Table of Contents
The electronic data interchange market is anticipated to race ahead at a fast pace and reach the value of $49,213.1 million by 2027. Applications of EDI have been responsible for enabling a myriad of small, medium, and large firms to spread their operations and improve efficiency. It has turned out to be a useful savior in the torrid year 2020, where most firms had to forcibly switch operations into the eCommerce sector.
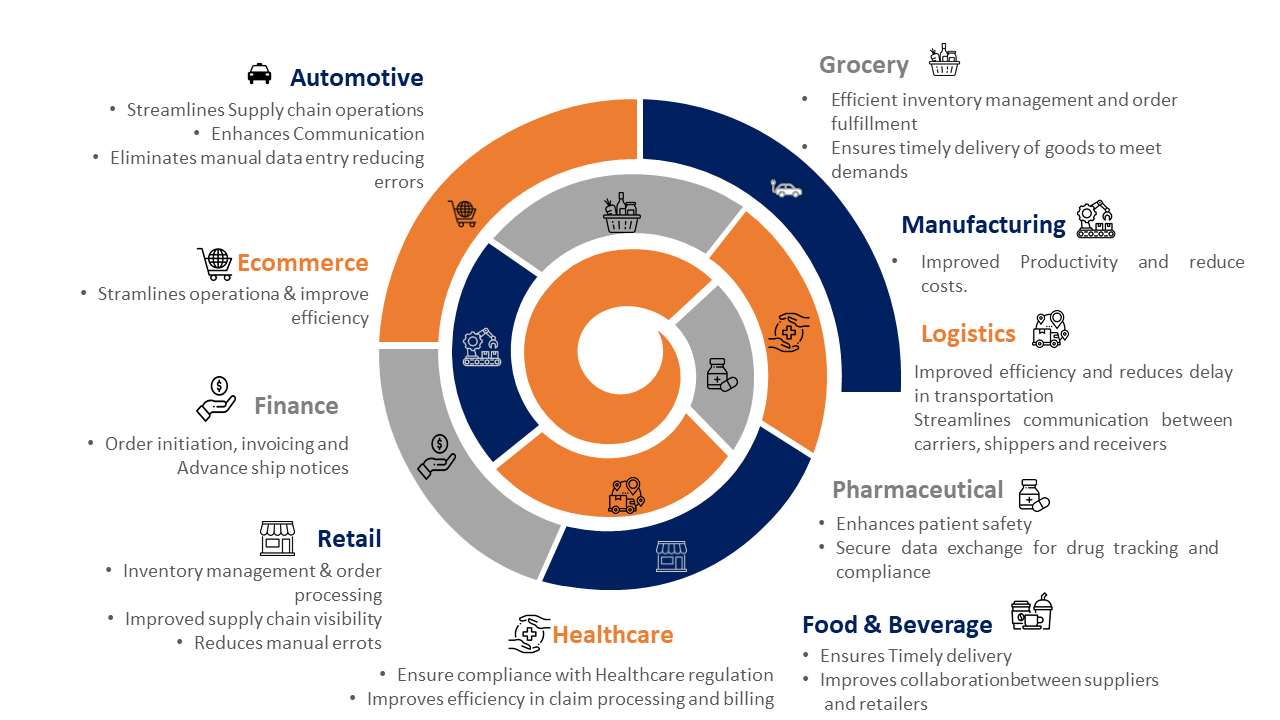
So, who uses EDI? The fact that EDI is industry-neutral is why many industries use EDI. Depending on what kind of EDI services your organization requires, there are numerous options accessible. EDI in industries are the best option for organizations due to its great adaptability, versatility, and ease of integration. When implemented properly, EDI can help you concentrate your attention in the appropriate places and uncover supply chain efficiencies. You may save time on laborious operations, forge closer bonds with your suppliers, and quickly adapt to shifting global trends. This is how electronic data interchange functions in many sectors.
EDI in Healthcare
To guarantee appropriate EDI in healthcare industry, comprehensive EDI testing is crucial. Using pre-established EDI communication protocols and standards, electronic data exchange in healthcare refers to a safe method of data transmission between healthcare providers, insurers, and patients.
When EDI was first implemented in the 1960s, there were over 400 distinct standards in use. During that period, conversion errors, low interoperability, expensive IT, and security flaws were frequent problems. By addressing those issues, EDI integration made sure that data transfer and interpretation happened quickly and easily.
