EDI, short for Electronic Data Interchange, is a technology that facilitates the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in a standard electronic format. It replaces traditional paper-based documents like invoices, purchase orders, and shipping notices with their electronic-based variants.
Without EDI, a typical manual process would involve lots of people and paper and will look something like this –
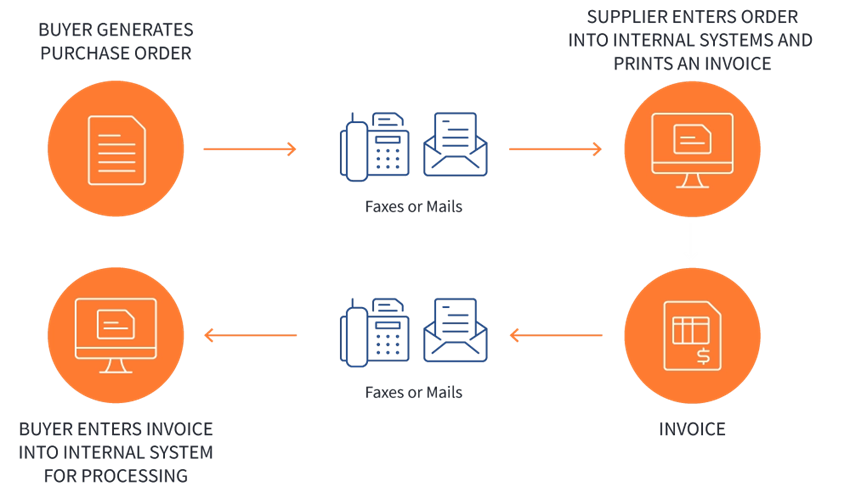
Source – EDIbasics
With EDI in place, with no people or paper involved, the process would look like this –
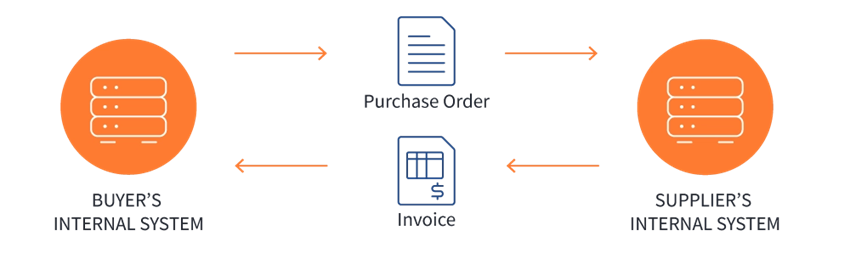
Source – EDIbasics
Table of Contents
What Does EDI Capable Mean?
EDI capability means having all the requisite resources to select and implement EDI software. For example, if you are an EDI-compliant company, you needn’t fill out physical paper forms and mail them to your trading partner. Instead, you can exchange data electronically, maximize efficiency, and remove manual processes.
When a company is said to be EDI capable and compliant, it has the resources (processes and technology) to electronically exchange business-related documents between trading partners. The company’s EDI capability lets it share all kinds of business documents such as invoices, purchase orders, shopping notices, etc., directly with partners in an EDI-compliant format.
Key Components of EDI Capable Systems
EDI capable systems have several components that work together to ensure seamless data exchange between trading partners. Let’s discuss some of the key components of systems demonstrating EDI capabilities –
EDI Software
Also known as translation software, EDI software facilitates EDI format capability by converting data from internal systems to a standardized EDI format. Translation is important as it ensures that data is accurately interpreted and used by the recipient’s system.
The EDI software processes incoming messages, converts them into a readable format, validates that data is EDI compliant and error-free, and automatically handles data transformation.
Communication Network
In EDI, communication networks are protocols and infrastructure used to exchange business-related documents electronically between organizations. Let’s discuss some standard protocols –
VAN (Value-Added Network)
Third-party network that manages data transmission between trading partners. It provides reliability, security, and management services, such as tracking and archiving, that improve the overall EDI communication process.
AS2 (Applicability Statement 2)
This protocol is a popular choice for secure EDI-based transactions. It uses digital certificates and encryption to transmit data over the internet. AS2 ensures confidentiality, data integrity, and authentication.
