. Strict compliance is critical for businesses to maintain legitimacy, trustworthiness, operational security and legal standing. Electronic data interchange provides this compliance in several important ways.
EDI Standards
EDI adheres to established standards for electronic data interchange set by organizations like the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe (UN/CEFACT). These standards ensure interoperability between trading partners and industries. They also mandate security, privacy, integrity and accountability requirements that EDI implementations must meet. Aligning with standards demonstrates compliance and legitimacy.
Many laws and regulations have provisions for electronically exchanging and securing business information, including HIPAA, GDPR, PCI DSS, and SOX. EDI aligns with these regulations by implementing security controls, access restrictions, auditing, encryption and partner management needed to comply. Proper adherence mitigates legal risks from non-compliance, such as penalties, lawsuits, loss of partners, or damaged reputation. It also ensures you can continue operating legally and ethically.
EDI provides an auditable trail of all electronic exchanges, modifications, access events and business transactions between trading partners. It includes details of who accessed what information and when. Audits allow monitoring for policy compliance, detecting suspicious behavior or threats, and investigating any issues. Oversight deters non-compliant actions and facilitates containment of issues to minimize risks. Regular audits verify the controls and practices maintaining regulatory compliance.
On-boarding new partners, off-boarding old partners, and reviewing all partners is a vital compliance practice. It verifies that only approved and legitimate partners remain connected to the EDI network with appropriate access. It limits risks from unauthorized or irrelevant partners able to access data or systems. Strong partner lifecycle management assures that only compliant business relationships exist electronically.
Conclusion
If implemented responsibly, EDI technology enables the secure electronic exchange of business-critical information between trading partners. EDI can deliver significant benefits without compromising confidential data or operational integrity by integrating security, ensuring compliance, and following critical best practices at every stage.
When implemented poorly, EDI exposes businesses to severe risks like fraud, hacking, theft, and data breaches that threaten financials, reputation, partnerships, and legal standing. Malicious actors can gain unauthorized access to trade secrets, intellectual property, financial details, customer records, or any sensitive information shared between partners over an insecure EDI network.
For EDI to provide value without vulnerability, security must be approached strategically with the mindset that information protection is always the top priority. Purposeful integration of security at every stage builds trust in electronic partnerships and allows continued sharing of sensitive information with minimal risks. If you wish to implement EDI security in your business, select the top EDI solution providers in the USA.