The HIPAA EDI Rule requires covered entities (i.e., clearinghouses, health plans, and providers) that share medical information electronically to utilize uniform standards for all healthcare EDI transactions. In order to comply with HIPAA EDI, industries must communicate HIPAA documents—that is, any documents containing information that could be considered sensitive to health—using the ASC X12 protocol.
Medical data security and accuracy are guaranteed by the ASC X12 standard, which is the only format approved for HIPAA EDI transactions. All parties engaged in the transmission must adhere to certain data requirements. Specifically, the data is transformed into computer (non-human) language prior to being sent to a recipient computer. Additionally EDI in healthcare industry, consists of uniform codes that are allocated to each documentation package.
Organizations employ HIPAA electronic data interchange software solutions to create standardized EDI documents and translate them into common business forms.
Meet HIPAA Compliance Requirements
EDI in Financial Services
It is a highly regulated sector of financial services since it deals with a mass of sensitive data for various client types on a daily basis. One of the most used applications of electronic data interchange is getting the invoices electronically and paying for them electronically.
A lot of companies are unaware of how expensive paper-based services may be. Many companies might save money by not having to print and maintain this financial information in a secure manner. You can save costs and maintain the security of client data by doing away with this expense and moving to a secure EDI application in its place.
Numerous inaccuracies are frequently the result of manual processing. It will be impossible for an error to occur if your company switches to an electronic data interchange system. A further advantage is that the formats are always the same. In the financial services sector, it can be difficult to produce consistent documentation due to the types of EDI and systems used worldwide. EDI facilitates the implementation of file format standardization globally by simplifying this process.
EDI in Retail
For many years, the retail industry has benefited from EDI. Nonetheless, a lot of businesses continue to process orders, invoices, and dispatch notes using paper-based procedures. This demonstrates that electronic data interchange in retail still has a lot of room to grow in the sector, something that many retail business managers have seen and find essential to generating competitive value for their companies.
Vendor-managed inventory, pioneered by firms like Walmart and Procter & Gamble in the 1980s, has really emerged to become a major driver of this industry’s quest to lower costs while improving service to the consumer. It underpins the so-called “quick response” strategy for managing grocery goods flows throughout the supply chain.
Under VMI, the consuming organization’s primary decision-maker for inventory replenishment is the supplier. As a result, the supplier has considerably more control over inventory, which reduces waste and overstock. Additionally, the replenishment cycle frequently shifts from a monthly to a weekly or daily schedule, improving customer service. Naturally, this is crucial during promotions since more demand puts more pressure on the supplier’s capacity to resupply.
The acceleration of global data synchronization (GDS) and the simplification of direct store delivery (DSD) processes are two further important uses of electronic data interchange in retail. According to data from a Forrester research study including over 20 vendor firms, 41% of corporations employ an EDI message format, transmitting more than 20 billion messages annually.
EDI in Manufacturing
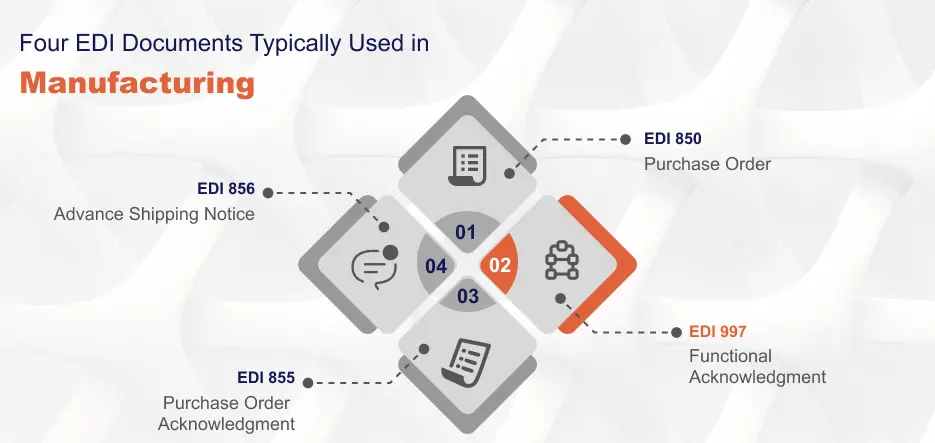
EDI is still essential for document exchange in the manufacturing sector. When it comes to purchase orders, invoices, shipment notifications, and other common documents, EDI is the de facto standard throughout a company’s digital ecosystem, from trading partners to customers. Although EDI systems are used by most industries, they are particularly important in manufacturing for trading partner communication. Manufacturing electronic data interchange software can also automate various procedures in a way that ensures effective communication, hence freeing up manufacturers to handle other equally significant responsibilities like quality assurance, other areas of customer service, and manufacturing new products.