FTP/SFTP (File Transfer Protocol/ Secure FTP)
FTP, short for File Transfer Protocol, transfers files over the network. Secure FTP or SFTP secures data transfer by adding a layer of encryption and protects information from unauthorized access.
Data Mapping
Data mapping ensures that both parties understand data transmitted via EDI. It essentially aligns data fields from a company’s internal system to corresponding fields in the EDI standard. It also involves rules that define how data fields from a source system (CRM or ERP) are translated in EDI formats like EDIFACT or ANSI X12 or vice versa.
System Integration
A capable Electronic Data Interchange system integrates seamlessly with internal business systems such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management), ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), and WMS (Warehouse Management Systems). It facilitates smooth and efficient business processes and allows automatic data input and extraction in the EDI-based system.
Compliance & Security
EDI compliance implies adhering to established EDI protocols and standards that dictate how data is formatted and exchanged. Some examples include following EDI standards like HIPAA, GDPR, etc. EDI security, on the other hand, refers to the set of measures, features, and practices to protect the exchange of crucial business information. Examples include protocols like FTP and SFTP, which we have discussed above.

How to become EDI Capable?
Since most organizations worldwide are EDI capable, you must comply with EDI standards to work with them. Here are the main steps –
Understanding Trading Partner Requirements
Considering that there are multiple EDI formats, it is important to research whether you have the capability to meet your partner’s requirements. This step is crucial before you invest in an EDI system or make any other important decision.
Choosing an EDI Solution
In the next step, you must choose between an in-house or outsourced EDI system. Let’s understand when you should choose one kind of EDI solution over the other.
In-house EDI
- Gives more control but needs more resources. You’ll need a team of experienced IT professionals to install and maintain the EDI system.
- In the absence of an experienced in-house IT team, outsourcing IT services can prove to be expensive.
- You’ll also need employees and hardware with mapping skills to onboard new trading partners.
Outsourced EDI (Managed EDI)
- It is a cloud-based solution, which means you can access it from anywhere, provided you have an active internet connection.
- Outsourced EDI doesn’t require any special software or hardware.
- If you wish to focus more on sales and build customer relationships, you can seek outsourced EDI services, such as cloud-based EDI service providers. We’ll touch upon Cloud EDI in the next section.
Cloud EDI
Unlike traditional EDI setups, cloud EDI involves hosting the EDI platform on the cloud and accessing it over the internet. By moving EDI to the cloud, businesses can gain real-time visibility into partner data, accelerate document exchange, and improve supply change efficiency, all by subscribing to an EDI service provider. To learn more, check out our comprehensive post on cloud-based EDI.
Selecting an EDI Standard and Compliance
ANSI X12 (Primarily Used in North America)
The ANSI X12 standard is a standard EDI format developed by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). It is widely used across North America and consists of comprehensive transaction sets for various business processes, such as shipment notices, invoices, and purchase orders.
EDIFACT (Primarily Used Internationally)
EDIFACT stands for Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport. It is also known as UN/EDIFACT. It is primarily used outside North America and supports a wide range of business processes and industries.
TRADACOMS (UK Retail Industry)
It is primarily used in the United Kingdom. TRADCOMS, or the Trading Data Communications Standard, includes specific document types for retail transactions.
HL7 (Healthcare Industry)
Health Level Seven, or HL7, is a standard for exchanging documents in the healthcare industry. It is used for administrative and clinical data exchange.
Implementing and Testing
Once you have selected the right EDI platform, implement and rigorously test your EDI workflows before deploying them. This phase confirms that your system does exactly what it is intended to do. You check the end-to-end flow of EDI documents between organizations and internal systems to ensure that the data exchange is smooth.
Integrate with ERP
EDI and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software continue to grow and develop. Almost all businesses need an ERP at some point. The EDI market is expected to grow from $1.88 billion in 2022 to $4.04 billion in 2029.
An aspect of being EDI capable is the smooth integration between EDI and ERP systems. An ERP connector connects the EDI solution with the ERP system to automatically transfer messages between the two.
Also, an EDI converter is required to convert data from ERP to standardised EDI messages. This implies that the organization must be ready to transmit data in formats like EDIFACT, ANSI X12, GALIA, ODETTE, HIPAA, Tradacom, VDA, EDIFICE, etc.
