Table of Contents
The Current State of IoT and Connectivity
According to Statista, the number of IoT-connected devices will increase significantly from 15.9 billion to more than 32.1 billion in 2030. This staggering growth underlines how IoT is changing industries and our lifestyles. However, this rapid expansion comes with challenges, as current connectivity solutions, such as 4G and Wi-Fi, are unable to meet demands for better and more efficient connectivity.
IoT has enabled real-time data collection, automation, insights, and more. Yet, the growing number of devices has strained traditional networks. Latency issues, limited bandwidth, and inconsistent reliability often hinder IoT’s potential, especially in applications like autonomous vehicles and industrial automation that require instantaneous responses.
In this blog, we’ll explore IoT and 5G in addressing these challenges, how the synergy of these tech unlocks new possibilities across sectors, and what the future holds for 5G IoT applications.
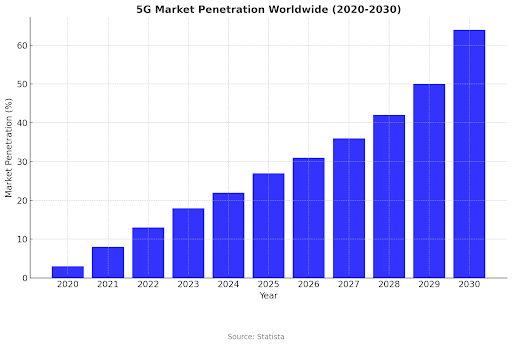
What is 5G Technology?
5G, the fifth generation of wireless communication technology, is faster than its predecessor, 4G. This represents a giant leap forward in connectivity. 5G provides high-speed data transmission, ultra-low latency, and the ability to connect millions of devices that can fit into a single network.
Unlike earlier generations that focused on enhancing personal communication, 5G is tailored for machine-to-machine interaction, forming the backbone of the 5G Internet of Things ecosystem. This infrastructure empowers IoT devices to communicate seamlessly, supporting applications that require instantaneous data exchange and decision-making.
Key Features of 5G
- Ultra-Low Latency: 5G can enable real-time applications such as autonomous vehicles and remote surgeries by drastically reducing the response time.
- Enhanced Speed: 5G tech is 100 times faster than 4G, delivering smooth, uninterrupted connectivity.
- Massive Device Connectivity: It can handle a large number of connections, which is vital in the spread of IoT and 5G in smart cities, agriculture, and everywhere else.
Why 5G is Perfect for IoT
As IoT continues to grow, so does the demand for networks capable of supporting billions of devices. This is where 5G for IoT shines. Its ability to support large-scale, low-power IoT networks ensures devices like sensors, cameras, and trackers can function effectively, even in remote or resource-limited environments.
Key Benefits of 5G for IoT Applications
IoT and 5G are revolutionizing how devices interact, enabling smarter, faster, and more efficient systems across industries.
1. Ultra-low latency for Real-Time Applications
One of the standout benefits of 5G is its ultra-low latency, reducing response times to milliseconds. In latency-sensitive use cases like self-driving cars, this is a revolution because everybody stays safe without delay. Real-time control of industry machinery reduces time and increases accuracy and efficiency. Low latency means health intervention will be done without delays in sensitive contexts such as remote surgeries.
2. Enhanced Speed for Data-Intensive Operations
5G IoT deployment in smart cities makes transporting considerable datasets to their destinations possible, keeping traffic and public safety up to date in real time. 5G’s capability to stream high-definition content without buffering is also applied to entertainment and gaming industries to enhance user experiences.
3. Massive Device Connectivity
A hallmark of the Internet of Things and 5G is the ability to connect millions of devices simultaneously. This scalability is critical for smart factories, where thousands of sensors and actuators must operate cohesively. Similarly, in agriculture, IoT-enabled devices like drones and soil sensors rely on 5G to provide synchronized, real-time data, ensuring efficient farming practices on a large scale
4. Energy Efficiency and Scalability
5G is designed with energy-efficient protocols, making it ideal for IoT applications where devices often run on limited battery power. Smart home systems, for instance, can operate longer on a single charge. The scalability of 5G networks also ensures future readiness, accommodating the growing number of IoT devices without compromising performance. This capability is particularly beneficial for expanding IoT ecosystems like smart cities and industrial automation.
5. Reliability and Security
5G networks provide unparalleled reliability, ensuring consistent connectivity even in densely populated or remote areas. This reliability is critical for the uninterrupted operation of IoT applications like wearable health monitors or logistics tracking systems. Security is also enhanced with advanced encryption and authentication protocols, addressing vulnerabilities often associated with IoT devices. Securing data exchanges, 5G fosters trust and promotes wider IoT adoption.