EDI is a time-tested proven way to increase efficiency in a manufacturer’s supply chain: increasing the speed of each relevant transaction, visibility, and accuracy. For example, an EDI 850 Purchase Order, which initiates the supply chain process in motion.
EDI for manufacturing is a vital tool for engaging with a dynamic, complex ecosystem since EDI transactions propel the supply chain forward across numerous industries. To efficiently engage with a variety of trading partners, including suppliers and vendors, clients, distributors, fulfillment businesses, and retailers, manufacturing enterprises need to be able to do modern EDI.
In their EDI business, manufacturers usually have two main components: an e-commerce platform for end users and direct transactions with wholesalers that frequently interact with their ERP system. However, those businesses frequently fall back on their outdated—in a very good way—legacy EDI gateway and translator, which are now unreliable and inflexible when it comes to integrating with modern systems and apps.
Manufacturers can get the information integration, protocol, EDI, and flat file support they want from a contemporary EDI solution. Modern EDI solution providers also enable manufacturers to decrease chargebacks for EDI issues, shorten customer connection times, and improve visibility and monitoring across their global ecosystem.
EDI in Automotive
To operate JIT and Lean Manufacturing models efficiently, the car sector needs EDI. Electronic data interchange in supply chain management shares commercial information, production specifications, shipping notices, CAD/CAM engineering specifications, and more to optimize production, purchasing, and logistics.
Just In Time manages the supply chain and production to deliver items on time, decreasing inventory. Lean Manufacturing replaces redundant processes and non-value-adding activities to improve company efficiency and reduce errors.
These two models are interchangeable and utilized in vehicle manufacturing to boost efficiency and cut costs. EDI allows secure, real-time communication between manufacturers and suppliers at all levels. This enables accurate inventory management and fast demand responses. Instantaneous information transmission makes EDI applications ideal for supply chain management, production efficiency, and quality and process improvements.
From OEMs to Tier 1 and Tier 2 suppliers, the automotive industry is a complex ecosystem. OEMs use a large, diverse supply chain to assemble vehicles. TIER 1 vendors distribute directly to OEMs, while TIER 2 and later suppliers supply components. For uninterrupted manufacturing, suppliers and manufacturers must communicate and coordinate.
OEMs and TIER suppliers need reliable communication systems. OEMs require accurate order status and component availability information to avoid delays and assure timely deliveries. However, suppliers need precise demand estimates and production requirements to plan operations, manage stocks, and maintain quality and delivery standards. Electronic data interchange specialists help OEMs and suppliers adjust to unanticipated demand shifts and supply chain interruptions.
EDI in Logistics
EDI aims to streamline logistics companies’ workflows by standardizing, automating, integrating, and simplifying crucial data transfers. Modernizing your EDI is the proper option to make these things happen. EDI has been used by worldwide supply chain companies since the late 1960s. FedEx, UPS, XPO Logistics, and other major transportation companies use EDI to speed up document transfers and B2B communication, reducing costs and delays, improving data accuracy, and increasing customer satisfaction.
EDI integration solutions allows transport data throughout a multi-enterprise supply chain is crucial. Today’s EDI logistics software can link data flows into core applications to boost a company’s eCommerce and marketplace presence. Logistics companies worldwide seek to scale swiftly. Modern EDI systems give companies the control they need to do business with customers and partners. These vital corporate data exchanges must be standardized, automated, integrated, and simplified. Logistics firms will suffer without those four ingredients. The logistics industry relies on EDI and the supply chain. EDI has long been essential to the logistics business, from its communication standards to its messaging.