EDI Capabilities: Key Advantages
Enhanced Efficiency and Speed
With EDI in place, businesses can focus on more critical operational areas, further reducing manual data and order processing as transactions take place electronically. As a result, human errors are reduced, and profitability and productivity significantly increase. EDI also helps verify data, thereby enhancing accuracy and helping to carry out operations quickly.
Improved Accuracy and Reduced Errors
As mentioned, an EDI-based system eliminates manual data entry and replaces it with electronic means. It automates the whole process digitally and eliminates paper-based processes. Both of these reduce instances of human error that may otherwise occur if data is manually entered. All in all, EDI improves the accuracy of business operations and reduces the chances of errors.
Cost Savings
In paper-based processes, costs related to mailing, printing, and document storage are involved. By automating the supply chain and removing paper-based processes, EDI reduces the costs associated with paper-based processes. It also reduces labor costs, improves operational efficiency, and reduces order processing time.
Stronger Partner Relationships
EDI ensures that data is automatically transmitted in real time, keeping the partners involved aligned. The fully streamlined and automated approach enhances efficiency, making the overall trade more profitable and effortless for all parties involved. As a result, EDI forges stronger partner and vendor relationships.
Improved Supply Chain Efficiency
EDI can help improve supply chain efficiency in more ways than one. To begin with, real-time invoicing with EDI lets you conduct an effective cost-to-serve analysis, with which you can accurately estimate profit margins. Next, it helps forecast product demands by updating all your data, such as invoicing, returns, shipping, etc. Being EDI compliant also allows you to stand out from others who are not compliant and improve trading partner relationships.
Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Integrating Electronic Data Interchange, or EDI, means improving customer experience in several ways. One way is automating order invoicing and communicating information digitally. This way, consumers can get accurate invoices on time. Secondly, EDI automates your buying process, letting customers place orders electronically. As a result, there is faster communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and other involved parties, leading to quick customer service.
Increased Data Security
Compared to paper-based methods of transmitting information, EDI uses robust security standards, encryption, and authentication technologies. It is virtually impossible for an unauthorized party to intercept data, creating a secure environment free from security threats and data breaches.
Streamlined Business Processes
The EDI process enforces several steps to ensure a seamless and secure exchange of business documents between trading partners: document preparation, transmission over a secure network, receipt and integration, and, lastly, acknowledgement.
Industries That Require EDI Capability
Industries use EDI for its versatility, adaptability, and ease of integration. With proper implementation, EDI can help uncover supply chain inefficiencies and divert attention to the right places. This graphical representation demonstrates how EDI functions across various industrial sectors –
Now, let’s look at how EDI capabilities are used across industries.
Insurance & Healthcare
EDI in insurance and healthcare refers to transmitting data safely between healthcare providers, patients, and insurers. The HIPAA EDI rule requires covered entities like providers, clearinghouses, and health plans that share medical information electronically to utilize uniform standards for healthcare-related EDI transactions. The healthcare industry must use ASC X12 protocol to share documents to be HIPAA compliant.
Retail & E-Commerce
Electronic Data Interchange accounts for 75% of digital B2B sales. It automates the exchange of business documents and provides real-time updates on inventory levels through automated EDI processes. Talking of automation, EDI removes the manual processing of paper documents and even reduces labor costs, thereby leading to cost savings. For example, a retailer can use EDI to receive purchase orders from suppliers, send shipping notices to logistics providers, and receive invoices from vendors.
Logistics & Transportation
Supply chain companies like UPS, FedEx, XPO Logistics, and many others have been using EDI since the late 1960s. They use it to speed up B2B communication and document transfers, reduce costs, improve data accuracy, and increase customer satisfaction. An EDI logistics software can link data flows into core applications. Common EDI documents in Logistics include Purchase Orders (850), Advance Shipping Notices (856), Invoices (810), and Purchase Order Acknowledgments (855).
Manufacturing
In the manufacturing sector, EDI is important for document exchange and trading partner communication. It is the de facto standard for invoices, shipment notifications, purchase orders, and other documents from customers to trading partners. It provides a platform for manufacturers to see and track their inventory in real time and allows them to implement just-in-time inventory practices. Some of the common EDI standards used in manufacturing include EDIFACT, ODETTE, and ANSI X12.