Future Applications of 5G with IoT
Explore some of the most promising 5G IoT use cases across various sectors.
1. Smart Cities
Imagine a city where traffic, waste disposal, and energy consumption are coordinated in real-time. Smart cities essentially use 5G IoT as the prime node, wherein many devices such as smart meters, traffic sensors, and surveillance cameras can easily communicate and collectively assess and control a city.
For instance, Barcelona provides smart sensors that manage the street lighting and water supply and save millions annually. These systems can be deployed to run over 5G networks; hence, they will robustly respond with minimal latency to incidences such as shocks and will effectively and efficiently allocate resources.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, the 5G IoT devices can enable breakthroughs such as remote surgeries, constant monitoring of patients, and telemedicine. For instance, Smart glucose wearables send real-time data to healthcare providers for timely action
Approximately 31% of patients in the United States had remote health monitoring devices in 2021, and with the confidence that comes from 5G ultra-reliability, this figure will grow exponentially. Further, 5G delivers high-definition video calls that make the solution more accessible and effective to implement even in remotely connected areas.
3. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars require numerous short signals to exchange information and instantly make decisions. 5G IoT use cases in this field include vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication.
For example, Tesla’s self-driving cars use IoT sensors to assess road traffic conditions and constantly change routes. This way, the latency is minimal with 5G, making transportation safer and more efficient. States such as Nevada, including its largest city, Las Vegas, introduced its 5G-ready system for smart traffic management, with a specific focus on helping self-driving cars avoid jams.
4. Agriculture
5G IoT devices have increased precision farming. Farmers can now monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns with IoT sensors and make data-driven decisions. This significantly improves yields while conserving resources. For instance, drones with 5G connectivity can generate real-time imaging and analytics for extensive farmlands, detecting areas that require irrigation or pest control.
5. Consumer IoT
From smart homes to wearable gadgets, consumer IoT applications are becoming more intelligent and more efficient with 5G. Devices like Amazon Echo and Google Nest rely on constant connectivity to provide real-time updates and automate tasks. With 5G, these devices can process commands faster and handle complex integrations across multiple systems.
For instance, a 5G-connected home can simultaneously manage security cameras, thermostats, and entertainment systems without lag, creating a seamless user experience.
6. Smart Education
5G IoT is bringing immersive learning experiences and personalized instruction into education. 5G is making classrooms interactive with virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). For instance, students can virtually dissect real physical organisms, explore ancient ruins in real time using VR headsets, or work with colleagues to solve the latest exercise on their smartphones.
Moreover, IoT-powered smartboards and wearable trackers help teachers monitor student engagement and design lesson plans. 5G will also help the global EdTech market grow to more than $404 billion by 2026.
7. Public Safety and Emergency Services
IoT and 5G union is a game changer for first responders. Real-time visuals of disaster-hit areas provided by connected drones with cameras and sensors can help with search and rescue projects.
5G IOT devices will help firefighters’ smart helmets transmit real-time temperature and gas readings, which will help command centers make better decisions during an emergency. Indeed, the New York Fire Department has already experimented with 5 G-connected drones to improve situational awareness in fire incidents.
8. Retail
Retailers are leveraging IoT and 5G to improve inventory management and increase customer experiences. Smart shelves with sensors alert staff whenever stock gets low, while IoT shopping carts provide personalized recommendations based on customers’ preferences.
In 2018 Amazon introduced Just Walk Out technology in Go stores through a 5G network. The end result of this combo is a faster and more streamlined shopping experience.
Challenges in the Future of 5G IoT
1. Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
While the number of IoT devices is increasing, so is the risk of cyberattacks. Robust security measures are essential because a single vulnerable device will compromise an entire network. Therefore, securing data is the first priority for any IoT development company. For example, the healthcare industry needs to have airtight protocols when sensitive patient data is being transmitted, ensuring privacy and compliance with regulations.
2. Scalability of Infrastructure
5G networks need robust infrastructure to support the massive volume of IoT devices. This involves deploying small cell towers and upgrading existing systems to ensure consistent connectivity. For rural or underserved areas, scalability remains a challenge, requiring significant investments in infrastructure. Companies may need to hire IoT developers with expertise in optimizing networks for large-scale deployments to address this issue.