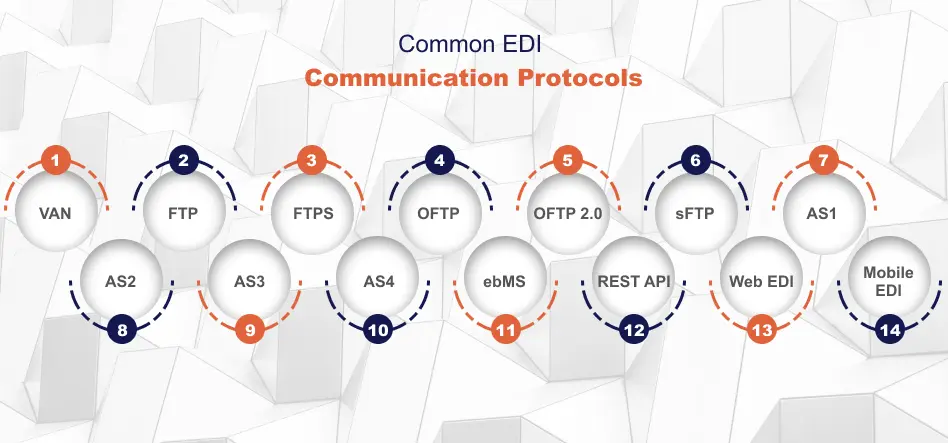
Logistics companies must scale swiftly, if not more so than other industries. Companies must send and receive X12, EDIFACT, Tradacoms, ODETTE, EANCOM, HIPAA, VDA, and other electronic documents. EDI capability in the logistics business implies efficiently and quickly accommodating and using all these EDI communication protocols.
Electronic Data Interchange in Food and Beverages
EDI is probably one of the most extended technologies in the food and beverage business, sharing a huge array of documents that include orders, invoices, shipping notifications, and product information. It will no doubt make corporate operations smoother and reduce the possibility of problems when exchanging information. As an example, an EDI application can track shipment, manage inventory, order with suppliers, etc., automatically. It would reduce expenses and improve the supply chain management of food and beverage industries.
Another example of EDI in food and beverage may be one of the options that companies use to communicate with government organizations and regulatory authorities, in addition to exchanging information in the supply chain with suppliers or other business partners. EDI, for instance, can offer information on food safety or to comply with product recall and traceability requirements. It is implemented with a wide scope in the Food & Beverage industry, is driving a sea change in how companies not only interact with but also do business with each other. EDI automates supply chains, decreases manual error rates, and offers a more responsive and integrated ecosystem by standardizing and digitizing the interchange of vital information, such as orders, invoices, and inventory data.
For an industry that deals with time and accuracy, EDI support services are presented as the force that will introduce optimized procedures, better correspondence between distributors and suppliers, and productivity enhancement. EDI is one of the key technology enablers. This will help the food and beverage industry in managing global supply chain complexity. It showcases agility, transparency, and sustainability as themes that will define the future of the industry.
EDI in Government
Electronic Data Interchange is one such innovative technology that’s changing the way the government engages with its supply chain. EDI provider automates information exchange between the government agencies, manufacturers, suppliers, contractors, and vendors. With the elimination of manual data entry and paper-based communication, it saves money and enhances efficiency.
One of the most impactful applications of EDI in government is in import/export trade. By using EDI , governments can seamlessly send and receive customs documents electronically, significantly simplifying the process. This leads to faster clearance times and smoother movement of goods across borders.
Several organizations, including the Government, Defense Supply Center, Underground Station, Veterans Canteen Service, and GS1 – Government & Public Sector, are actively collaborating to promote the use of EDI application within the government industry.
Popular EDI messages used in government operations encompass a wide range of functions:
- Customs documents: Streamlining import and export processes by exchanging data electronically for air, road, rail, and ocean freight.
- Healthcare and Insurance: Facilitating the secure exchange of medical records and insurance information.
- Food Grains and Traceability: Tracking the movement and origin of food products to ensure safety and quality.
- Government Tendering: Streamlining the procurement process for government contracts.
- Homeland Security: Enabling secure information sharing for enhanced border protection.
- Banking & Financial transactions: Facilitating secure and efficient electronic payments.
By embracing EDI industry standards, the government can significantly enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve transparency across its operations.
EDI in Transportation
To define electronic data interchange it is the method by which trading parties exchange data in the transportation sector using EDI standards that are unique to that sector. Every EDI document has a specific purpose in the transportation industry and aids in the automated correctness of numerous activities. Shippers, carriers, warehouses, 3PLs, brokers, and other parties, like manufacturers and retailers, employ EDI integration with TMS. Let’s examine the significance of EDI for your transportation company.