Finance
Let’s understand the role of EDI in finance with the help of a workflow. Financial EDI sets up a seamless flow between several parties (combinations) involving the seller and the buyer, the buyer and the bank, and the bank and the seller. The data that revolves has EDI format capability. This means it is in an EDI standard format that the buyer’s bank, for instance, can understand. Furthermore, an ACH or Automated Clearing House delivers the payment to the seller.
To get a more detailed understanding of how EDI is transforming industries, check out our blog on the top 10 industries that are using EDI.
Challenges in Implementing EDI and How to Overcome Them
Throughout this blog, we have established that being EDI capable and having EDI capabilities is advantageous. That said, being EDI capable doesn’t come without challenges. In this section, we won’t just discuss the challenges, but we’ll also discuss how you can overcome them.
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
| Scalability | Adding more trading partners to your network can pose scalability issues. | Using a cloud-based EDI service can help overcome these challenges. |
| Increases Costs | Hardware and software expenses may come your way as EDI solutions reduce operational costs for you. | Outsourcing EDI can be of help. |
| Lack of Expertise | You may not have an in-house IT team to help you develop EDI systems. | Getting the help of a third-party provider with a skilled IT team can help mitigate this challenge. |
Future of EDI and Emerging Trends
For a long time, electronic data interchange (EDI) has been a cornerstone of modern business operations. It has evolved in recent years, and we can foresee significant innovations and trends in the years to come. Here’s a look at what EDI might look like in the future –
EDI Will Enjoy The Benefits of Blockchain
Blockchain can ensure the authenticity and integrity of exchanged data. For instance, all transaction data in the supply chain, from shipping notices to invoices and purchase orders, could be stored on the blockchain. Any disputes could be resolved easily by referring to this record.
AI and ML Will Impact EDI’s Future
AL and ML could both impact the future of EDI by automating data input and data mapping tasks in the EDI processes. The algorithms used in AI and ML can train different data formats and automatically map them to an appropriate EDI standard.
IoT Integration Will Shape EDI Trends
IoT-based smart devices (for example, IoT-based sensors in a warehouse) can be used to collect a vast amount of business data in real time. EDI can help send real-time notifications, for instance, when inventory falls below a designated level. This can help expedite operations.
Growth In Cloud-based EDI Solutions
While various businesses use cloud-based EDI solutions, many have yet to adopt them. In the future, we may see more businesses opt for cloud-based solutions. This way, businesses will be able to scale their operations while accessing EDI services from anywhere.
Enhanced Security Protocols
EDI solutions are integrating enhanced advanced security protocols such as intrusion detection systems, multi-factor authentication, military-grade encryption, and more to ward off security threats. Plus, more and more EDI providers prioritize features that follow regulatory compliance.
How can A3Logics Help to become EDI Capable?
Wish to know how to become EDI capable but lack resources and expertise? You can seek an expert EDI solution provider.
A3Logics is an industry-leading EDI service provider that can help you gain EDI capabilities. It makes the process of becoming EDI capable stress-free and straightforward. Here are the reasons why you should choose A3Logics as your preferred EDI partner –
- A3Logics supports multiple EDI standards making it easy for businesses to communicate with various kinds of trading partners.
- Businesses can monitor and manage EDI transactions efficiently since A3Logics provides real-time data visibility.
- We ease the process of trading partner onboarding by easing the process of connecting with new trading partners.
- Our proactive team monitors EDI processes 24/7. As such, we can identify and resolve any issues before they hamper your operations.
- We are industry experts when it comes to integrating and deploying EDI maps. We are seasoned in transforming raw data into EDI-compatible formats.
To learn more and find out how A3Logics can help your business become EDI capable, book a consultation call with us today!
Final Thoughts On Becoming EDI Capable
Being EDI compliant isn’t just a requirement; it’s becoming a norm as more businesses rely on digital transactions to streamline operations. It ensures seamless electronic collaboration and communication within supply chains across complex business trading environments. All said, if you wish to meet compliance standards in your chosen industry, and stay competitive in this fast-changing market, it is essential that you become EDI capable.
We don’t deny that gaining EDI capabilities is not without challenges. However, you can easily overcome these with an expert EDI solution provider. Do let us know if the post delivered value.