3. High Implementation Costs
The integration of IoT and 5G technologies demands substantial financial resources. From upgrading hardware to deploying new 5G base stations, the cost can be prohibitive for small and medium enterprises (SMEs). Additionally, industries transitioning to 5G IoT ecosystems must invest in skilled professionals, such as IoT developers and network engineers, further increasing operational expenses.
4. Interoperability and Standardization
Ensuring seamless interoperability across platforms is a complex challenge for IoT devices using different communication protocols. The lack of standardized frameworks often leads to compatibility issues, hindering smooth integration. Industry-wide initiatives, like the Matter protocol, aim to address these gaps, but more collaboration is needed to simplify integration processes.
5. Energy Efficiency Concerns
While 5G promises low power consumption, IoT devices deployed in remote or hard-to-reach locations still face energy constraints. Prolonged battery life is crucial for agriculture or environmental monitoring sensors, where frequent maintenance is impractical. Addressing these concerns requires innovations in energy-efficient device design and alternative power sources like solar or kinetic energy.
Upcoming Trends in 5G and IoT
1. Massive IoT Growth
The market for 5G IoT is estimated to reach $59.7bn by 2028. This growth is due to increasing IoT device adoption among various industries, from smart cities to healthcare. This ability to support many devices concurrently at high performance guarantees that IoT ecosystems can grow without sacrificing performance.
2. Edge Computing Integration
In edge computing, IoT development is growing along the edge (closer to the source versus collectively aggregated data stored at cloud services). Reducing latency and improving efficiency make this especially suitable for applications that demand real-time processing, such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation. If businesses want to stay competitive, hire IoT developers with an edge computing specialization to build systems that take advantage of this trend.
3. AI-Driven IoT Solutions
IoT applications increasingly utilize artificial intelligence (AI) to allow devices to analyze data and make independent, intelligent decisions. For example, AI-driven healthcare IoT devices can predict patients’ health so that preventive care and hospital visits can be lowered. Combined with 5G ultra-fast systems, these systems quickly produce actionable insights that are quickly becoming a new standard for efficiency and innovation.
4. Growth of Private 5G Networks
Today, we can expect massive growth of private 5G networks in the manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics sectors. These networks are well-suited to provide improved security, dedicated bandwidth, and custom configurations. For example, factories deploying private 5G networks can use IoT devices to monitor the factory in real-time so that it can perform predictive maintenance and create workflows using automation.
5. Fixed Wireless Access (FWA)
5G fixed wireless networks are emerging as a cost-effective alternative to traditional fiber or cable connections. By delivering high-speed internet access even in remote areas, FWA enables businesses and communities to benefit from IoT applications without significant infrastructure investments. For example, rural schools can now implement IoT-enabled educational tools, bridging the digital divide for students.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT and 5G is changing how we live, changing how we work and driving innovation across all industries. The potential applications range from making real-time solutions for self-driving cars and remote healthcare to developing smarter cities and streamlining supply chains. But when it comes to bringing these techs to life, we have our challenges – maintaining security, scaling, and building the proper infrastructure.
To take advantage of these advancements, businesses must hire IoT developers who understand IoT and 5G. Collaborating with experts ensures that solutions are innovative but also practical and secure. Partnering with an experienced IoT development company can help companies overcome barriers and create systems that deliver real value.
At A3Logics, we focus on crafting IoT solutions that seamlessly leverage 5G technology. Our team works closely with businesses to develop reliable, scalable, and efficient systems that meet unique goals.
If you’re exploring how IoT and 5G can fit into your business, we’d be happy to share insights and discuss what’s possible. Contact us today!
FAQs
1. What are the key features of 5G that enhance ioT?
5G offers ultra-low latency, faster speeds, and massive device connectivity, making it ideal for IoT applications. These features enable real-time data processing, seamless device communication, and support for billions of connected devices across industries like healthcare, transportation, and smart cities.
How A3Logics could help you develop IoT solutions with the latest technology?
A3Logics, a leading tech service provider, specializes in creating innovative IoT solutions powered by the latest 5G technology. From designing custom IoT applications to deploying scalable and secure systems, A3Logics offers end-to-end services tailored to your business needs.
How will 5G transform developments in IoT?
5G is set to revolutionize IoT by enabling faster and more reliable communication and supporting real-time applications like autonomous vehicles and remote surgeries. Its scalability ensures seamless integration of new IoT devices, while enhanced security features address growing concerns about data privacy and network integrity.
Which industries benefit the most from IoT?
Industries like healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, transportation, and retail are among the top beneficiaries of IoT. With IoT-enabled devices, these sectors can optimize operations, improve efficiency, and provide better user experiences, all powered by 5G connectivity.