A transportation company can send, receive, and retain information with less human intervention thanks to electronic data interchange providers. It frees up workers to take on more senior roles, such as managing integrated systems or cultivating positive business relationships with clients and trading partners.
You can identify the ideal carriers for your goods with the aid of EDI . You can get a freight bid that meets your shipping needs at a fair price and save time because the data interchange with different carriers occurs quickly.
Because of the way the TMS workflow is designed, different supply chain participants are involved in maintaining a logical flow and successfully managing their respective tasks. The way a business serves its consumers is immediately impacted if one link breaks as a result of miscommunication. Throughout the whole supply chain, EDI streamlines and automates communication, guaranteeing the location of the order from the manufacturing plant to your customer’s door.
EDI in Energy
In the energy business, EDI application is essential. The technology facilitates simple communication amongst a wide range of industrial stakeholders by standardizing data formats. EDI solves the issues caused by incompatible systems and formats by creating a common language for data interchange, allowing information to move freely throughout the energy supply chain. There are numerous benefits of electronic data interchange in energy transactions. It includes improved inventory management, faster and simpler procurement procedures, and more accurate billing and invoicing procedures. Because it is real-time, it also facilitates prompt and well-informed decision-making, which is essential in a field where promptness is highly valued.
Furthermore, the cost savings and increased overall supply system reliability are a result of the efficiency gains made possible by EDI energy generation. The main way that EDI streamlines and accelerates operations is by drastically lowering the amount of manual steps needed to transfer data. Energy-related transactions have historically required a wide range of human labor, including data entry and document processing. This gave rise to chances of mistakes and delays. They are automated via EDI, which facilitates data sharing across parties.
EDI uses established formats to guarantee data accuracy. By creating a common language for information sharing, the technology lowers the possibility of errors that are frequently associated with different data formats. Precise data is one of the most crucial things in the energy sector. A reliable understanding of production, distribution, and consumption patterns is provided to stakeholders by having accurate information, which is essential for making wise decisions. This ultimately results in an energy infrastructure that is more resilient. A more adaptable and effective energy supply chain can be achieved with the implementation of EDI. Timely information sharing facilitates enhanced demand forecasting, streamlined inventory control, and increased operational efficiency.
Are You Looking For Solutions to Improve Your Business Efficiency With EDI?
Advantages of Electronic Data Exchange Implementation in Various Industries
For many firms, cost savings are the primary benefits of electronic data interchange, but there are also a number of crucial side benefits.
Reduced Prices
Because EDI use computer systems to communicate data, it reduces company operations like processing paper documents and printing, storing, and sending them. Businesses who exchange a lot of papers each month might save a lot of money in this way thanks to EDI.
Reduced Inaccuracies
Manual data entry is automated by electronic data interchange software, doing away with paper-based procedures. By doing this, the likelihood of human error during manual entry is greatly decreased. Consequently, EDI offers organizations increased accuracy, decreased errors, and better customer service.
Enhanced Rapidity and Precision
Transactions can be handled electronically thanks to EDI, which makes data entry more quicker and more accurate. By doing this, the significant mistake rate and time waste linked to manual operations based on paper are eliminated.
Thanks to its cutting-edge technology, Electronic Data Exchange Automation also assists enterprises with data verification. The businesses’ accuracy rates also guarantee that the processes are completed promptly.
Enhanced Effectiveness
EDI saves time by eliminating the need for manual order and data processing. It enables firms to concentrate on other aspects of their operations. Businesses can enhance productivity and profitability by decreasing expenses, minimizing human errors, and expediting data processing.
Better Support for Customers
Businesses can process customer orders more quickly and precisely thanks to applications of EDI, which leads to improved customer service and quicker delivery times.
Enhanced Safety
Technologies for authentication and encryption are used by Electronic Data Exchange Automation to stop unwanted access. It is far safer in this regard than conventional paper-based techniques. By shielding companies from security risks and data breaches, EDI enhance security and fosters a safe atmosphere for information sharing.
Future Trends in EDI Integration
“To stay competitive in the digital economy, enterprises have to continue to invest in modernizing B2B integration software,” says Chandana Gopal, research manager at IDC. Let’s examine four EDI developments that should have an impact on EDI integration and providers in the future.
1. Lack of IT Skills
Cloud computing is changing how EDI technology is deployed and how EDI services are consumed. An increasing number of companies are seeking to move their connections, integration, data, and apps to the cloud. This covers EDI on the cloud. But with cloud computing reaching unprecedented heights, there’s never been a greater demand for skilled personnel in IT departments.
Businesses have lost $258 million a year due to a lack of cloud skills, according to estimates from the London School of Economics. Cloud computing is meant to be elastic, flexible, and cost-effective; however, it is unlikely that an organization can modernize essential EDI operations to the cloud and come out unscathed if internal resources aren’t in place to manage cloud migration, cloud service adoption, or a cloud-first IT strategy.
Outsourcing has become a popular strategy used by many IT departments to address the skills shortage. An understaffed or inadequately skilled IT or integration competency center cannot offer the 24/7 coverage, cost savings, or overhead reductions that come with partnering with an outside IT service. Integration ability will no longer be an internal need due to the outsourcing of the EDI integration skillset. This will unavoidably boost the dependability of digital business transactions and provide you control over the support and service involvement that you need for a smooth changeover and upkeep.
2. Growth of E-commerce
E-commerce is without a doubt the fastest-growing part of the retail industry. A lifestyle, online shopping becomes part of the routine. For traditional bricks-and-mortar businesses, the allure of engaging in e-commerce is irresistible, if not exactly a lifeline, then as a way of life.
The e-commerce boom is still within a major impact on a number of different businesses, thanks to the ever-disruptive Amazon effect and headline-grabbing, paradigm-shifting acquisitions across the retail sector.
A new problem starts to emerge as the market for e-commerce grows at historically high rates. The challenge lies in the ever-growing complexity of data as well as the massive amount of data generated by e-commerce business processes. An e-commerce business model creates a particularly complicated environment since it depends on a wide range of technologies, including supply chain management tools, applications, data, and B2B connectivity capabilities.
Data from the e-commerce supply chain is interestingly composed. The information is provided by partners, retailers, and customers in all formats. Enterprises are faced with challenges related to data management, integration, and access. Because of this, businesses shouldn’t undervalue or disregard the importance of a modern B2B infrastructure strategy. Even businesses who can only just manage their present data requirements realize that complexity will only keep growing in the foreseeable future. When attempting to handle current and forthcoming difficulties related to the e-commerce boom, it is often the case that existing technology is more reliable and ought to be given priority.
A key tool for tying ecosystems together and facilitating the smooth flow of retail, inventory, and supply chain data is EDI. For the majority of supply chains with specialized needs, EDI still functions similarly to the current communications standards.
3. Business System Integration
The capabilities provided by Modern EDI in and around business system integration are broad.
Businesses today must be able to integrate business systems fast and effectively in order to boost business agility. For this reason, a lot of people update and modernize their enterprise resource planning (ERP) software to enable more dependable and flexible business operations. However, if business system integration is not included in a guiding strategy, ERP cloud migration is difficult, expensive, and dangerous. This is the application of electronic data interchange, or more accurately, contemporary EDI.
ERP systems, other essential business apps, and other linked business endpoints that power the firm must align with EDI. The data, applications, trading partners, and underlying business processes that generate income are all connected through EDI. The applications of EDI offers a flexible toolset to guarantee business process integration across all back-office systems, from your customer relationship management (CRM) program to the corporate financial solution.
4. Development of Blockchain Technology
Every few years or so, it seems like the newest and greatest technology shows up, and everyone declares that it will take the place of EDI. That was XML years ago. It was APIs a few years ago. Right now? Now for blockchain. Even Gartner admits that the hype machines in the sector have driven blockchain to an extreme before most businesses have really needed it.
But in reality, blockchain won’t completely replace B2B transactional technology, even while it works well for some kinds of transactions. Blockchain technology in EDI will only serve to enhance and complement current EDI systems, if anything.
The net effect is that businesses’ current B2B transaction processes don’t always need to alter significantly, if at all. Actually, it can carry on in the same manner, and at the same time, blockchain can provide more transparency between three parties, which will only serve to enhance EDI’s already potent capabilities.
In summary
EDI has developed over the years into one of the most basic constituents of business communication across industry borders. For every organization, whether small or big, it has become something of necessity due to its effectiveness and flexibility. The field of application continues to grow. Giving an indication of how pivotal electronic data interchange companies are in enabling transactions between trade partners. And also increasing collaboration, and simplifying corporate processes.
FAQs






